* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MUSCLES OF THE PECTORAL GIRDLE
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
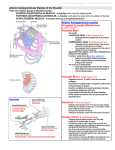
MUSCLES OF THE PECTORAL GIRDLE LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture the student should be able to: • Know the role of muscles of pectoral region in stabilizing the pectoral girdle. • Enumerate the muscle of pectoral girdle . • Describe the attachments of muscle of pectoral girdle, nerve supply and actions ( Pectoralis Major and minor, • Subclavius,Trapezius,Latissimus Dorsi,Rhomboid major and minor,Levator Scapulae and Serratus anterior). • Discuss the clavi-pectoral fascia. • Know the triangle of auscultation. • Mention the nerves and blood vessels of this region. PECTORAL GIRDLE • The pectoral girdle or shoulder girdle is the set of bones which connects the upper limb to the axial skeleton on each side. • Consists of the clavicle and scapula PECTORAL GIRDLE • The only joints between the shoulder girdle and axial skeleton are the sternoclavicular joints on each side. • No joint exists between each scapula and the rib cage; instead the muscular connection between the two permits relatively great mobility of the shoulder girdle in relation to the pelvic girdle. PERCTORAL GIRDLE MUSCLES: • Muscles of the pectoral girdle broadly are divided into • Anterior axioappendicular group • Posterior axioappendicular group ANTERIOR AXIOAPPENDICULAR MUSCLES Also called Thoracoappendicular or pectoral muscles • Four muscles – Pectoralis major – Pectoralis minor – Subclavius – Serratus anterior PECTORALIS MAJOR • • • • • Large fan shaped Covers superior part of thorax Has clavicular and sternocostal heads Its inferior border forms Ant. Axillary fold Pectoralis major and adjacent deltoid forms the narrow deltopectoral groove in which cephalic vein runs • Pectoralis major along with clavicle forms clavipectoral or deltopectoral triangle PECTORALIS MINOR • Lies beneath Pectoralis major • An imp.landmark for structures in axilla • With coracoid process makes a bridge beneath which vessels and nerves pass SUBCLAVIUS • Lies almost horizontally when the arm is in anatomical position • Located inferior to clavicle and affords some protection to the subclavian vessels and the superior trunk of brachial plexus if clavicle fractures SERRATUS ANTERIOR • Saw toothed appearance, also called boxer’s muscle • Overlies lateral part of thorax and forms medial wall of axilla • Holds scapula against thoracic wall while doing pushups Attachments of muscles of ant.axioappendicular group Posterior Axioappendicular Muscles • Also called scapulohumeral muscles • Divided into 3 groups • Superficial posterior Appendicular (extrinsic shoulder) muscles – Trapezius – Latissimus dorsi • Deep posterior Appendicular (extrinsic shoulder) muscles – Levator scapulae or rhomboids • Scapulohumeral (intrinsicshoulder) muscles; – Deltoid – Teres major – 4 rotator cuff muscles (supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor and subscapularis) TRAPEZIUS • Large, triangular muscle, covers the posterior aspect of neck and superior half of trunk • Have 3 types of fibres • Superior fibres; elevate scapula • Middle fibres; retract scapula • Inferior fibres; depress scapula • Origin Medial third superior nuchal line – External occipital protuberance – Nuchal ligament – Spinous processess of C7-C12 vertebrae Insertion – Lateral third of clavicle; – Acromion – Spine of scapula Innervation Motor – Accessory nerve (CN XI) Sensory – C3, C4 spinal nerves – • • • • LATISSIMUS DORSI • Widest muscle of the back • Climbing muscle • Large fan shaped muscle passes from trunk to humerus • Origin – – – – Spinous processes of inferior 6 thoracic vertebrae Thoracolumbar fascia Iliac crest Inferior 3 or 4 ribs • Insertion – Floor of intertubercular groove of humerus • Innervation – Thoracodorsal nerve (C6,C7,C8) LEVATOR SCAPULAE \ • Superior third lies deep to sternocleidomastoid,while inferior third lies deep to trapezius. • Function – Elevates scapula – Tilts its glenoid cavity inferiorly by rotating scapula • Origin – Posterior tubercle of transverse processes of C1-C4 vertebrae • Insertion – Medial border of scapula superior to root of spine • Innervation – Dorsal scapula (C5) – Cervical nerve (C3,C4) RHOMBOIDS • • • • Major and minor Forms oblique equilateral parrallelogram Lies deep to trapezius Innervation – Dorsal scapular nerve (C4,C5) • Function – Retract scapula and fix scapula to thoracic wall • Rhomboid minor • Origin – Nuchal ligament – Spinous processes of C7-T1 • Insertion – Scapular spine • Rhomboids major • Origin – Spinous processes of T2-T5 • Insertion – Medial border of scapula from spine to inferior angle SCAPULOHUMERAL (INTRINSIC SHOULDER) MUSCLES Deltoid Teres major Rotator cuff Supraspinatus Infraspinatus Teres minor Subscapularis • Thick ,powerful, coarse textured forming rounded contour of the shoulder • Shaped like delta • Has unipennate anterior and posterior parts • Multipennate middle part • Origin – Clavicle – Acromion – Spine of scapula • Insertion – Deltoid tuberosity of humerus • Function – Flexor and medial rotator of arm – Abducts and laterally rotates arm • Innervation – Axillary nerve (C5,C6) SUPRASPINATUS • Origin – Scapular supraspinator fossa • Insertion – Greater tubercle of humerus • Function – Abductor of arm • Innervation – Suprascapular nerve (C4,C5,C6) INFRASPINATUS • Origin – Scapular infraspinator fossa • Insertion – Greater tubercle of humerus • Function – External or lateral rotator – Upper posterior border of musculotendinous cuff TERES MINOR AND MAJOR • • • • • • • • • • Teres minor Origin – Lateral border of scapula Insertion – Greater tubercle of humerus Function – External or lateral rotator – Lower posterior border of musculotendinous cuff Innervation – Axillary nerve (C5,C6) Teres Major Origin – Inferior angle of scapula Insertion – Intertubercular groove of humerus Function – Adducts and medially rotates arm Innervation – Lower subscapular nerve (C5,C6) SUBSCAPULARIS • Origin – Scapular subscapular fossa • Insertion – Lesser tubercle of humerus • Function – Chief internal and medial rotator – Anterior border of musculotendinous cuff • Innervation – Upper and lower subscapular nerves (C5,C6,C7) REFERENCES • Gray’s textbook of anatomy ************************************************************************