* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2016 HS Algebra 2 Unit 11 Plan - Probability
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
Unit Design
Content Area
Grade/Course
Unit Title
Duration of Unit
Warren County Public Schools
Math
HS Algebra 2
Unit 11: Probability
5 days
Priority Standards
HSS-CP.B.6: Find the conditional probability of A given B as the fraction of B's outcomes that
also belong to A, and interpret the answer in terms of the model.
HSS-CP.B.7: Apply the Addition Rule, P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B) - P(A and B), and interpret the
answer in terms of the model.
HSS-CP.B.9: Use permutations and combinations to compute probabilities of compound
events and solve problems.
Quality Core Standards
H.1. Data Relations, Probability, and Statistics
A. Use the fundamental counting principle to count the number of ways an event can happen
B. Use counting techniques, like combinations and permutations, to solve problems (e.g., to
calculate probabilities)
C. Find the probability of mutually exclusive and non-mutually exclusive events
D. Find the probability of independent and dependent events
E. Use unions, intersections, and complements to find probabilities
F. Solve problems involving conditional probability
Supporting Standards
HSS-CP.A.1: Describe events as subsets of a sample space (the set of outcomes) using
characteristics (or categories) of the outcomes, or as unions, intersections, or complements of other
events ("or," "and," "not").
HSS-CP.A.2: Understand that two events A and B are independent if the probability of A and B
occurring together is the product of their probabilities, and use this characterizations to determine
if they are independent.
HSS-CP.A.3: Understand the conditional probability of A given B as P(A and B)/P(B), and
interpret independence of A and B as saying that the conditional probability of A given B is the
same as the probability of A, and the conditional probability of B given A is the same as probability
of B.
HSS-CP.A.4: Construct and interpret two-way frequency tables of data when two categories are
associated with each other being classified. Use the two-way table as a sample space to decide if
events are independent and to approximate conditional probabilities. For example, collect data
from a random sample of students in your school on their favorite subject among math, science,
Unit Design
Warren County Public Schools
and English. Estimate the probability that a randomly selected student from your school will favor
science given that a student is in 10th grade. Do the same for other subjects and compare results.
HSS-CP.A.5: Recognize and explain the concepts of conditional probability and independence in
everyday language and everyday situations. For example, compare the chance of having lung
cancer if you are a smoker with the chance of being a smoker if you have lung cancer.
Concepts (nouns)
Conditional Probability
Probability
Permutations and
Combinations
Fundamental Counting
Principal
Skills (verbs)
Find/Interpret
Calculate
Compute/Solve
Bloom’s Level (verb)
Analyze
Apply
Apply
Identify/Use
Apply
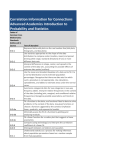
Learning Targets
LT1: Use the fundamental counting principle to count the number of ways an event can happen. (3)
LT2: Use permutations and combinations to compute probabilities of compound events and solve
problems. (3)
LT3: Calculate the probability of event A AND B and/or the probability of event A OR B (for both
mutually and non-mutually exclusive events) (3).
LT4: Find conditional probabilities and interpret the answer in terms of model. (4)
Determine Big Ideas (lifelong
understandings)
Probability can be used to determine the
chances of a real world event occurring.
Write Essential Questions (Answer Big Idea,
hook student interest.
What are your chances of winning the lottery?
What is the probability of Thanksgiving falling
on Sunday?
Formative Assessment Lesson(s):
“The teacher leaders for the Gates grant work recommend that Warren County
Administration adopt the practice that Warren County Math teachers do a minimum of
one Formative Assessment Lesson per quarter. Other choices for formative assessment
lessons may be found at http://map.mathshell.org/materials/lessons.php .
Common Assessment(s):
2016 HS Algebra 2 Unit 11 DCA – Probability Version A
2016 HS Algebra 2 Unit 11 DCA – Probability Version B
2016 HS Algebra 2 Unit 11 DCA – Probability Version C
Note: 2016 HS Algebra 2 Unit 11 DCA – Probability Review is to be used in conjunction
with the above assessments.