* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture 17: Pacific Northwest Earthquakes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
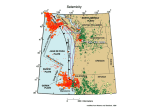
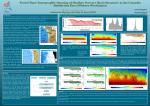
Giant Earthquakes in the Pacific Northwest I. Introduction A. Earthquakes • ______________ of the crust from the rapid release of stored _____________ • ____________, ruptures in crust allow release I. Introduction B. EQ’s & Tectonic Zones 1. Divergent boundaries spreading centers • • • I. Introduction 2. Transform boundaries • • I. Introduction 3. Convergent boundaries • • • I. Introduction C. Great or Giant Earthquakes • • most often associated with _______________ • _________________ EQ’s Subduction Zone EQ’s II. Cascadia A. Cascadian Subduction Zone 1. Evidence for subduction • • • II. Cascadia 2. No Giant Quakes in Cascadia? • apparent absence • historically, no biggies in last 300 years • Why? • • II. Cascadia B. Ancient Giant Quakes in PNW 1. Evidence • • esturaries & salt marshes _____________ • Layered Cycles Draw the picture here II. Cascadia 2. Dating of the Cycles • • • • • II. Cascadia 3. Human Record • • II. Cascadia C. Understanding the Modern • • • • • • II. Cascadia Results of Surveys • horizontal shortening • vertical bulging II. Cascadia D. Locked Subduction Zone • • • what’s causing the clog? • II. Cascadia E. Locked & Loaded • • • LOCKED & LOADED 1. Buildup of stress = strain to leading edge _____________________________ • Vertical (& horizontal) ____________________ 2. Rupture massive __________ rupture _____________ (surge of plate) ________ __________________________ 3. Subsidence behind _____________________ II. Cascadia F. Future Quakes • energy released (magnitude) depends • extent of mega-thrust rupture • B.C. to northern California? 100,000 km2 • 1700 quake evidence = ________________ Maule, Chile, 2010 • Magnitude = 8.8 • Depth ~ 35 km • NazcaS. America convergence ~ 7m/100 yr • .07m/yr = ~7cm/yr • 100km x 500km • 12 m of slip Chile vs. Haiti • Chile, 2010 80,000 km2 fault area movement • Haiti, 2010 600 km2 • Chile = 12 m slip • Haiti = 5 m slip • Chile __________________ more energy III. Quakes and Faults in Cascadia A. Mega-thrust related • • III. Quakes and Faults in Cascadia B. Shallow crustal faults • Seattle Fault 2001 Spokane Earthquake Sequence: a whole ‘lotta shaking going on! 2001 Spokane Earthquakes Summary • • • • 3 main “swarm” sequences June, July & November sequences Considered “unusual” by seismologists Lack of seismic stations=poor data 2001 Spokane Earthquakes June Sequence • • • • Mainshock = 3.9M (6/25/01) Total of 21 EQ’s recorded 11 reported “felt” EQ’s (3.4 M, <3.0M) Foreshocks? 5/24-6/24 (2.0M) 2001 Spokane Earthquakes Late July Sequence • • • • July 28-August 1 14 recorded EQ’s 3.2 maximum magnitude 4 EQ’s on Sept. 28 (1.6-2.8M) 2001 Spokane Earthquakes November Sequence • November 11th to January 2002 • 21 reported EQ’s (19 felt) • 4.0M (11/11/01) maximum magnitude 2001 Spokane Earthquakes Common Characteristics • • • • Relatively low magnitudes Explosion-like sounds = shallow depths Clustered “swarms” NW-trending linearity to aftershocks? 2001 Spokane Earthquakes What is going on here? Historical Seismicity Local Seismicity • • • • • 1915*, 1920, 1922* 1941, 1942, 1948*, 1952* 1961 & 1962 All “low” magnitudes events *Similar locations to 2001 Historical Seismicity Regional Events • • • • • 1872 Lake Chelan, WA (7.3M) 1936 Milton-Freewater, WA (6.4) 1959 Hebgen Lake, MT (7.5M) 1983 Borah Peak, ID (7.3M) 1987 Othello, WA “swarm” (3.3M) Northwest Regional Geology • • • • Rocky Mountains to east Columbia River Flood Basalt Plateau Cascade Volcanic Range to west Cascadian subduction zone Cascade Subduction Zone • Convergent plate boundary • Volcanic mountains • Compressional stress = crustal uplift Regional Tectonic Stress Fields • • • • Compressional stress in Cascadia Northward movement of CA-OR blocks S. Columbia Plateau compression E. Columbia Plateau extension & slip? Inland Northwest Faults • Lewis & Clark faults (northern ID-MT) • NNW-trending Latah Creek Fault? • Other NW-trending structures? Latah Creek Fault • • • • • Real or not? Robert Derkey, Washington DNR Definite NNW-trending lineament Intersects with NNW-trend Spokane River Geologically active 8-16 MY ago Other NW-trending structures NW-trending structures Future Seismicity ? Future Seismicity Cascadia: Puget Sound - Western Washington • Subduction continues=compression • Nisqually 2001 = NOT THE BIG ONE! • Seattle Fault • Shallow “giant” subduction EQ’s Future Seismicity Eastern Washington • Yakima Fold Belt = Rattlesnake Hills • Spokane & Latah Fault • Very little data = ? Spokane Seismicity & Hazards • M4 or less: minor damage potential • M4-M6: moderate to significant damage to older & unreinforced masonary structures • >M6: severe damage Potential of event magnitudes?