* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Valencia College
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Foot-and-mouth disease wikipedia , lookup
Influenza A virus wikipedia , lookup
Taura syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Orthohantavirus wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Lymphocytic choriomeningitis wikipedia , lookup
Canine distemper wikipedia , lookup
Canine parvovirus wikipedia , lookup
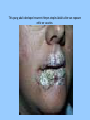
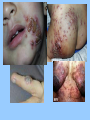
Herpes Simplex Virus I Cold Sores and Fever Blisters The Causative Agent • Caused by the herpes simplex virus • There are two strains of herpes: HSV-1 primarily causes symptom in and around the mouth; HSV-2 usually effects the genital area. Either virus can effect anywhere, but these are their preferred sites • Member of the family Herpes-viridae Herpes Simplex Virus -1 • Affects 25-40% U.S. population • Spread by contact with someone who is shedding the virus • Vesicles usually develop between 1-3 days after exposure • The acute phase is characterized by painful sores or blisters on the lips, mouth, face and sometimes in the throat. • Outbreaks may be preceded by “prodromal” tingling, pain, burning or itching in the site of the blister This young adult developed recurrent Herpes simples labialis after sun exposure while on vacation. But when it’s gone, it’s not really gone….. • After the blisters heal, the virus moves from the skin into the nerves and remains dormant there. • Reactivation occurs with fever, severe stress, sun exposure or other trauma to either the skin or the nerves • Most HSV-1 sufferers have 3-4 outbreaks per year Possible complications • Meningitis/encephalitis is an uncommon but very deadly complication. Without treatment it is fatal in 70% of cases; even with the best medical treatment there is a 20% mortality rate • Neonatal HSV disease, which is transmitted from mother to newborn during birth is fatal about 25% of the time • May also be spread to other areas of the body by the infected person touching the lesion and then other parts of his body. This can be especially serious if it involves the eye. Diagnosis • Normally diagnosed by the characteristic appearance of the lesions • May also be cultured Treatment • Administration of antiviral drugs such as Aciclovir and famciclovir has been shown to shorten the course of outbreaks • The drugs must be started within 24 hours of the outbreak to maximize their effectiveness. • The lesions will usually resolve on their own without any treatment • Taking the amino acid lysine has been helpful for many in both treating and preventing outbreaks Prevention • Avoid contact with lesions • Use sunblock on lips and face, if outbreaks are related to sun exposure