* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download (through chapter 2) Postulates, Theorems, Definitions, Properties
Duality (projective geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
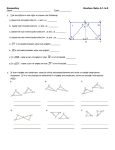
Name:__________________________________ Date:__________________ Period:_________ Justifying Statements in Proofs (through Chapter 2) - Worksheet Below are all of the postulates, theorems, definitions, properties (and a few others) that you can use as reasons in proofs to justify the statements you make. These have all been covered this year in lessons 1.1-1.7, 2.2, 2.4-2.7. Directions: Match the following word or phrase with its description. Each answer is used only once. Hint: Use the glossary in the back of the textbook, the lessons, your notes, your partners, or your teacher for help! 1. Midpoint: _____ 21. Substitution Property of Equality: _____ 2. Angle Bisector: _____ 22. Reflexive Property of Equality: _____ 3. Congruent Segments: _____ 23. Symmetric Property of Equality: _____ 4. Congruent Angles: _____ 24. Transitive Property of Equality: _____ 5. Perpendicular Lines: _____ 25. Postulate 2: Segment Addition Postulate: _____ 6. Supplementary Angles: _____ 26. Postulate 4: Angle Addition Postulate: _____ 7. Complementary Angles: _____ 27. Postulate 5: _____ 8. Linear Pair: _____ 28. Postulate 6: _____ 9. Segment Bisector: _____ 29. Postulate 7: _____ 10. Reflexive Property of Segment Congruence: _____ 30. Postulate 8: _____ 11. Symmetric Property of Segment Congruence: _____ 31. Postulate 9: _____ 12. Transitive Property of Segment Congruence: _____ 32. Postulate 10: _____ 13. Reflexive Property of Angle Congruence: _____ 33. Postulate 11: _____ 14. Symmetric Property of Angle Congruence: _____ 34. When the information is already provided: _____ 15. Transitive Property of Angle Congruence: _____ 35. When you combine like terms: _____ 16. Addition Property of Equality: _____ 36. Right Angles Congruence Theorem (Thm2.3): _____ 17. Subtraction Property of Equality: _____ 37. Congruent Supplements Theorem (Thm2.4): _____ 18. Multiplication Property of Equality: _____ 38. Congruent Complements Theorem (Thm2.5): _____ 19. Division Property of Equality: _____ 39: Postulate 12: Linear Pair Postulate: _____ 20. Distributive Property of Equality: _____ 40: Vertical Angles Congruence Theorem(Thm2.6): _____ Description: a.) If a=b, then ac=bc. b.) c.) Angles that have the same measure. d.) For any real numbers a, b, and c, if a=b and b=c, then a=c. e.) If two angles form a linear pair, then they are supplementary. f.) g.) Two adjacent angles whose noncommon sides are opposite rays. h.) Given. i.) For any real numbers a and b, if a=b, then b=a. j.) Line segments that have the same length. k.) If a=b, then a/c=b/c. l.) A point, ray, line, segment, or plane that intersects a segment at its midpoint. m.) Vertical angles are congruent. n.) a(b + c) = ab + ac, where a, b, and c are real numbers. o.) If two planes intersect, then their intersection is a line. p.) Simplify. q.) r.) A point that divides, or bisects, a segment into two congruent segments. s.) If a=b, then a + c = b + c. t.) u.) A line contains at least two points. v.) w.) For any real number a, a = a. x.) If two angles are complementary to the same angle, then they are congruent. y.) Through any three noncollinear points there exists exactly one plane. z.) Two angles whose measures have a sum of 90 degrees. aa.) All right angles are congruent. bb.) If a=b, then a – c = b – c. cc.) Through any two points there exists exactly one line. dd.) If two lines intersect, then their intersection is exactly one point. ee.) If a=b, a can be substituted for b in any equation or expression. ff.) If two points lie on a plane, then the line containing them lies in the plane. gg.) hh.) ii.) If two angles are supplementary to the same angle, then they are congruent. jj.) Two lines that intersect to form right angles. kk.) A ray that divides an angle into two angles that are congruent. ll.) A plane contains at least three noncollinear points. mm.) Two angles whose measures have a sum of 180 degrees. oo.)