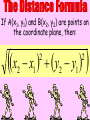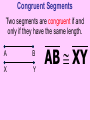* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download B - Cobb Learning
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
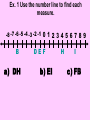
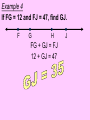
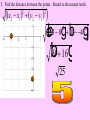
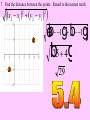
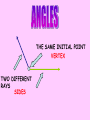
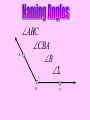
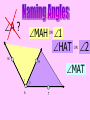
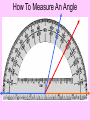
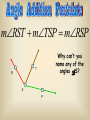
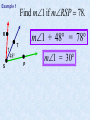
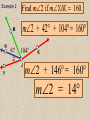
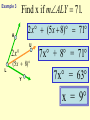
Session 2 Draw six segments that pass through every dot in the figure without taking your pencil off the paper. Counterexample It only takes 1 false example to show that a conjecture is not true. Example 4: Find a counterexample for these statements… All dogs have spots. All prime numbers are odd. Counterexample Example 5: Find a counterexample: For all real numbers x, the expression x2 is greater than or equal to x. 0.52 = 0.25 and 0.250.5 Point • Has no size, no dimension • Is represented by a dot • Named by using a capital letter We would call this one “point E.” Line • Has one dimension • Is made up of infinite number of points and is straight • Arrows show that the line extends without end in both directions • Can be named with a single lowercase cursive letter OR by any 2 points on the line • Symbol Names of these lines: COLLINEAR Points lie on the same line NONCOLLINEAR Points do NOT lie on the same line Example A D • Points D, B, & C are in a straight line so they are _______________ C B E • Points A, B, & C are ________________ Plane • 2 dimensions • Extends without end in all directions • Takes at least 3 noncollinear pts. to make a plane • Named with a single uppercase script letter or by 3 noncollinear pts. Names of these planes: M COPLANAR Points lie in the same plane NONCOPLANAR Points do NOT lie in the same plane Line Segment Is straight and made up of points • • Has a definite beginning and definite end • Name a line segment by using the endpoints only • You will always use two letters to name a segment • Symbol Name of these segments: Name of segment from 3 to 0. Ray Is straight and made up of points • • Has a beginning but no end • Starting pt. of a ray is called the endpoint • Name a ray by using the endpt. 1st and another point on the ray • You will always use two letters to name a ray • Symbol Names of these rays: Postulates • Postulates are facts about geometry that are accepted as true. Ruler Postulate Do not copy all of this • Every point on a line can be matched with a coordinate on P the number line. • The distance between two points is the absolute value of the difference of the coordinates. Q Ruler Postulate (in other words) If P is at 15 and Q is at 18, the distance from P to Q is 3. P 15 Q 18 The distance from P to Q is written: PQ How is this different from PQ? Ex. 1 Use the number line to find each measure. -8 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 B a) DH DE F b) EI H I c) FB Segment Addition Postulate If B is between A and C, then AB + BC = AC. A A B B A C + B C C = Example 2 Points X, Y, and Z are collinear. If XY = 12, YZ = 47, and XZ = 35, determine which point is between the other two. 35 X Z 12 X Y 47 Y Z Example 3 If QS = 29 and QT = 52, find ST. P Q R S QS + ST = QT 29 + ST = 52 ST = 23 T Example 4 If FG = 12 and FJ = 47, find GJ. F G H FG + GJ = FJ 12 + GJ = 47 J If A(x1, y1) and B(x2, y2) are points on the coordinate plane, then: x x y y 2 1 2 1 2 2 5. Find the distance between the points. Round to the nearest tenth. x 2 x1 y2 y1 2 2 eb3 0g b0 4gj 2 b9 16g 25 2 6. Find the distance between the points. Round to the nearest tenth. x 2 x1 y2 y1 2 2 eb4 1g b2 0gj 2 b9 4g 13 2 7. Find the distance between the points. Round to the nearest tenth. x 2 x1 y2 y1 2 2 eb4 1g b1 1gj 2 b25 4g 29 2 Congruent Segments Two segments are congruent if and only if they have the same length. A B X Y AB XY THE SAME INITIAL POINT VERTEX TWO DIFFERENT RAYS SIDES A ABC CBA B 1 1 B C A ? MAH 1 OR HAT M H 1 A OR 2 MAT 2 T A B C How To Measure An Angle mRST mTSP mRSP Why can’t you name any of the angles S? T R S P Example 1 Find m1 if mRSP 78. m1 + 48 = 78 R 1 T 48 S P m1 = 30 Example 2 M N 42 2 Find m2 if mYJK 160. m2 + 42 + 104 = 160 104 J Y K m2 + 146 = 160 m2 = 14 Example 3 Find x if mALY 71. 2 x (5x 8) 71 A U 2x (5x 8) L Y 7 x + 8 = 71 7x = 63 x = 9 ACUTE ANGLES = Greater than 0 and less than 90 RIGHT ANGLES = Measure exactly 90 OBTUSE ANGLES = Greater than 90 and less than 180 STRAIGHT ANGLES = Measure exactly 180