* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plants: Roots, Stems, Leaves
Plant tolerance to herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
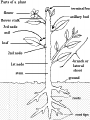
Plants: Roots, Stems, Leaves Students will be able to describe the aspects of roots, stems, and leaves and their impact on our daily lives. Plants • Plants and Animals interact on a daily basis. • Plants are used by animals for food. • Plants are used to make the oxygen necessary for animals to breathe. • Plants are different from animals, however their cells do contain a nucleus. Plants: The Root • 1) 2) 3) 4) The root is a very important part of the plant and it has the following functions: To help grip the plant to the soil. To absorb water and minerals from the soil. To store food. To propagate or make new plants. Plants: The Roots • The typical root has four parts: 1) Primary root- Grows downward and is the thickest. 2) Secondary root- Connected to the primary root, they are smaller and grow to the side. 3) Root cap- Protects the root and allows it to “drill” through the soil. Plants: The Roots 4) Root hairs- absorb water and nutrients from the soil. • Some of the food we eat are plant roots– Potatoes – Carrots – Onions – Beets Plants: The Stem • The stem has two primary functions: 1) Maintain the flowers and leaves at a certain distance from the soil. 2) Carry the nutrients and water. Plants: The Stem • The stem has several different parts: 1) Main stem- The most important stem, it is the stem that is most easily identified (trunk of a tree). 2) Secondary stem- Smalls stems that grow from the main stem (tree branches). 3) Nodes- Bulges in the stems were leaves grow. Plants: The Stem • Internodes- Spaces between the nodes. • We do eat plant stems: – Celery – Asparagus – Sugar Cane Plants: The Buds • Buds are responsible for plant growth. Buds can either be new stems, leaves, or flowers. • Buds are three parts: 1) Main terminal bud- The bud in charge of the upward growth of the plant. 2) Secondary terminal buds- Come from secondary stems, they make the secondary stems grow. Plants: The Buds 3) Lateral buds- Are on the stem nodes, leaves and flowers grown from them. • We do eat buds from plants– Artichokes – Cabbage Plants: The Leaves • The leaves are probably the most important aspect of the plant, because they are in charge of photosynthesis. • There are many different sizes and shapes of leaves but leaves tend to have the same parts. Plants: The Leaves 1) The Blade- The expanded part of the leaf. When people think of a leaf or draw a leaf it is usually the blade. – Veins- Wrinkles or pipes in the leaves, the central vein is called the midrib. 2) The Petiole- Connects the stem to the blade. Not every leaf has a petiole and are called stalkless. Plants: The Seeds • Seeds are necessary for some plants to reproduce. • Each seed has several parts: 1) Embryo- the little plant 2) Endosperm- food supply in the seed 3) Seed Coat- outer layer of the seed Gymnosperms • Gymnosperms (“naked seed”)- cone bearing plants are gymnosperms. • Pinophyta - Conifers • Ginkgophyta - Ginkgo • Cycadophyta - Cycads • Gnetophyta - Gnetum, Ephedra, Welwitschia Angiosperms • Plants that produce flowers or fruits are called angiosperms (“flowering plants”). • Most species on the planet are angiosperms. Plants: The Seeds • We do eat the seeds or fruits of plants– Apples – Oranges – Beans – Grains – Nuts – Spices