* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download artificial acquired immunity
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Microbicides for sexually transmitted diseases wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Epidemiology of HIV/AIDS wikipedia , lookup
Diagnosis of HIV/AIDS wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
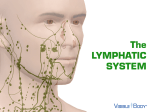
Are you Ready! Let’s Go! ■ ■ LYMPH – Straw-colored, similar to plasma Composed of H2O lymphocytes, O2, digested nutrients, etc., but no red cells or protein (too large) ■ 1. 2. 3. 4. Lymph – fluid that goes between capillary blood and tissues. Carries digested food, O2, and hormones to cells Carries wastes back to the capillaries for excretion Since lymphatic system has not pump, skeletal muscle action squeezes lymph along Lymph in tissues is interstitial fluid. • Lymph vessels- transport excess tissue fluid back into circulatory system • Located in almost all tissues and organs that have blood vessels Lymph Vessels 1.Valves prevent backward flow 2.Lymph flows in only one direction-from body organs to heart 3. Closely parallel veins 4.Tissue lymph enter small lymph vessels which drain into larger lymph vessels (lymphatics) into two main lymphatics –the thoracic duct and right lymphatic duct Thoracic duct – largest lymph vessel Lymph Nodes ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ Tiny oval shaped; size of a pinhead to size of an almond Located in the neck Produce lymphocytes Filter out harmful bacteria If substance can’t be destroyed, node become inflamed. ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ Masses of lymphatic tissue that produce lymphocytes and filter bacteria – they get smaller in size as person gets older Get smaller as person gets older Palatine tonsils- located in back of throat Adenoids tonsils on upper part of throat Lingual tonsils located on the dorsal surface of the base of the tongue Tonsils Spleen ■ ■ Filters blood ■ Blood reservoir- Stores large amounts of RBCs – contracts during vigorous exercise or loss of blood, to release RBC’s ■ Recycles-destroys old or fragile RBC’s • Sac-like mass of lymphatic tissue • Upper left abdominal cavity just below diaphragm. Produce lymphocytes and monocytes Thymus ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ Upper anterior chest above the heart Thymus is lymphatic and endocrine gland Largest and most active during the neonatal and preadolescent periods Produces lymphocytes Completes its work by puberty and is replaced by adipose (fat) tissue. Structure . cont. . Immunity- the body’s ability to resist disease. ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ NATURAL IMMUNITY – at birth, inherited and permanent. Includes: Unbroken skin Mucus and tears Blood phagocytes Local inflammation Body’s reaction to invaders. PASSIVE ACQUIRED IMMUNITY From injecting antibodies, only lasts a few weeks Lasts longer NATURAL ACQUIRED IMMUNITY – result of having had and recovered from a disease. For example, a child who had measles will usually not get it again – child’s body has manufactured antibodies. ARTIFICIAL ACQUIRED IMMUNITY comes from being vaccinated IMMUNIZATION Antigen injected into a person to stimulate production of antibodies Disorders of the Lymphatic System TONSILLITIS 1. In childhood, they may become infected, enlarged, 2. cause difficulty swallowing 3. Tonsillectomy in extreme cases Lymphadenitis generalized enlargement of the lymph nodes (adenitis) 1. Enlargement of the lymph glands 2. Occurs when infection is present and body is attempting to fight off the infection. HODGKIN’S DISEASE 1. Cancer of the lymph nodes, 2. Painless swelling of lymph nodes is early symptom. 3. Rx – chemotherapy and radiation INFECTIOUS MONONUCLEOSIS 1. Caused by virus 2. Frequently in young adults and children 3. Spread by oral contact (kissing) 4. Symptoms – enlarged lymph nodes, fever, physical and mental fatigue, ↑ leukocytes 5. Rx- bedrest Hypersensitivity 1. Abnormal response to a drug or allergen. 2. Antibodies made in response to foreign material ALLERGEN irritate certain body cells 3. Allergen - is an antigen that causes allergic responses. (Examples of allergens – ragweed, penicillin, bee stings, foods, etc.) Anaphylaxis 1. Severe, sometimes fatal allergic reaction 2. Antigen-antibody reaction stimulates a massive secretion of histamine 3. Symptoms – breathing problems, headache, facial swelling, falling blood pressure, stomach cramps, and vomiting 4. Rx – adrenaline 5. Those who have hypersensitivity to bee stings should wear a medic alert bracelet HIV/AIDS 1. Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome 2. Caused by HIV 3. Three responses to HIV infection: a. AIDS – full disorder b. ARC – AIDS – related complex c. Asymptomatic infection 4. Screening tests for HIV available. 5. AIDS victim subject to opportunistic infections (cancer, infections) that a healthy person would fight off but AIDS victim has compromised immune response. 6. Incubation period – 1 month to 12 years. 7. RX and prevention- advances being made. 8. ARC – AIDS- related complex – HIV but not AIDS – less severe symptoms. 9. Transmission a. Sex with someone HIV positive b. Sharing needles with infected drug users. c. At birth from infected mother 10. Cannot be spread by casual contact, coughing, sneezing, shaking hands and sharing eating utensils. 11. Prevention – avoid risky behaviors and observe standard precautions. ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ Patient care equipment and linens Handle with care, Don’t let it touch your or clothing, clean or discard appropriately. ■ Guidelines to be used in patient care setting Must be used when there is contact with blood, any body fluid (except sweat), mucous membranes and non-intact skin. Handwashing – the single most effective way to prevent infection. Wash hands after touching body fluids, even if gloves are worn. Wash hands immediately after removing gloves, between patient contacts. Use a plain (non-antimicrobial) soap Wash for a minimum of 10 seconds Personal protective equipment Gloves – worn when touching blood, body fluids, etc. Mask, eye protection, face shield and gown – during patient care activities that may generate splashes or sprays of blood, body fluids, etc. Occupations Health and Bloodborne Pathogens Beware of needles! ■ Never recap used needles. ■ Dispose of all needles and sharp objects in sharps container. ■ Use mouthpieces, resuscitation bags, or other ventilation devices as alternative to mouth-to-mouth resuscitation. ■ A patient who contaminates the environment should be in a private room or relatively isolated area. The AIDS Patient ■ Sometimes treated as outcasts ■ Healthcare worker should be supportive ■ Use of gloves for normal patient contact is not necessary ■ Neat Internet Site ■ ■ http://www.nanobugs.com/index.php http://www.kidshealth.org/kid/closet/movies/h ow_the_body_works_interim.html