* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 13-4 Levers in the Body 2013
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
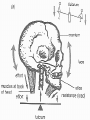
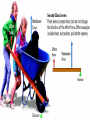
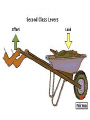
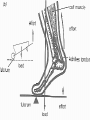
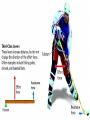
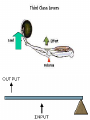
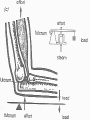
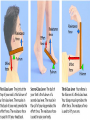
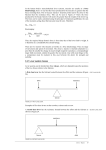
• Levers in the Body PH 532 EQ: How does your body work as a machine? 1. What is a force? • A push or pull on an object. • Force is represented by arrows • The units of force are: Newton (N) 2. What is work? • When a force makes an object move • Why does it take more work to lift a heavier plant? Because a greater force is required! 3. What is a machine? • Devices that help you do work 4. What is a lever? • A rigid object that rotates about a fixed point (fulcrum) A) A simple machine…helps you do work! Fulcrum: a fixed point …where a lever rotates Diagram: 5. How does a lever make work easier? 1. Changing the amount of force, 2. Changing the distance, 3. Changing the direction. • Why does the girl place the fulcrum close to the crate? To increase the force as much as possible! 6. What is mechanical advantage? • A measure of how much easier it is to do work by using a machine 7. How do you find the mechanical advantage of a lever? Mechanical advantage = resistance force effort force 100 N 25 N • Or: Length of Effort Arm Length of Resistance Arm 8. What are the 3 kinds of levers? • 1. First Class • 2. Second Class • 3. Third Class 9. Draw a first class lever. 1st class Example: see-saw, scissors, crowbar Body: neck! 2nd class Examples: wheelbarrow Body: foot! 3rd class Example: broom, rake, catapult Body: arm • How many different classes of levers are there? Three! 9. How do levers function on the body? • Bones and muscles work as lever systems joint = fulcrum bone = lever muscles = provide force