* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download International Marketing
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Perfect competition wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
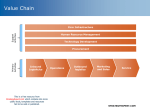
Topic 9 International Distribution & Logistics Getting the product to the target market can be a costly process Forging an aggressive and reliable channel of distribution may be the most critical and challenging task facing the international firms Each market contains a distribution network with many channel choices In some markets the distribution structure is multilayered, complex, inefficient, even strange Competitive advantage will reside with the marketer best able to build the most efficient channel Principles of distribution Transactional cost minimisation Reinforcement of corporate image Reactivity to customer requirements Reactivity to competition (use as an SCA) Intermediary reduction / Integration / Out sourcing Power relativities in the distribution system Movement to source of production or selling What is different internationally? Customer expectations / competitive offers Transport costs / availability / topography Market structure / Distributive responsibility Distributor chains / power / location Logistical networks Wholesaler / Retailer Agent / traditions Distributive culture / norms Customer characteristics Nature of product Demand Competition Legal Regulations Local practices Cost - capital - maintenance Control Market coverage (channel width) Intensive Selective exclusive Channel length Control (Integration) Consider customer service needs Positive motivators – win-win approach (1) financial rewards (2) psychological rewards (3) communications (4) company support Agree performance targets Periodically monitor 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Middlemen Services Product Line Breadth Costs and Margins Channel Length Nonexistent Channels Blocked Channels Stocking Power and Competition Complex Japanese Distribution System Manufacturer or Importer Speciality Distributor Primary Wholesaler Secondary Wholesaler Tertiary Wholesaler Retailer Consumer Self-Service Store Department Store High density of middlemen Channel control by manufacturers Business philosophy shaped by a unique culture Laws that protect the small retailer International Patterns Of Retailing Traditional retailing Intermediary retailing Structured retailing Advanced retailing Interactive customer marketing Mass customisation Data mining Category management Effective consumer response Traditional Advanced Typical in: Developing Countries Mature economies Power Concentration Low High Outlet size Small Large Retail marketing Rarely used Very Important Retail technology Rarely used Vital International Electronic Forms Of Retailing Pure Exchanges Internet Markets Single Buyer Markets Auctions Market conditions conducive to electronic channels of distribution • Inefficiencies in traditional distribution channels • • • • Market fragmentation Minimum scale barriers Commodity-type products Short life-cycle products Source: Klein & Quelch (1997) Distance involved Currency variations Conformance to national regulations Transportation systems Infrastructure Availability of modes Choice of modes Order cycle times & Customer service levels JIT delivery EDI (electronic data interchange) ESI (early supplier involvement) ECR (efficient customer response) International storage issues International packaging The concept of EPZ duty-free manufacture or processing of products for export purposes within a customs-controlled environment Advantages All goods entering the EPZ are exempted from customs duties and import permits Firms can use foreign currency to settle transactions EPZs can be used for assembly of products and so help reduce transportation costs EPZs give greater flexibility, and help avoid unwanted bureaucracy of customs and excise The Nature of Global Logistics and Channel Decisions I International distribution encompasses two areas of responsibility: – Channel management • identifying, selecting and supporting distribution partners • distribution partners bridge the gap between manufacturer and customer – Global logistics • ensuring adequate supply • the right products are made available to customers when and where they want them The Nature of Global Logistics and Channel Decisions II The value chain Information & Research Target Marketing Selection Purchasing Inbound Logistics Product Policy & Strategy R&D Pricing Policy & Strategy Assembly & Manufacturing Distribution Policy & Strategy Outbound Logistics Communication Policy & Strategy Marketing Installation & Testing Service Margin - Messages, appeals - Media Strategy & Plan - Advertising Plan - Promotion Plan - Personal Selling - Direct Marketing Plan - Direct Mail - Telemarketing The Nature of Global Logistics and Channel Decisions III The value chain provides a useful framework for integrating various organisational activities related to global distribution Today, distribution activities are becoming increasingly intertwined, i.e. – sourcing material and parts for production – taking care of product shipment – selecting suitable distribution partners In-Bound Logistics I In-bound logistics describes the process of moving products and materials from suppliers to the factory Six factors must be taken into account – – – – – – factor costs and conditions transport costs country infrastructure political risk market access currency issues In-Bound Logistics II Factor costs and conditions – land – labour, including the cost of workers • manufacturing and production • professional and technical • management – capital cost The cost of these factors depends on – availability – relative abundance In-Bound Logistics III World factor costs that affect manufacturing – industrialised countries • factor costs are tending to equalise – industrialising countries (Singapore, other Pacific Rim countries) • offer significant factor costs savings • offer an increasingly developed infrastructure and political stability – Russia and other countries • lower factor costs (especially wages) are offset In-Bound Logistics IV Transport Costs Country Infrastructure Political Risk Market Access Foreign Exchange Out-Bound Logistics Moving products from the factory to customers It involves aspects of – transportation, – inventory control, – order processing and – warehousing International Channel Strategies The purpose of marketing channels is to create utility for customers – place – time – form – information Two forms of channel strategy – direct involvement – indirect involvement Characteristics Impacting on Channel Design and Strategy I Customer characteristics – customer number, geographic distribution, income, shopping habits, reactions to different selling methods Product characteristics – perishability, service requirements or unit price Characteristics Impacting on Channel Design and Strategy II Middleman characteristics – attitude towards the manufacturer • selection and care of distributors and agents • distributor and agent performance • termination Environmental characteristics – economic, social and political dimensions Global Trends in Channel Design and Strategy I Global Retailing – today – future Direct Marketing – distribution system, where sales to customers are carried out via telephone, mail or door-to-door – one-on-one approach is effective for products which need demonstration or complex explanation Global Trends in Channel Design and Strategy II E-Commerce and International Distribution Strategies – Design of appropriate distribution systems E-Tailing – describes the increasing trend of retail operations globalising via the Internet – presenting and selling a product range over the Internet gains increasing importance Global Trends in Channel Design and Strategy III Alternative Channel Responses Channel Decision Electronic Commerce Manufacturer Direct Physical Distribution Existing Retailer Online Cybermediary Traditional Retailer