* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download WORLD WAR 1 - ebruggeman
Home front during World War I wikipedia , lookup
History of Germany during World War I wikipedia , lookup
Economic history of World War I wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War I wikipedia , lookup
Bosnian crisis wikipedia , lookup
Assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the causes of World War I wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War I wikipedia , lookup
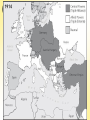
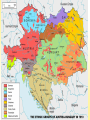
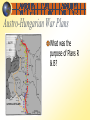
BELLWORK 1/8 Out of all of the European powers…. 1. Who were the biggest rivals? Why? 2. Which government abused their power the most? 3. Who had the strongest military? 4. Who had the most problems? Why? 5. THINKER: What is a “power vacuum?” How did the decline of the Ottoman Empire create a “power vacuum” in Europe? Impact? European Powers Review Before we study the causes of WWI, it’s important to understand the status of each European power in 1900. For this review activity, you will be divided into five groups. Each group will represent a different European power. Your task: review/re-teach the class about your European power. Emphasize the main ideas and anything that will help understand their role in WWI. It’s up to you how you do it – but make it clear, concise, easy to understand, and good review! Germany KAISER (Wilhelm – Prussian King) CHANCELLOR (Otto von Bismarck – military leader; unified Germany) REICHSTAG (Elected house of the German parliament) Map of the North German Confederation (red), the Southern German States (orange) and Alsace-Lorraine (beige) Reading and Homework: LongTerm Causes of World War I Monday we will study the Long-Term Causes of WWI: Militarism, Alliances, Imperialism, and Nationalism. In order to prepare for Monday’s lesson, you need to read pages 13-18. As you read, fill in the corresponding notes on pages 2-3 of your note packet. BELLWORK 1/11 1. Describe the naval arms race. How did this create problems between the powers? 2. Describe the growing system of alliances. Who did Germany want to align with? Who did Austria-Hungary target? 3. Why did European powers want to colonize Africa and the Far East? How did this lead to problems between the powers? 4. How did Austria-Hungary view the Balkans? How was this different than the Russian view? 5. THINKER: In your opinion, which one of the long term causes had the biggest impact on starting WWI? Explain! WORLD WAR I CAUSES, PRACTICES & EFFECTS OF WAR World War I The War was also known as THE GREAT WAR and famously “THE WAR TO END ALL WARS” It was a global military conflict that took place mainly in Europe between 1914 & 1918. It was a total war which left great devastation, millions dead and shaped the modern world. World War I created a decisive break with the old world order that had emerged after the Napoleonic Wars. The results of World War I would be important factors in the development of World War II; 21 years later. Long-Term Causes 1870-1904 Long-term Causes: Why did the war break out? Napoleon Bonaparte and the Rise of Nationalist Sentiment Colonial Expansion Anglo-German Naval Race Tension in the Balkans Ascension of Kaiser Wilhelm II Web of alliances MAIN CAUSES OF WWI Militarism Alliances Imperialism Nationalism ***These background causes were building for 40-50 years before the actual outbreak of WWI. Cause #1: Militarism Militarism: building up armed forces in preparation for war Characteristics: Army and military forces are given a high profile by the government Increased military spending and production Implementation of the draft Led to an arms race The armies of both France and Germany had more than doubled between 1870 and 1914 and there was fierce competition between Britain and Germany for naval superiority. What was the Naval Arms Race? The British had introduced the 'Dreadnought', an effective battleship, in 1906. The Germans soon followed suit introducing their own battleships. MILITARISM European Military Spending Year 1870 1880 1890 1900 1910 1914 Millions of $ 94 130 154 268 289 398 Britain maintained a large lead over Germany in all categories of warships. Both nations believed that command of the seas was vital to a great nation. The naval strength of the powers in 1914 Country Soldiers Large Naval Vessels Tonnage Size/Carrying Capacity Russia 54,000 4 328,000 France 68,000 10 731,000 Britain 209,000 29 2,205,000 331,000 43 3,264,000 Germany 79,000 17 1,019,000 Austria-Hungary 16,000 3 95,000 20 TOTAL TOTAL 249,000 1,268,000 Cause #2: Alliances An alliance is an agreement made between two or more countries to give each other help if needed. A number of alliances had been signed by countries between the years 1879 and 1914. These alliances meant that some countries had no option but to declare war if one of their allies declared war first Describe the growing system of alliances. Who did Germany want to align with? Who did Austria-Hungary target? Formation of the WWI Alliances In 1879 Germany and Austria- Hungary agreed to form a Dual Alliance. This became the Triple Alliance when in 1882 it was expanded to include Italy. The three countries agreed to support each other if attacked by either France or Russia. It