* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Population Measures File
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
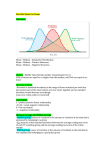
POPULATION MEASURES Mean, Median and Mode Quartiles and Standard Deviation Measures of Central Tendency • The average of a set of data can be quoted at the mean, median or mode. • In different situations it is more appropriate to choose one of these over the other two. • Mean = 𝑠𝑢𝑚 𝑜𝑓 𝑎𝑙𝑙 𝑛𝑢𝑚𝑏𝑒𝑟𝑠 𝑡𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑛𝑢𝑚𝑏𝑒𝑟 𝑜𝑓 𝑝𝑖𝑒𝑐𝑒𝑠 𝑜𝑓 𝑑𝑎𝑡𝑎 • Median = middle number when the data is ranked in order • Mode = the number that occurs most often The mean • If the results are symmetrical and continuous then can legitimately use the mean. • The main disadvantage with the mean is that it includes every piece of data. This can be a problem when you have especially large/small outliers in the data set. The Median • The median is usually preferred when the data set is skewed or you are dealing with ordinal data e.g. when you can rank the selections in order but the data is not numerical. • The main problem with the median is that when you have a very large data set it can take a large amount of time to sort the data into order. The Mode • The mode is the average used less frequently. It is usually used when you have nominal/categorical data. E.g. How do you travel to school? • The main disadvantage with the mode is that it may not be unique and it can be very misleading when the most common result is a large distance away from the rest of the data. Quartiles • The lower quartile shows us where a quarter (25%) of the data items are less than and three quarters (75%) are greater than. • The upper quartile shows us where three quarters of the data items are less than and one quarter greater than. Standard Deviation • The standard deviation gives us an idea of how spread out the data is. • Low SD means less spread out, high SD means more spread out. • Technically, for a symmetrical and unimodal data set, 95% of the data should be within two SD’s of the mean.