* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture 14: Power Amplifiers - BJT
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Radio transmitter design wikipedia , lookup
Standby power wikipedia , lookup
Thermal runaway wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Captain Power and the Soldiers of the Future wikipedia , lookup
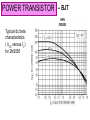
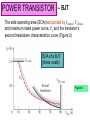
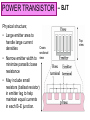
EMT 112/4 ANALOGUE ELECTRONICS 1 Power Amplifiers Syllabus Power amplifier classification; class A, class B, class AB and class C, amplifier distortion, transistor power dissipation, thermal management. POWER AMPLIFIERS Part I Power Transistor – BJT & MOSFET POWER TRANSISTOR Transistor limitations • Maximum rated current, • Maximum rated voltage, • Maximum rated power. The maximum rated power is related to the maximum allowable temperature of the transistor. POWER TRANSISTOR – BJT Large-area devices – the geometry and doping concentration are different from those of small-signal transistors Examples of BJT rating: Parameter VCE (max) (V) IC (max) (A) PD (max) (W) fT (MHz) Small-signal BJT (2N2222A) 40 0.8 1.2 35 – 100 300 Power BJT Power BJT (2N3055) (2N6078) 60 250 15 115 7 45 5 – 20 0.8 12 – 70 1 POWER TRANSISTOR – BJT Current gain depends on IC and is smaller in power BJT. The maximum rated collector current, IC(rated) may be related to the following: 1. maximum current that the wires connecting the semiconductor to the external terminals can handle 2. The collector current at which the gain falls below a minimum specified value 3. current which leads to maximum power dissipation when the transistor is in saturation. POWER TRANSISTOR – BJT Typical dc beta characteristics ( hFE versus IC) for 2N3055 POWER TRANSISTOR – BJT The maximum voltage limitation: • Avalanche breakdown in the reverse-biased basecollector junction (involves gain and breakdown at the p-n junction) • Second breakdown – nonuniformities in current density which inreases temperature in local regions in semiconductor. POWER TRANSISTOR – BJT Avalanche Breakdown (Figure 1) • In Figure 1, the breakdown voltage when the base terminal is open-circuited (IB=0) is VCEO, approx. 130V (Figure 1). • All the curves tend to merge to the same collectoremitter voltage, denoted as VCE(sus) once breakdown has occurred. • VCE(sus) is the voltage necessary to sustain the transistor in breakdown. • In Figure 1, VCE(sus) is approx. 115V POWER TRANSISTOR – BJT IC–VCE characteristics showing breakdown effect Figure 1 POWER TRANSISTOR – BJT The total instantaneous power dissipation in transistor pQ vCE iC vBE iB The second term is usually small, hence; pQ vCE iC The average power over ONE CYCLE of the signal: 1 PQ T T 0 vCE iC dt POWER TRANSISTOR – BJT The average power dissipated in a BJT must be kept below a specified maximum value to ensure that the temperature of the device does not exceed the maximum allowable value. If collector current and collector-emitter voltage are dc quantities, the maximum rated power, PT PT VCE I C The power handling ability of a BJT is limited by two factors, i.e. junction temperature, TJ and second breakdown. Safe Operating Area (SOA) must be observed, i.e. do not exceed BJT power dissipation. POWER TRANSISTOR – BJT The safe operating area (SOA) is bounded by IC(max); VCE(sus) and maximum rated power curve, PT and the transistor’s second breakdown characteristics curve (Figure 2) SOA of a BJT (linear scale) Figure 2 POWER TRANSISTOR – BJT SOA of a BJT (log scale) Figure 3 POWER TRANSISTOR – BJT EXAMPLE 8.1 Determine the required ratings (current, voltage and power) of the BJT. POWER TRANSISTOR – BJT EXAMPLE 8.1 – Solution For VCE 0 the maximum collector current; VCC 24 I C max 3A RL 8 For I C 0 the maximum collectoremitter voltage; VCE max VCC 24 V POWER TRANSISTOR – BJT EXAMPLE 8.1 – Solution The load line equation is; VCE VCC I C RL The load line must lie within the SOA The transistor power dissipation; PT VCE I C VCC I C RL I C VCC I C I C2 RL POWER TRANSISTOR – BJT EXAMPLE 8.1 – Solution dPT 0 The maximum power occurs when dI C i.e. when VCC 2 I C RL 0 Differentiating or when I C 1.5 A At this point; VCE VCC I C RL 12 V and; PT VCE I C 18 W POWER TRANSISTOR – BJT EXAMPLE 8.1 – Solution Thus the transistor ratings are; I C max 3 A VCE max 24 V PT 18 W In practice, to find a suitable transistor for a given application, safety factors are normally used. The transistor with I C max 3 A, VCE max 24 V, PT 18 W will be required. POWER TRANSISTOR – BJT Physical structure; • Large emitter area to handle large current densities • Narrow emitter width to minimize parasitic base resistance Crosssectional view • May include small resistors (ballast resistor) in emitter leg to help maintain equal currents in each B–E junction. Top view