* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
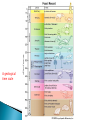
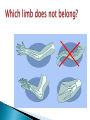
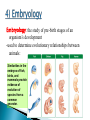
SBI3U1 The theory of evolution by natural selection was proven by the following methods: 1)Fossil Record 2)Biogeography 3)Anatomy 4)Embryology 5)DNA Fossils are found within the layers of sedimentary rock. Specific fossils are found in specific strata (rock layers). Fossil groups are unique to each stratum. ◦ paleontologists use this to determine dates A geological time scale Youngest Fossils (closest to the surface) Oldest Fossils Evidence from Fossil Record: Fossils within the younger layers are most similar to species alive today. Fossils appear in chronological order within the sedimentary layers. Not all organisms appear in the fossil record at the same time. Paleontologists have used fossils to trace the evolution of the modern camel. The Paleocene, Eocene,Oligocene, and Miocene epochs are subdivisions of the Cenozoic era. Scientists are always looking for transitional fossils that show an intermediary link between past and present groups of organisms. Vestigial structures are reduced versions of what were once functional structures in an ancestral species Biogeography=Study of geographical distribution of species 1)Geographically close environments are more likely to be populated by related species. 2)Animals found on islands often closely resemble animals on the nearest continent. 3)Fossils of the same species can be found on the coastlines of neighbouring continents Notice that these vertibrates have the same basic arrangement of bones but the bones have different uses. Human Homologous structures = structures that have similar structural elements and origin but may have a different function. They originate from a common ancestor. Ie. Limbs, hair • Analogous structures= structures that do not have a common evolutionary origin but perform similar functions. These provide evidence for adaptation to suit the environment. Ie. the fins of a porpoise and a fish. • All of these organisms have a similar bone structure. They were inherited from a common ancestor Example: Insects, Birds, and Bats all have wings used for flight (function) but insects do not come from a common ancestor because there are no bones. *Note: Your textbook describes bird and bat wings as analogous, this is NOT true. Example: Penguins and fish both has fins for swimming. The fin evolved as a structural adaptation, not from a common ancestor. Both types of squirrels have evolved from different lineages Elvis Fans Have a common ancestor (mother) Evolved from separate lineages Sisters Homology Analogy Embryology: the study of pre-birth stages of an organism’s development -used to determine evolutionary relationships between animals: Similarities in the embryos of fish, birds, and mammals provide evidence of evolution of species from a common ancestor. By comparing organisms’ genetic sequences, scientists can determine their level of similarity. Two organisms with similar patterns of DNA, suggests that they inherited this information from a common ancestor. Read and make notes 8.2 Complete pg. 340 Q# 1- 3, 8-12