* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Tissues
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Central nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
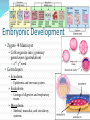
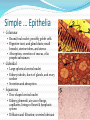
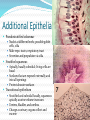
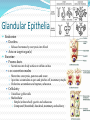
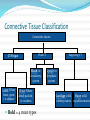
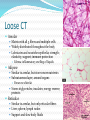
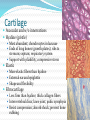
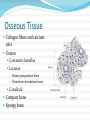
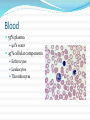
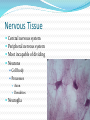
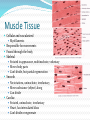
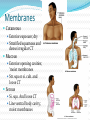
Chapter 4 Klennex isn’t the Only Tissue Tissues are groups of cells with similar structures and functions Histology is the study of them 4 primary types Epithelial – covering an boundary formation Connective – support, protect, and bind Muscle – contractions cause movement Nervous - control and communication Organs often composed of all 4 Embryonic Development Zygote blastocyst Cells organize into 3 primary germ layers (gastrulation) 2nd- 3rd week Germ layers Ectoderm Epidermis and nervous system Endoderm Linings of digestive and respiratory tracts Mesoderm Skeletal, muscular, and circulatory systems Epithelial Tissue Covers or lines; glands too Functions reflect structure Protection, absorption, filtration, excretion, secretion, sensory reception, and gas exchange Characteristics Cellularity: cells packed tight together, bound by tight junctions and desmosomes Polarity Apical and basal surfaces Connective tissue attachment Basal lamina (noncellular) to reticular lamina (ECM) Resists stretching and tearing Avascular, but innervated Regeneration Friction and external substance exposure Classifying Epithelia Layer Shape Simple: 1 Absorbtion, secretion, and filtration Stratified: 2+ Protection Pseudostatified: looks 2+, but Squamous: flattened, scale-like not Cuboidal: sides equal, box-like Columnar: taller than wide Transitional: varies Nuclei shape and apical layer Simple … Epithelia Columnar Round/oval nuclei; possibly goblet cells Digestive tract, and gland ducts; small bronchi, uterine tubes, and uterus Absorption, secretion of mucus, cilia propels substances Cuboidal Large spherical central nuclei Kidney tubules, ducts of glands, and ovary surface Secretion and absorption Squamous Disc-shaped central nuclei Kidney glomeruli, air sacs of lungs, capillaries, linings of heart & lymphatic system Diffusion and filtration; secretes lubricant Additional Epithelia Pseudostratified columnar Nuclei at different levels; possible goblet cells, cilia Male repo. tracts; respiratory tract Secretion and propulsion via cilia Stratified squamous Apically, basally cuboidal; living cells are basal Surfaces that are exposed externally and into all openings Protect abrasive surfaces Transitional epithelium Stratified and cuboidal basally, squamous apically as urine volume increases Ureters, bladder, and urethra Change as urinary organs collect and excrete Glandular Epithelia Endocrine Ductless Release hormones by exocytosis into blood Acts on target organ(s) Exocrine Possess ducts Secretions onto body surface or within cavities 1 or 2 secretion modes Merocrine: exocytosis, pancreas and sweat Apocrine: accumulate at apex and pinches off, mammary maybe Holocrine: accumulate and rupture, sebaceous Cellularity Unicelluar: goblet cells Multicellular Simple (unbranched): gastric and sebaceous Compound (branched): duodenal, mammary, and salivary Connective Tissue Never exposed to environment outside the body Functions Protect, insulate, transport, support, and bind other tissues together Characteristics Composed of multiple cell types Mesenchyme origin Range of vascularity Primarily extracellular matrix (ECM) Non-living; responsible for CT strength and abrasion CT Structure Ground substance Unstructured space filler Liquid, gel-like, or solid Fibers Collagen: tough with lots of collagen protein; white fibers Elastic: flexible and stretchable with lots of elastin protein; yellow fibers Reticular: add extra support with collagen and glycoprotein Cells (-blast or –cyte) Fibroblast Chondroblast Osteoblast Hematopoietic stem cell Connective Tissue Classification Connective tissues Fluid CT CT Proper Blood: in circulatory system Loose: Fibers loose, open; i.e. adipose Dense: Fibers densly packed; i.e. tendons Bold = 4 main types Supporting CT Lymph: in lymphatic system Cartilage: solid, Bone: solid, rubbery matrix crystalline matrix Loose CT Areolar Matrix with all 3 fibers and multiple cells Widely distributed throughout the body Lubricates and nourishes epithelia; strength; elasticity; support; immune protection Edema: inflammatory swelling of liquids Adipose Similar to areolar, but stores more nutrients Subcutaneous layer; around organs Brown vs white fat Stores triglycerides; insulates; energy reserve; protects Reticular Similar to areolar, but only reticular fibers Liver; spleen; lymph nodes Support and slow body fluids Dense CT Dense regular Mostly parallel collagen fibers, some elastic Wavy for stretch Attaches muscle to bone (tendon), muscle to muscle (aponeuroses), bone to bone (ligament) Resists tension (1 direction), support, and stabilization Irregular dense Collagen is thicker and not parallel Dermis; joint and organ capsules Resists tension (multiple directions) Cartilage Avascular and w/o innervations Hyaline (gristle) Most abundant; chondrocytes in lacunae Ends of long bones (growth plates); ribs to sternum; septum; respiratory system Support with pliability; compressive stress Elastic More elastic fibers than hyaline External ear and epiglottis Shape and flexibility Fibrocartilage Less firm than hyaline; thick collagen fibers Intervertebral discs; knee joint; pubic symphysis Resist compression; absorb shock; prevent bone rubbing Osseous Tissue Collagen fibers and calcium salts Osteon Concentric lamellae Lacunae Osteocytes produce bone Osteoclasts breakdown bone Canaliculi Compact bone Spongy bone Blood 55% plasma 90% water 45% cellular components Erthrocytes Leukocytes Thrombocytes Nervous Tissue Central nervous system Peripheral nervous system Most incapable of dividing Neurons Cell body Processes Axon Dendrites Neuroglia Muscle Tissue Cellular and vascularized Myofilaments Responsible for movements Found through the body Skeletal Striated in appearance, multinucleate, voluntary Moves body parts Can’t divide, but partial regeneration Smooth No striations, uninucleate, involuntary Moves substance (object) along Can divide Cardiac Striated, uninucleate, involuntary Heart, has intercalated discs Can’t divide or regenerate Membranes Cutaneous Exterior exposure; dry Stratified squamous and dense irregular CT Mucous Exterior opening cavities; ‘moist membranes Str. squ or si. cub. and loose CT Serous Si. squ. And loose CT Line ventral body cavity; moist membranes