was renewed at five-yearly intervals. France felt threatened by this alliance. Britain was also concerned by the growth in the Germany Navy and in 1904 the two countries signed the Entente Cordiale (friendly understanding). The objective of the alliance was to encourage co-operation against the perceived threat of Germany. Three years later, Russia who also feared the growth in the German Army, joined Britain & France to form the Triple Entente. The Russian government was also concerned about the possibility of Austria Hungary increasing the size of its empire. It therefore made promises to help Serbia if it was attacked by members of the Triple Alliance The formation of the Triple Entente in 1907 by Britain, France and Russia reinforced the need for the Triple alliance. Cause #3 - Imperialism Why did European powers want to colonize Africa and the Far East? How did this lead to problems between the powers? Due to industrialization, countries needed new markets & resources Imperialism! Imperialism: establishing political, economic and military dominance over weaker nations By 1900, all large European powers had colonies in Africa or Asia (not Austria-Hungary) Imperialist rivalries formed as countries competed and fought over new territories and resources The great powers had come into conflict over spheres of influence in Asia (Open Door Policy – China & Japan) and over territories in Africa (Moroccan Crisis) Germany embarked late, but aggressively, on colonial expansion under Emperor Wilhelm II Cause #4: Nationalism The French Revolution resulted in chaos and the ascent of Napoleon to power. Napoleon's armies marched all over Europe, bringing not only French control, but French ideas. The rise of ideas of nationalism, devotion and pride for one's common people and ethnicity, increased in popularity during the Napoleonic Wars. Napoleon encouraged the spread of nationalism, which he saw in his troops, to better the French war machine. The French people began to feel pride in their culture and ethnicity. The world watched nationalism for the first time and saw the power the French gained from it. Following the Napoleonic Wars, all of Europe was sharing these ideas There were two types of nationalism that emerged during the era: Desire for dominance Oppressed groups’ desire for independence Nationalism How did AustriaHungary view the Balkans? How was this different than the Russian view? Discussion In your opinion, which of the four background causes (militarism, alliances, imperialism, nationalism) was the biggest cause of WWI? Explain! Homework Read about the short term causes of WWI (pgs. 18-26) and complete the graphic organizer on page 3 of your note packet. BELLWORK 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. In one sentence, explain how each of the short-term effects increased hostilities between the European Powers: First Moroccan Crisis Bosnian Crisis Second Moroccan Crisis First Balkan War Second Balkan War THINKER: Every one of the short-term causes made a future war more likely, but why didn’t any of these conflicts lead to an actual war? How did European powers avoid war following these conflicts? Short-Term Causes 1905-1913 Short-Term Causes Storyboard For this review activity, you will work in a group to create a large-scale storyboard representation of one of the short-term causes. Requirements: Large-scale (pics/writing needs to be big! Easy to see! 100”) Legible and neat Easy to understand (a simplistic representation) Show understanding of the event (use five stages to represent event) Analyze why it created tension between the powers leading to WWI Use this to “re-teach” the class (everyone must contribute!) You are NOT being assessed on artistic ability, you are being graded on your ability to demonstrate understanding of the short-term causes of war in a visual/creative way What is at stake??? 30 classwork points! You will also be going head to head (WWI STYLE) with the other HOA class. Whichever period has the best, most creative, and accurate representations of short-term causes will win something special…… TBD…….. Make it neat! Have fun! The events Moroccan Crisis (1905) Bosnian Crisis (1908) Second Moroccan Crisis (1911) First Balkan War (1912) Second Balkan War (1913) Moroccan Crisis: 1905 In 1904 Morocco had been given to France by Britain, but the Moroccans wanted their independence. In 1905, Germany announced her support for Moroccan independence. War was narrowly avoided by a conference which allowed France to retain possession of Morocco. However, in 1911, the Germans were again protesting against French possession of Morocco. Britain supported France and Germany was persuaded to back down for part of French Congo. ***Why did Germany interfere in Morocco in both 1905 and 1911? Bosnian Crisis: 1908 In 1908, Austria-Hungary took over the former Turkish province of Bosnia. This angered Serbians who felt the province should be theirs. Serbia threatened Austria-Hungary with war, Russia, allied to Serbia, mobilized its forces. Germany, allied to Austria-Hungary mobilized its forces and prepared to threaten Russia. War was avoided when Russia backed down. There was, however, war in the Balkans between 1911 and 1912 when the Balkan states drove Turkey out of the area. The states then fought each other