* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 14_Finish-contestability-and-intro-to-govt
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Grey market wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Price discrimination wikipedia , lookup
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
Dumping (pricing policy) wikipedia , lookup
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Darknet market wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
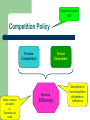
Contestability recap Lesson objectives Recap how markets can become more contestable Differentiate the level of contestability between markets and what determines it using industry examples Explain using a diagram the implications of contestable market theory on firms in the industry Introduce the economic underpinnings of “competition policy” Contestable Markets Recap – New entrants ‘Hit and Run’ tactics – enter the industry, take the profit and get out quickly (possible because of the freedom of entry and exit) Cream-skimming – identifying parts of the market that are high in value added and exploiting those markets Contestable Markets Recap Key characteristics: No (low) barriers to entry or exit No (low) sunk costs Note that the threat of new entrants may encourage positive OR negative behaviour by incumbents Firms’ behaviour influenced by the threat of new entrants to the industry Firms may deliberately limit profits made to discourage new entrants entry - limit pricing Firms may attempt to erect artificial barriers to entry – e.g… Contestable Markets Over capacity – provides the opportunity to flood the market and drive down price in the event of a threat of entry Aggressive marketing and branding strategies to ‘tighten’ up the market Potential for predatory or destroyer pricing Find ways of reducing costs and increasing efficiency to gain competitive advantage Barriers to Contestability No market is perfectly contestable – there are always some barriers! Existing firms can engage in predatory behaviour to make entry more costly to new rivals Raising rivals’ costs – – Vertical integration means that some firms act as component suppliers to other firms in their industry – they have control over the supply-chain (also known as vertical restraint) The use of import tariffs to increase the relative prices of overseas output Reducing rival’s revenues – “bundling” A monopoly can use profits in one market to boost market power in another (cross-subsidisation) Bundling – Anti-Competitive Behaviour? Product bundling is a marketing ploy of giving away a relatively cheap product with a relatively expensive one to attract customers Bundling can have the effect of tying the consumer to both products This is particularly prevalent in computer manufacturing where the product comes with specific items of software already pre-loaded Use your checklist sheet Banking Where are the opportunities to skim or hit and run? Barriers to entry? Barriers to exit? Banking Where are the opportunities to skim or hit and run? Barriers to entry? – – – – Brand loyalty Marketing Legal Financial Barriers to exit? Evaluating Contestable Markets There are no perfectly contestable markets What matters is the degree of competition / contestability The idea is that what matters is not so much competition within a market, but rather competition for a market. What also matters is the threat of entry of new suppliers – but this may not be enough to affect the behaviour of existing firms The absence of competition in a market over a long period of time does not necessarily suggest a lack of contestability Structural changes in costs in different industries can change the degree of contestability Contestability may force existing firms away from profit-maximising behaviour (e.g. towards sales-revenue maximisation) Over to you… – Revenue Draw Monopolist’s profit maximising equilibrium – How might the monopolist react to the threat of hit and run entry by removing the new entrants’ incentive? Output (Q) Normal Profit Contrasted with Profit Maximisation Price No one in the industry has any advantage over anyone else If the monopolist charges the profitmaximising price, then - if the market is contestable – the P1 firm will be vulnerable to hit and run entry The only way the P2 monopolist can avoid this happening is to set the price equal to average cost, so that there are no supernormal profits to act as an incentive for entry MC Got this far in this lesson ATC AR MR Q1 Q2 Output (Q) Implications of contestable market theory The number of firms in an industry is irrelevant in terms of economic efficiency Abnormal profits attract new entrants driving down prices and ensuring economic efficiency All markets (excluding natural monopoly) can be efficient so long as they are contestable Shifts the emphasis of government competition policy away from number of firms towards reducing barriers to entry in an industry Potential competition may be more important for economic efficiency than actual competition Contestable Markets Examples of markets exhibiting contestability characteristics: – – – – – Financial services Airlines – especially flights on domestic routes Computer industry – ISPs, software, web development Energy supplies The postal service? N.B. Exam board likes the topic of contestability Remember the threat of competition can be as effective as actual competition Key is the relationship between sunk costs and the degree of contestability Contestability 10 minute essay “To what extent is the UK banking market a contestable market” Agree a structure as a group Divide up the work amongst yourselves Write the bullet points of an essay Government intervention to maintain competition in markets OR Why does the Government seek to make markets more contestable? Why does the Government intervene to maintain competition? Toughened since 1997 Competition Policy Promote Protect Competition Consumers Enhance Better resource allocation vs. Economies of scale Efficiency Assumption is that competition eliminates xinefficiency Competition Policy At the heart of competition policy is the comparison between Perfect Competition and Monopoly Draw the two LR equilibrium diagrams Big Assumption! No cost difference between the two market structures PC and “Multi-plant” Monopoly compared Part of consumer surplus transferred to Monopoly as profits Price Deadweight loss = cost on society B Pm Thank PC You! Ppc Consumer Surplus E LRS (=LMCm) PC firms prepared to supply any quantity at this price C MR O Monopolist supplies Qm at price Pm Qm The Monopolist at constant returns to scale can continue to supply with no change in MC Qpc D=AR Quantity PC firms supply Qpc at price Ppc Homework Read and make notes on Anderton Ch 58 P380-382 Be prepared to hand in your notes at next lesson Plenary Define the term “Competition Policy” and explain why it exists