* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Flip-flop (electronics) wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Sound reinforcement system wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Scattering parameters wikipedia , lookup
Dynamic range compression wikipedia , lookup
Negative feedback wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Public address system wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope types wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
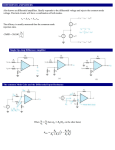
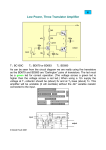
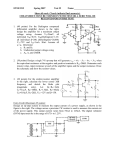
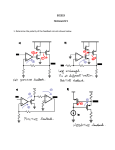
Date:- 16-11-2011 AMPLIFIERS • What is an amplifier? • Literally amplifier means an increaser. In broad term, an amplifier is defined as “A device that enables an input signal to control an output signal. OR • Amplifier is an electronic device that gives an output signal of having the same characteristics and morphology of the input signal but will generally be larger than the input signal on the basis of voltage, current or power. CLASSIFICATION OF AMPLIFIERS • Amplifiers are classified on the basis of the following types. • 1. Power/Current Amplifier • 2. Frequency Amplifier • 3.Voltage Amplifier D.16-10-2011 POWER/CURRENT AMPLIFIER: The power amplifier is an amplifier in which the power of output signal is greater than the power of input signal. Or simply the power amplifier amplifies the power of the input signal, thus the output signal power is stronger (increased/larger). At the same time voltage is decreased or dropped. e.g. Frequency Amplifiers: The frequency amplifier increases the frequency component of that system according to its designed power of amplification. e.g. Fan speed regulator • VOLTAGE AMPLIFIER: • In EEG machine, the voltage amplifiers are designed to serve the following two main functions. • 1. Differential Discrimination: • It differentiates between two incoming signals (input I and II) on the basis of voltage/Potential and current. • 2. Amplification: • It amplifies (increases) the voltage difference of two inputs in terms of sensitivity and gain. VOLTAGE AMPLIFIER : The voltage amplifier amplifies (increases) the input voltage and gives larger output signal voltage. Or simply in a voltage amplifier the output signal voltage is larger (amplified) than the input signal voltage. • i.e. Voltage amplifier is further characterized with its different types and functions. Types of Voltage Amplifiers: Voltage amplifiers are divided into the following types • • • 1. Pre-amplifier (Buffer Amplifier) 2. Differential Amplifier 3. Single ended amplifier 1.Pre-ampifier (Buffer Amplifier): “All small input signals are received at pre-amplifier circuit which has the ability to pick the signal of 5uV-100uv. It has the following properties; • High input impedance (resistance): Which reduces distortion of the source waveform by minimizing the input reactance and limiting the current drawn by the source. • If the DC potentials from the input terminals of a bio-potential are not minimized, the patient can get micro or macro-shocks. • Low output impedance (resistance): Which allows to pass the received actual signal (activity) to maintain maximal fidelity (accuracy of a description, translation ) and range in readout. Potential Difference • “The difference between two electrical signals is called potential difference”. • The differential amplifier that subtracts one signal voltage (input I) from another signal (input II) & amplifies the difference of these signals as output signal. This type of amplification is called differential or balanced amplification. Common Mode Rejection (CMR): The differential amplifier cancels out (rejects) those signals which are common to both inputs (I &ll), this is called common mode rejection and signals are said to be “in Phase or in Common Mode”. • In EEG machines the polarities of both inputs (I &II) work with convention as : • If Input I is more negative than Input II deflection would be upward. • Input I is less negative than Input II deflection would be downward. • Signal have equal potentials on both input l and ll will be canceled out and there would be no deflection. Common Mode Rejection Ratio (CMRR): • This is the ratio of the common mode input voltage over the output voltage. • The common-mode rejection ratio (CMRR) of a differential amplifier measures the ability of the device to reject the input signal common in both input leads (1 & 2). • Good EEG amplifiers should have CMMR ratio of 10,000:1 or more. 3.SINGLE ENDED AMPLIFIER: Amplifier that doesn’t have the ability to subtract one input from another is considered as Single Ended Amplifier because It just compares the difference b/w a single input and the electrical ground, which has a voltage close to zero. These amplifiers actually have the signals which already been amplified. AMPLIFICATION: • The amplifier increases the voltage difference b/w the inputs so that the output voltage is used to drive the pens of the analog EEG instrument or analog to digital converter of the digital EEG machine. Amplification is characterized in terms of: • 1. Sensitivity. • 2. Gain • SENSITIVITY: The ratio of input voltage to the signal deflection is called sensitivity, which is measured in uV/mm. / Sensitivity = Input Voltage Pen deflection Gain: “Gain is the ratio of output signal voltage to input signal voltage which is expressed in dB. • i.e • If an amplifier is set to be given the output voltage of 5V for the input of 5uV, then the gain of the EEG amplifier would be 1 million dB. • Usually 1 million is the maximum gain of an EEG analog amplifiers. The End.. • Thank You For Your Patience. The road to progress is always in progress.