* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mid-Ocean Ridges
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic reversal wikipedia , lookup
History of navigation wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
Deep sea community wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
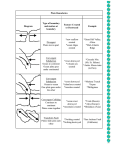
Earth is made of three layers The earth is layered similar to a hardboiled egg Earth HardBoiled Egg Shell is thin and hard Crust—thin and rigid Mantle—hot Core—made of iron Egg white is thick and softer Yolk is small and at the center •Lithosphere—upper mantle and crust •Asthenosphere— hot upper part of mantle •Ocean crust— thinnest crust, very dense •Continental crust— thickest crust, not as dense Plate Tectonics The theory that states: The plates are moving •Earth’s lithosphere is broken into separate sections called plates. •Edges of plates meets at lines called plate boundaries. •The theory that explains the formation, movement and subduction of the earth’s plates. Present Day Tectonic Plates Fault Plate Boundary Evidence for Plate Tectonics • Mid-Ocean Ridges • Age of the ocean crust • Ocean Trenches • Magnetic stripes on the sea floor SEA FLOOR •Scientists started mapping the ocean floor in the 1950’s, •At the center of the ocean, They found huge underwater mountain ranges, This was a surprise because they expected the ocean to be flat in the middle of the ocean •Scientists called the huge underwater mountain ranges MidOcean Ridges. •Scientists collected rock samples and determined the shape of the sea floor using a ship named the Glomar Challenger. •Ages of rocks •youngest rocks were closest to the ridge, •oldest rocks were farthest away, next to the continents. Mid Atlantic Ocean Ridge Youngest rocks Oldest rocks A B C Which rocks are older? A or B C or D D •Ocean Trenches are DEEP canyons in the sea floor that are parallel to the continent. •Ocean Trenches are located close to a plate boundary. •Deepest trench on Earth is the Mariana’s Trench next to the Philippine Islands SEA FLOOR MAGNETIC STRIPES 1. Earth is like a giant Bar Magnetic a) b) 2. Magnetic north pole is near the geographic north pole Magnetic field formed by the motion of the hot molten metal in the outer core Occasionally magnetic poles flip flop: though a process called magnetic reversals. a) b) c) Normal polarity: Magnetic north pole points to south Pole Reverse polarity: Magnetic south pole point to the north pole The cause of reversal s unknown Divergent Boundary: occurs where plates move apart Convergent Boundary: Occurs where plates push together Transform Fault Boundary: Occurs where plates scrape past each other. Transform divergent convergent Divergent Boundaries ON LAND •Two plates move away from each other leaving a gap between the plates IN THE OCEAN •A rift valley is a deep valley that forms in the gap between the moving plates Ocean Crust Rift valley Ocean Crust Divergent Boundaries •New ocean crust is created at Divergent Boundaries as the plates pull away from each other. Krafla Volcano in Iceland Aerial view of the area around Thingvellir, Iceland, showing a fissure zone (in shadow) that is an on-land exposure of the MidAtlantic Ridge. Map showing the Mid-Atlantic Ridge splitting Iceland and separating the North American and Eurasian Plates. Features of Divergent Boundaries •In the Ocean •Mid-ocean Ridges (Also called spreading centers) •Rift Valleys Krafla Volcano in Iceland Aerial view of the area around Thingvellir, Iceland, showing a fissure zone (in shadow) that is an on-land exposure of the MidAtlantic Ridge. Map showing the Mid-Atlantic Ridge splitting Iceland and separating the North American and Eurasian Plates. Features of Divergent Boundaries •On Land •Rift Valleys form when continents split •If the continents spread far enough apart, new ocean crust will form Rift valley Newest rock A Older rock B Mid-ocean ridge •When new crust forms at mid-ocean ridge, the magnetic minerals line up with the earth’s magnetic field. •When the magnetic field reverses, the rocks record the new polarity HOT SPOTS are relatively small, long-lasting hot regions where magma rises in plumes. Magma plumes develop into volcanoes that can build up and eventually become a volcanic island or mountain. Hot spots occur far from plate boundaries, yet tell us how fast and in what directions plates are moving. The Hawaiian Islands and Yellowstone are examples of hot spot volcanoes. CONVERGENT BOUNDARIES 1. Ocean crust is destroyed at convergent boundaries at the same rate it is created at Mid-Ocean Ridges . 2. The location where this happens is called the SUBDUCTION ZONE 3. Subduction is when one plate sinks beneath another at a convergent boundary 4. Oceanic crust will subduct under the continental crust 1.Oceanic crust is more dense than continental crust CONVERGENT BOUNDARIES • Three types of convergent boundaries – Continental-Continental Convergent – Oceanic-Oceanic Convergent – Oceanic-continental convergent • The name tells you the type of crust involved. 1. Continental-Continental Convergence: Creates mountains a) Happens when two continental plates crash together b) Neither plate wants to subduct so the edges crumples forming mountains c) Example: a) India crashed into Asia 50 million years ago b) This caused the Eurasian Plate to crumple up and form the Himalayas c) The collision is still happening. Scientist now know how some types of mountains form. 3. Oceanic-Oceanic Convergence: Creates deep ocean trenches at subduction zones, and island arcs. Deep OceanTrenches occur where two oceanic plates meet; the denser of the two plates will subduct and melt. The magma from the melted palte will rise back to the surface and form an Island Arc Island arc’s are chains of volcanic islands that form on the top plate, parallel to a deep ocean trench. EXAMPLES Mariana trench is the deepest at 36,000 ft below the sea floor. Subduction zone Japan and the Aleutian islands of Alaska are island arc volcanic chain Oceanic-continental convergence: Creates ocean trenches, and coastal mountain ranges 1. Oceanic -continental subduction occurs where an oceanic plate sinks beneath a less dense continental plate. 2. Deep ocean trenches form where the ocean plate subducts. 3. Coastal mountains from where the less dense continental crust is folded upward. Some of these mountains may form volcanoes. Subduction Zone Subduction Zone The Cascade mountains, home of Mt. St. Helen, are coastal mountains. Transform Boundaries 1. The location where plates scrape by each other is called a transform boundary. 2. Crust is neither created nor destroyed, it is just relocated. 3. Most transform faults are found on the ocean floor. 4. They commonly offset the active spreading centers, The San Andreas fault is a transform boundary between the North American plate and Pacific plate. The San Andréa's Fault is the reason why California ha sso many Earthquakes Zig-zag pattern on ocean floor Convection is the movement of a material due to rising and sinking of hot and cool materials. Convection Currents create motion of hot molten rock upward and as it cools it sinks down where it is heated again and rises. Convection Currents move the lithosphere only a few centimeters per year, but over a million years plates are carried thousands of kilometers.