* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Gut Tube and Digestion
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
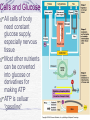
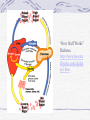
Diabetes and Obesity Type I is simple—no insulin Type II is complicated—”resistance” to insulin Factors are multiple Lifestyle and culture important On the rise, especially in “developed” or “first world” settings The Pima Indian case study “Traditional” and “Modern” Diets Glucose Regulation What is diabetes? Cells need sugar—ATP and the Krebs Cycle What comes in through the gut—basic nutrition Role of liver in processing nutrients, storing glucose Absorptive Pathways and role of insulin from pancreas Post-absorptive Pathways Understanding Diabetes Diabetes mellitus—”starvation amidst plenty” Type I Juvenile onset Pancreas beta cells die, no insulin produced Type II Adult onset Complicated set of factors, some insulin production Goal—understand why we need insulin Cells and Glucose All cells of body need constant glucose supply, especially nervous tissue Most other nutrients can be converted into glucose or derivatives for making ATP ATP is celluar “gasoline” Why not eat just sugar? What factors affect diabetes and obesity? Weight Activity level Genetics Cultural-social-economic (class?) Educational Can these be controlled? Pima Indian Study Pima Indians and Diabetes Pima Indians and Breastfeeding Pima study to justify low carb diet? “How Stuff Works” Diabetes: http://www.howstu ffworks.com/diabet es1.htm Glucose metabolism Liver receives blood from intestines (don’t forget hepatic portal system After meal, in response to insulin from pancreas, glucose stored as complex carbohydrate--glycogen--in liver Between meals, in response to glucagon from pancreas, glucose is released Pancreas releases insulin when sugar levels in blood go up Inadequate or zero insulin production results in hyperglycemia or high blood sugar Overproduction or over-dosing of insulin results in hypoglycemia or low blood sugar--insulin shock Diabetes is insufficient production of insulin Type I--juvenile onset with elimination of Islets of langerhans and zero insulin production Type II--adult onset with gradual loss of insulin production