* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Exploring Parallel Lines and Related Angles
Duality (projective geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Lie sphere geometry wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Perspective (graphical) wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Compass-and-straightedge construction wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
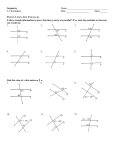
Project AMP Dr. Antonio Quesada – Director, Project AMP Exploring Parallel Lines and Related Angles Lesson Summary: Students investigate the special angles formed by parallel lines. Key Words: parallel, transversal, alternate interior angles, exterior angles, same side interior angles, supplementary angles, corresponding angles Background Knowledge: This lab is designed with the assumption that students know where to find most tools and how to use them. A brief description of a tool and how to use it can be found by selecting a tool and pressing F1. A help screen will appear across the bottom of the screen and will describe each tool as it is selected. Further assistance and direction can be found by referring to the instruction manual. The extension activity has students write formal proofs of the theorems discovered in this activity. Learning Objectives: Students will observe the relationship between the angles formed by two parallel lines and a transversal. Materials: Geometry software such as Cabri Geometry Suggested Procedure: Split students into groups of two or three. Pass out worksheets and have students complete the activity. Project AMP Dr. Antonio Quesada – Director, Project AMP Exploring Parallel Lines and Related Angles Team Members’ Names: _________________________________________________ File Name: _____________________________________________________________ Lab goals: Observe the relationship between the angles formed by two parallel lines and a transversal. 1. Construct two parallel lines. (use parallel tool) 2. Construct a point on each line. Label them point A and B. (point on object tool) 3. Construct a line through these two points. This line is called a transversal. A transversal is a line that intersects two coplanar lines at two distinct points. (line tool) 4. This is the time to investigate about the angles. Label each of the eight angles formed by the parallel lines and transversal with the numbers 1 though eight tool and measure each of them. Write down the measurements of the angles and your observations. What is the relationship between the angles? (comment tool, measure angle tool) m∠1 = m∠3 = m∠5 = m∠7 = m∠2 = m∠4 = m∠6 = m∠8 = Observe the relationship between the angles formed by two lines and a transversal of those two lines. Be able to identify alternate interior, same-side interior, exterior, and corresponding angles. Project AMP Dr. Antonio Quesada – Director, Project AMP 5. Open a new file. Create two lines that are not parallel to each other and label them l and m. Now make a third line t that is a transversal to lines l and m. 6. Label the points where the t intersects lines l and m as points A and B. Again there are eight angles formed by the transversal and the two lines. Label them with numbers 1 through 8. (comment tool, angle measure tool) 7. Interior angles are those angles formed by lines l and m and the segment AB . Two interior angles, one having vertex A and the other having vertex B, whose interiors lie on opposite sides of t are called alternate interior angle. Name the pairs of alternate interior angles of l and m. 8. Two interior angles, one having vertex A and the other having vertex B, whose interiors lie on the same side of t are called same-side interior angles. Name the pairs of same-side interior angles of l and m. 9. Exterior angles are those angles formed by the transversal t, the halfplain created by l that does not contain line m, and the half-plain created by m that does not contain line l. Name the pairs of angles in the exterior of l and m. 10. Two angles are said to be corresponding if both lie on the same side of t and if ones orientation with respect to line l is the same as the other’s orientation with respect to m. Name all the corresponding angles. Project AMP Dr. Antonio Quesada – Director, Project AMP Extension Activity Use the angles in the diagram for the following proofs. 11. Prove: If two parallel lines are cut by a transversal, then alternate interior angles are congruent. Given: l || m Prove: ∠3 ≅ ∠6 12. Prove: If two parallel lines are cut by a transversal, then the pairs of same side interior angles are supplementary. Given: l || m Prove: ∠3 and ∠5 are supplementary. Project AMP Dr. Antonio Quesada – Director, Project AMP Journal Activity Exploring Parallel Lines and Related Angles 1. What was your favorite thing about this activity? 2. What was the most challenging thing? 3. What did you gain the most confidence about through completing this lesson? 4. Where do you possibly see yourself using this knowledge in the future?