over which area should belong to which state. Austria-Hungary then intervened and forced Serbia to give up some of its acquisitions. Tension between Serbia and Austria-Hungary was high. International Situation by 1913 Increased division between the two alliances Increased militarism (arms race, conscription) Increased nationalism Literature, press & education prepared public for war Was war inevitable at this point? War Plans The powers prepare war plans……for a war that has not yet happened….. #thirstyforwar German War Plans What was the goal of Germany’s Schlieffen plan? Was this plan a success? French War Plans What was France’s war plan? Russian War Plans Invade Central Powers!!!!! Austro-Hungarian War Plans What was the purpose of Plans R & B? How did the short-term causes effect alliances? Kaiser Wilhelm II Last German Emperor (Kaiser), ruled from June 1888 - November 1918. When Kaiser Wilhelm II came to power, he quickly retired Chancellor Bismarck, and upset the balance of power by refusing to renew Germany's friendship with Russia. Launched Germany on a "New Course" in foreign affairs that culminated in his support for Austria-Hungary in 1914. Germany soon found itself as a minority. Its only European ally was the weakest of the European powers, Austria-Hungary. BELLWORK 1. What was the Black Hand? What was their objective in the assassination? 2. After the assassination, why was Austria-Hungary hesitant to declare war on Serbia? What changed this? 3. Summarize the Kaiser’s “blank cheque” to Austria (28). What did this promise? 4. After the assassination, it seemed like this would just be another short term conflict, so why was this conflict impossible to contain in the Balkans? 5. THINKER: Do you think countries should be required to take the blame for starting war? If so, should they be punished following the war? Why or why not? Immediate Cause of WWI The assassination of Ferdinand and the outbreak of war The Black Hand In May 1911, ten men in Serbia formed the Black Hand Secret Society. Early members included Colonel Dragutin Dimitrijevic, the chief of the Intelligence Department of the Serbian General Staff. The main objective of the Black Hand was the creation, by means of violence, of a Greater Serbia. Its stated aim was: "To realize the national ideal, the unification of all Serbs. This organization prefers terrorist action to cultural activities; it will therefore remain secret." The Black Hand By 1914 there were around 2,500 members of the Black Hand. The group was mainly made up of junior army officers but also included lawyers, journalists and university professors. Three senior members of the Black Hand group, Dragutin Dimitrijevic, Milan Ciganovic, and Major Voja Tankosic, decided that Archduke Franz Ferdinand should be assassinated. The political objective of the assassination was to break off Austria-Hungary's south-Slav provinces so they could be combined into a Greater Serbia or a Yugoslavia. The People chosen for the task Gavrilo Princip, Nedjelko Cabrinovic and Trifko Grabez from Serbia made plans to assassinate him. Assassination• at Sarajevo On 28 June 1914, the Archduke Franz- Ferdinand and his wife visited Sarajevo, the capital of Bosnia, to review the troops. It was also Serbia's National Day - the anniversary of the battle, in 1389, when Serbia had been conquered by the Turkish Ottoman Empire, yet at which a Serb hero, Milos Obilic, had assassinated the Ottoman Sultan. This day was inextricably linked with Serbian nationalism, and with the assassination of foreign rulers. Waiting for Franz Ferdinand, lined up along the Appel Quay, Sarajevo's main road, were six young men. They were armed with pistols and bombs supplied by the Black Hand. They were going to try to murder Franz Ferdinand Austrian spies in Serbia had reported that there was going to be an assassination attempt. Panicked, the Prime Minister of Serbia, had also told the Austrian government that there was going to be trouble. Franz Ferdinand ignored these warnings. Only 120 policeman were on duty in Sarajevo, and they were so excited that they forgot to watch the crowds, and looked at the procession instead. Franz Ferdinand was disguised in the uniform of an Austrian cavalry general. To reach the Town Hall the procession had to drive along the Appel Quay. The six conspirators had posted themselves along the route; the Appel Quay was `a regular avenue of assassins.' At 10.10 am, as the procession drew near the Cumuria Bridge. Near the Cumuria bridge: 1st Mehmed Mehmedbasic: told a friend that he could not get a clear opportunity and that a policeman had approached him just as he was to throw the bomb. 2nd Vaso Cubrilovic: told investigation that felt sorry for the Duchess; said that he was badly placed. 