* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Economics of the Great Depression
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
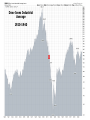
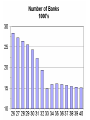
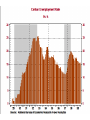
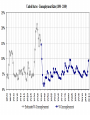
The Great Depression A Cross-Curricular Analysis History, Economics & Mathematics Resources Federal Reserve Bank of St Louis http://www.stlouisfed.org GDP - Gross Domestic Product Market value of all goods and services produced Depression vs Recession A drop of more than 10% in GDP or a drop in GDP for more 2 successive quarters. Inflation A rise in the general price of goods and services over time…. Or A decrease in the purchasing power of money caused by too much money chasing too few goods and services. Deflation A decrease in the general price level of goods and services – below 0% inflation. CPI - Consumer Price Index The CPI measures changes in the price level of consumer goods and services purchased by households. The Gold Standard A monetary system in which gold does not circulate but in which the government agrees to sell gold at a fixed price in exchange for the circulating currency. In the US, that fixed price was 40%. What started it and why did it continue? October, 1929 Date Change October 24, 1929 -33.02 October 28, 1929 −38.33 October 29, 1929 −30.57 % Change -11.00 −12.82 −11.73 Close 298.97 260.64 230.07 Westinghouse lost 66% of it’s SEP value. Dupont lost 30%. If one had invested in the market in SEP, 1929 and held their stock, they would not have been able to recoup their losses for most of their adult life. Dow-Jones Industrial Average 1920-1940 X Smoot Hawley Tariff June 17, 1930 20% average tariff rate but 60% on common items Imports – 1929..$4.4B (4.2%) 1933..$1.5B Exports – 1929..$5.4B(5.1%) 1933..$2.1B Bank Failures – 1929 - 1935 Year Number as of DEC 31 Suspensions 1929 24,633 659 1930 22,773 1350 1931 19,970 2293 1932 18,397 1453 1933 15,015 4000 1934 16,096 57 Data are from Banking and Monetary Statistics, Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, 1943, pages 18 and 283. The New Deal - Did it work? SEC Acts of 1933 and 1934 Banking Act of 1933 (Glass-Steagall) CCC- Civilian Conservation Corps What finally pulled us out? Allied vs Axis GDP - WWII Country 1938 1939 1940 1941 1942 1943 1944 1945 Austria 24 27 27 29 27 28 29 12 France[1] 186 199 164 130 116 110 93 101 Germany 351 384 387 412 417 426 437 310 Italy[2] 141 151 147 144 145 137 117 92 Japan[3] 169 184 192 196 197 194 189 144 Soviet Union[4] 359 366 417 359 274 305 362 343 British Isles 284 287 316 344 353 361 346 331 USA[5] 800 869 943 1094 1235 1399 1499 1474 Allied Total:[6] 1629 1600 1331 1596 1862 2065 2363 2341 Axis Total:[7] 685 746 845 911 902 895 826 466 Allied/Axis GDP:[8] 2.38 2.15 1.58 1.75 2.06 2.31 2.86 5.02 Lessons It’s a worldwide problem. The best solution is to keep it from happening. Money flow is essential.