* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 31 Internal Fluids and Respiration
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
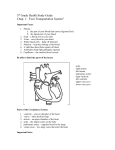
Chapter 9 - Internal Fluids and Respiration Chapter 9 Internal Fluids and Respiration Multiple Choice Questions 1. In multicellular animals, body fluids are divided into two main phases, a. Blood plasma and interstitial fluid b. Blood plasma and lymph c. Bloodstream and digestive fluids d. Bloodstream and cerebrospinal fluids E. Intracellular and extracellular 2. Extracellular fluid is subdivided into A. Blood plasma and interstitial fluid b. Blood plasma and lymph c. Bloodstream and digestive fluids d. Bloodstream and cerebrospinal fluids e. Intracellular and extracellular 3. Interstitial fluid is constantly formed by a. The lymphatic system producing it B. Lightweight elements in the blood plasma filtered through capillary walls c. Absorption across the gut lining d. Absorption across the lung surface e. Reabsorption in the kidney tubules 4. Which of the following is correct? a. Blood plasma—fewer large protein molecules B. Interstitial spaces—three times more water than bloodstream c. Intracellular—sodium, chloride, and bicarbonate ions d. Extracellular—potassium, magnesium, and phosphate ions e. Blood plasma—half of the body's water 31-1 Chapter 9 - Internal Fluids and Respiration 5. Blood in vertebrates constitutes a. An organ b. An organ system C. A tissue d. A cell assemblage e. Merely a fluid matrix 6. Which of the following associations of blood components and functions is NOT correct? a. Albumin—large protein that maintains osmotic balance b. Serum—plasma minus the proteins involved in clotting c. Fibrinogen—large protein for blood clotting d. Erythrocytes—red blood cells E. Globulins—carriers of simple sugars 7. Which statement of red blood cell (RBC) structure or function is NOT correct? A. In mammals and birds, RBCs continuously form from erythroblasts in the red bone marrow b. Mammal RBCs do not lose their nucleus when they mature c. Over 90% of the cell by weight is hemoglobin d. The completely flat shape of RBCs provides greater surface area for osmosis e. The average life of an RBC is several years after which its components are salvaged by the liver 8. A blood clot is formed by a fibrin meshwork in a reaction that is catalyzed by the enzyme a. Platelet factor b. Prothrombin C. Thrombin d. Fibrinogen e. Fibrinase 31-2 Chapter 9 - Internal Fluids and Respiration 9. Platelets a. Are specialized red blood cells b. Carry the blood type protein C. Initiate clotting by releasing thromboplastin d. Transport carbon dioxide in the blood e. Are responsible for the buildup of plaques on artery walls 10. The long, insoluble threads of fibrin of a blood clot originated from A. Fibrinogen b. Thrombin c. Collagen d. Prothrombin e. Platelets 11. ____________ carry blood away from the heart. a. Capillaries b. Venules c. Veins D. Arteries e. Lymph vessels 12. The ____________ is involved with pumping blood to and from the lungs. a. Systemic circuit b. Internal respiration circuit c. Hepatic circuit D. Pulmonary circuit e. Renal circuit 13. The systemic circuit ultimately circulates blood from the a. Right ventricle to left atrium b. Left ventricle to left atrium c. Right ventricle to right atrium D. Left ventricle to right atrium e. Pulmonary artery to the lungs 31-3 Chapter 9 - Internal Fluids and Respiration 14. The pulmonary semi-lunar valves prevent the backflow of blood into the a. Right atrium b. Left atrium C. Ventricles d. Aortic arch e. Pulmonary trunk 15. Oxygenated blood enters the heart at the A. Left atrium b. Left ventricle c. Right atrium d. Right ventricle e. None of the choices are correct 16. Contraction of the right ventricle forces blood initially into the a. Left atrium b. Right atrium c. Aorta d. Pulmonary vein E. Pulmonary artery 17. In the tetrapod heart, the pacemaker is in the a. Atrioventricular bundle b. Purkinje fibers c. Vagus nerves d. Cardiac control center E. Sino-atrial (SA) node 18. The heartbeat rate is controlled by the cardiac center located in the a. Cerebellum B. Medulla c. Cerebrum d. Midbrain e. Heart wall 31-4 Chapter 9 - Internal Fluids and Respiration 19. In some invertebrates, if we cut the nerves leading to the heart and the heart stops beating, the heart is considered a. An open system b. Myogenic C. Neurogenic d. A deferred pacemaker e. Asynchronous 20. The blood vessel that provides oxygen to the heart tissue is the a. Pulmonary artery B. Coronary artery c. Left carotid artery d. Renal artery e. Left subclavian artery 21. If a person has a blood pressure of 110/60, the "110" refers to the a. Diastolic pressure B. Systolic pressure c. Pulse pressure d. Capillary pressure e. Venous pressure 22. The exchange of nutrients, oxygen, and wastes (including carbon dioxide) takes place across the walls of the a. Lymph vessels b. Arteries C. Capillaries d. Veins e. Lymphatic vessels 31-5 Chapter 9 - Internal Fluids and Respiration 23. Which blood vessels will have walls only one cell thick? A. Capillaries b. Venules c. Veins d. Arterioles e. Arteries 24. Opposing the blood hydrostatic pressure that forces water across capillaries is the a. Cellular hydrostatic pressure b. Albumin concentration gradient C. Colloid osmotic pressure d. Lymphatic hydrostatic pressure e. Law of coupled balanced flow 25. The lymphatic system drains lymph back into the a. Large intestine b. Heart c. Vena cava d. Veins of the liver E. Veins of the lower neck 26. Specialized tubules in insects that make direct contact with the tissues to provide oxygen and remove carbon dioxide are called a. Dermal branchiae B. Tracheae c. Gills d. Lungs e. Branchial tufts 31-6 Chapter 9 - Internal Fluids and Respiration 27. A dung beetle journeys into a ball of dung to lay eggs. To avoid being poisoned by the noxious gases, it closes its a. Papulae b. Branchial tufts c. Book lungs d. Bronchi E. Spiracles 28. Which association is NOT correct? a. Pleura—lung and chest epithelium b. Trachea—windpipe c. Alveoli—gas exchange D. Esophagus—vocal cords e. Nasal—inhalation 29. A mammal is masked and must breathe into and out of the same balloon over and over again. A. Its breathing rate would increase in response to more carbon dioxide b. Its breathing rate would increase in response to less oxygen in the blood c. Its breathing rate would slow down as it suffocated d. It is not possible to predict since breathing rate is controlled consciously in mammals e. None of the choices are correct 30. At sea level, air pressure is 760 mm of mercury (Hg). If we altered the oxygen content in a hospital room to 30% oxygen and 70% nitrogen, the partial pressure of oxygen would be a. 70% - 30% = 40% B. 760 x 30% = 228 mm Hg c. 760 x 40% = 304 mm Hg d. 760 x 70% = 532 mm Hg e. There is not enough information to calculate it 31-7 Chapter 9 - Internal Fluids and Respiration 31. Oxygen is carried in circulation primarily a. As a dissolved gas in the plasma b. As carbonic acid C. Bound to hemoglobin in the red blood cells d. By white blood cells e. None of the choices are correct 32. About two-thirds of our waste carbon dioxide is carried back to the lungs in higher animals by a. Red blood cells on the empty hemes B. Dissolved in blood plasma as bicarbonate and hydrogen ions c. Dissolved in lymph in lymph ducts d. On myoglobins e. None of the choices are correct 33. Which of the following can NOT serve as a respiratory pigment? a. Hemoglobin b. Hemocyanin c. Chlorocruorin d. Hemerythrin E. All of the choices are correct 31-8