3rd Nedeljko Cabrinovic: threw a bomb. Wearing a long black coat and a black hat, he asked a policeman to tell him which car the Archduke was in; seconds later he had knocked the cap off a hand grenade against a metal lamp-post and aimed it at the Archduke seated in the open car. Franz Ferdinand later claimed that he had knocked away the bomb with his hand; witnesses at the trial, however, all agreed that the bomb had bounced off the folded-back hood of the Archduke's car. It blew up the car behind, killing two officers and injuring about twenty people. Cabrinovic swallowed poison, but it failed to work. After stopping to see what had happened, Franz Ferdinand's car sped to the Town Hall. 4th (landward side) Cvetko Popovic: told a friend that could not see which was Franz Ferdinand because he was short-sighted; told the trial the lost his nerve. In order to avoid the city center, the royal car traveled straight along the Appel Quay and took a right turn into Franz Joseph Street. One of the conspirators, Gavrilo Princip, was standing on the corner at the time. An advisor immediately realized the driver had taken the wrong route and shouted "What is this? This is the wrong way! We're supposed to take the Appel Quay!" The driver put his foot on the brake, and began to back up. In doing so he moved slowly past the waiting Gavrilo Princip. The assassin stepped forward, drew his gun, and at a distance of about five feet, fired several times into the car. Franz Ferdinand was hit in the neck and Sophie in the abdomen. Princip's bullet had pierced the archduke's jugular vein but before losing consciousness, he pleaded "Sophie dear! Sophie dear! Don't die! Stay alive for our children!“ Franz Urban drove the royal couple to Konak, the governor's residence, but although both were still alive when they arrived, they died from their wounds soon afterwards. Princip Bridge: sight of Archduke Ferdinand’s assassination Nedjelko Cabrinovic, statement in court (23rd October, 1914) We did not hate Austria, but the Austrians had done nothing, since the occupation, to solve the problems that faced Bosnia and Herzegovina. Ninetenths of our people are farmers who suffer, who live in misery, who have no schools, who are deprived of any culture. We sympathized with them in their distress. We thought that only people of noble character were capable of committing political assassinations. We heard it said that he (Archduke Franz Ferdinand) was an enemy of the Slavs. Nobody directly told us "kill him"; but in this environment, we arrived at the idea ourselves. I would like to add something else. Although Princip is playing the hero, and although we all wanted to appear as heroes, we still have profound regrets. In the first place, we did not know that the late Franz Ferdinand was a father. We were greatly touched by the words he addressed to his wife: "Sophie, stay alive for our children." We are anything you want, except criminals. In my name and in the name of my comrades, I ask the children of the late successor to the throne to forgive us. As for you, punish us according to your understanding. We are not criminals. We are honest people, animated by noble sentiments; we are idealists; we wanted to do good; we have loved our people; and we shall die for our ideals. Name Gavrilo Princip Nedjelko Čabrinović Trifun Grabež Vaso Čubrilović Cvjetko Popović Lazar Đukić Sentence Life in prison 20 years 20 years 16 years 13 years 10 years Danilo Ilić Death by hanging (executed 3 February 1915) Veljko Čubrilović Death by hanging (executed 3 February 1915) Nedjo Kerović Death by hanging; commuted to 20 years in prison by Kaiser FranzJoseph based on Finance Minister's recommendation Mihaijlo Jovanović Death by hanging (executed 3 February 1915) Jakov Milović Death by hanging; commuted to life in prison by Kaiser Franz-Joseph based on court's and Finance Minister's recommendation Mitar Kerović Ivo Kranjcević Branko Zagorac Marko Perin Cvijan Stjepanović Life in prison 10 years 3 years 3 years 7 years Review: Events leading to the outbreak of war Time to play a game…… THE BLAME GAME!!! Who is to blame for starting WWI? Read “what was the contribution of each of the European powers during the July Crisis to the outbreak of war?” (pgs. 29-31) As you read, complete the note packet Be ready to defend your opinion….. Who is the most at fault? Who should be blamed? Who is to blame for starting WWI? You will be assigned a group, and each group will be responsible for blaming a different country for their involvement in WWI. In your group you must prepare a speech/presentation to present to an International Tribunal which will decide….. Who is to blame? Take into consideration: Their involvement in short/long term causes, responsibility for the beginning of the war, their acts of aggression, lack of prevention of war, and historians arguments GERMANY Ayham, Rachel, Coleman, Calli, Cezanne, Bridgette AUSTRIA-HUNGARY Liam, Hannah, Hunter, Katja, Chandni RUSSIA Matt, Sarah, Courtney, Andres, Sophia, Afrooz BRITAIN Joseph, Cassie, Nate, Kim, Lauren, Genevieve Which countries were bound to each other by which alliance? How did imperialism contribute towards Germany’s increasing anger with Britain and France? Why was nationalism an important factor? Describe the part played by Germany in increasing European militarism. What links were there between the two crises and: Alliances Imperialism Militarism Nationalism BELLWORK - 13 March 2013 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Time to review over the background causes of WWI! For each of the four causes, explain how and why that cause created problems/tensions in Europe and pushed them closer to war. Militarism Alliances Imperialism Nationalism THINKER: In your opinion, which of the four causes had the biggest impact or created the most problems eventually leading to WWI?