* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download P2 511KB
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
Zobel network wikipedia , lookup
Lumped element model wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
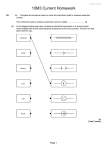
Electric circuits 1 Symbol Name Description of how it works. Open switch Breaks the circuit. No current flows. Incomplete circuit Closed circuit Completes the circuit. Current flows. Lamp Current flows through giving off charge and lighting the lamp Cell Battery Lots of cells together voltmeter Measures potential difference Resistor Fuse Ammeter Measures current Variable resistor Thermistor As the temperature goes up, the resistance goes down Light dependant resistor As light intensity goes up, resistance goes down 1) On the table, draw the symbol, write its name and give a brief description of what is does. 1. What electrical component does this circuit symbol represent? …………………LDR – light dependant resistor…..(1 mark) 2. In this circuit there are three light bulbs connected to the same battery. If one of the bulbs blew, what would happen to the other bulbs? ……………stay lit with same brightness…………… ………………………………………………………………..(1 mark) 3. Which of these ammeters is wired correctly and why? …………C – ammeters must be wired in series……… ………………………………………………………………..(2 marks) 4. What is the reading on the ammeter labelled A1 in this circuit? …………0.4 = 0.3 + A1 A1 = 0.1………………… ………………………………………………………………..(2 marks) S A A B V V 5. a.i. On the above circuit, draw an ammeter to measure the current going through the second lamp. (1 mark) ii. On the above circuit, draw two voltmeters to measure the potential difference of the two lamps. (1 mark) iii. On the above circuit, mark where the best place to insert a switch is. Label it S. (1 mark) b.i. Once you had found the current and potential difference, how could you calculate the resistance of the two lamps? ……V = IR R = V/I…………(1 mark) ii. The current flowing round the circuit was found to be 0.15A. The potential difference across lamp A was 1.5V. What is the resistance of lamp A? Show all working. …… R = V/I R = 1.5/0.15 = 10 Ohms ……………………………………………………………..(2 marks) 6 The circuit shown has four identical ammeters. (a) The table gives the current through two of the ammeters. 0.5 0.5 (i) Complete the table to show the current through the other two ammeters. (2 marks) (ii) Which one of the following statements is correct. Tick (√) the box next to your choice. The resistance of P is more than 20 Ω. The resistance of P is equal to 20 Ω. The resistance of P is less than 20 Ω. Give a reason for your choice. √ more current is flowing through the 20 Ohm resistor than P. Given that R = V/I with less current there is more resistance (2 marks) (b) (i) Write down the equation that links current, potential difference and resistance. .....V = IR (1 mark) (ii) Calculate the reading on the voltmeter. Show clearly how you work out your answer. V = 20 x 0.3 = 6 Voltmeter reading = .........6.................... volts. (2 marks) (iii) State the potential difference of the power supply. ................... 6 V ........................................... (1 mark) (c) A second circuit contains an unknown component labelled X. As component X is heated, the reading on the ammeter goes up. What is component X? ............Thermistor........................... Give a reason for your answer. resistance goes down (as temperature of thermistor goes up) (2 marks)