* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download RIVAROXABAN: chemical structure
Adherence (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Intravenous therapy wikipedia , lookup
Theralizumab wikipedia , lookup
Dydrogesterone wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of direct thrombin inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of direct Xa inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
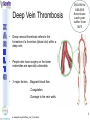
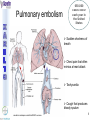
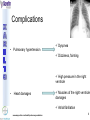
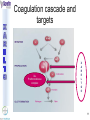
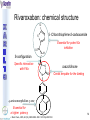
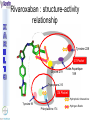
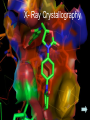
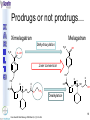
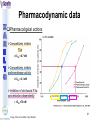
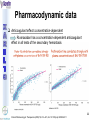
® Xarelto Rivaroxaban The first oral direct factor Xa inhibitor Eric Alsac Thomas Bar Marie Crétal 1 2 Deep Vein Thrombosis • Deep venous thrombosis refers to the formation of a thrombus (blood clot) within a deep vein. • People who have surgery on the lower extremities are specially vulnerable. • 3 major factors: . Stagnant blood flow 350.000 to 600.000 Americans each year suffer from DVT . Coagulation . Damage to the vein walls 3 en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Deep_vein_thrombosis Consequences • Phlebitis • • • • Pulmonary Embolism www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/dci/Diseases/Dvt/DVT_SignsAndSymptoms.html Swelling of the leg Pain or tenderness on the leg Red or discoloured skin on the leg 4 Pulmonary embolism 650.000 cases occur each year in the United States Sudden shortness of breath Chest pain that often mimics a heart attack Tachycardia Cough that produces bloody sputum emedicine.medscape.com/article/300901-overview 5 Complications • Pulmonary hypertension Dyspnea Dizziness, fainting High pressure in the right ventricle • Heart damages Muscles of the right ventricle damages Atrial fibrillation www.mayoclinic.com/health/pulmonary-embolism 6 Atrial fibrillation 2.2 Millions Americans suffer from atrial fibrillation Speed or rhythm of the heartbeat disorder. Inefficience of the pumping of the upper cardiac chambers. blood stagnancy in the atria a thrombus can appear Cerebrovascular accident ( hemiplegia) en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Atrial_fibrillation 7 Space for a new medicine 8 Ideal Anticoagulant Characteristic Consequence High oral bioavailability Oral administration Efficiency • Rapid onset • Predictable pharmacokinetics and Predictable response No need for overlap with parenteral anticoagulant No need for anticoagulation monitoring Safety • • • • • Large therapeutic index No food-drug interactions Rapid offset of action Availability of antidote 2 ways of elimination No need for anticoagulation monitoring No need for anticoagulation monitoring Simplified management in bleeding event Rapid reversal in hemorrhagic event Safer for patient with renal impairment selectivity • No off-target effect Reasonable cost No need for monitoring Improve acess 9 Pharmacology 10 Coagulation cascade and targets XaProthrombinase complex X A R E L T O ® 11 12 Rivaroxaban : Discovery IC50 = 120 nM Product from HTS R=H 4 R = Cl 3 IC50 = 20 µM IC50 = 90 nM Optimisation IC50 = 8 nM Reevaluation of the HTS hits IC50 = 0.7 nM Ki = 0.4 nM BAY 59-7939 13 J. Med. Chem., 2005, 48 (19), 5900-5908 • DOI: 10.1021/jm050101d Rivaroxaban: chemical structure Cl 5 -Chlorothiophène-2-carboxamide S Essential for potent Xa inhibition O N H S-configuration Specific interaction with FXa 4-aminomorpholine-3-one Essential for a higher potency H O oxazolidinone N O N O O J. Med. Chem., 2005, 48 (19), 5900-5908 • DOI: 10.1021/jm050101d Cental template for the binding 14 Rivaroxaban : structure-activity relationship Tyrosine 228 S1 Pocket Glycine 219 Acide Aspartique 189 Tryptophane 215 S4 Pocket Hydrophobic Interactions Tyrosine 99 Phénylalanine 174 Hydrogen Bonds X- Ray Crystallography Prodrugs or not prodrugs… Rivaroxaban does not need any liver conversion…. UNLIKE Ximelagatran Withdrawn on 14 February 2006 17 EMEA/60465/2006 0.13, CURRENT Prodrugs or not prodrugs… Ximelagatran Melagatran Dehydroxylation H2N H2N NH N OH Liver conversion HN O HN O O N O O H NH O N O H NH OH CH3 Dealkylation . Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2006 March; 2(1): 49–58 18 Pharmacodynamic data 19 Pharmacodynamic data Selectivity Human Protease Selectivity profile of Rivaroxaban Inhibition of Factor Xa Concentration (nM) IC50 = 0.7 Ki = 0.4 +/- 0.002 Other Serin Protheases : thrombin, Trypsin plasmin FVIIa, FIXa, FXIa urokinase activated protein C IC50 > 20 000 20 Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 3: 514–521 Pharmacodynamic data Pharmacological actions Competitively inhibits FXa IC50 = 0.7 nM Competitively inhibits prothrombinase activity IC50 = 2.1 nM Inhibition of clot-bound FXa concentration-dependently i IC50=0.7nM IC50=2.1nM IC50=75nM IC50 =75 nM 21 Drugs of the Future 2006, 31(6): 484-493 Pharmacodynamic data Anticoagulant effects concentration-dependent Rivaroxaban has a concentration-dependent anticoagulant effect in all tests of the secondary hemostasis 22 Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics (2005) 78, 412–421; doi: 10.1016/j.clpt.2005.06.011 Pharmacodynamic data Anticoagulant effects in human plasma Relative Change in PT Relative Change in aPPT Rivaroxaban prolonged PT, aPTT independently of ATIII Time (h) 1.25 mg BAY 59-7939 5 mg BAY 59-7939 10 mg BAY 59-7939 20 mg BAY 59-7939 40 mg BAY 59-7939 80 mg BAY 59-7939 Placebo Time (h) PT : prothrombin time aPPT : (activated) partial thromboplastin time Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics (2005) 78, 412–421; doi: 10.1016/j.clpt.2005.06.011 Summary of Pharmacodynamic Studies selective inhibitor proved pharmacological properties concentration dependent action 24 25 ABSORPTION : DISTRIBUTION : - Plasma protein binding: high (92-95% SA) - Volume of distribution: moderate (50L 0.62L/kg) - Fabs : 60-80% for the 10mg dose - Cmax : 2-4h after tablet intake - Food does not affect AUC and Cmax - low affinity to tissues METABOLISM & ELIMINATION : -2/3 of dose undergoes metabolic METABOLISM & ELIMINATION : degradation -Metabolised by CYP3A4, -1/3 of the dose undergoesCYP2J2 direct and renalCYP-independent elimination mechanisms Low-clearance drug: half-life: 7-11h Half eliminated renally Half eliminated by the fecal route 26 EMEA: CHMP ASSESSMENT REPORT FOR Xarelto Doc.Ref.: EMEA/543519/2008 Pharmacokinetic properties • Elderly – No dose adjustment • Hepatic impairment – Contraindicated: hepatic disease with coagulopathy and bleeding risk – Used with caution: moderate hepatic impairment • Renal impairment – Not recommended: creatinine clearance<15mL/min – Used with caution: creatinine clearance 1529mL/min • Inter-individual variability: moderate 27 Inter-individual variations: gender, weight and renal impairment « Les nouveaux anticoagulants » N. Rosencher 28 Summary of Pharmacokinetic studies High oral bioavailibility No food and drug interactions 2 ways of elimination Reversible effect 29 Reproduction toxicity 30 Pre-clinical studies: Reproduction toxicity • Fertility was unaffected by treatment of male and female animals (rat and rabbit) • Target organs in foetus: skeleton (incomplete progressed ossification and malformations), liver and spleen, heart blood vessels rivaroxaban administration during pregnancy is contraindicated Xarelto is contraindicated during breast-feeding because it is secreted into milk 31 EMEA: CHMP ASSESSMENT REPORT FOR Xarelto Doc.Ref.: EMEA/543519/2008 32 Rivaroxaban : clinical studies Target: evaluate rivaroxaban in the prevention and treatment of a broad range of acute and chronic blood-clotting disorders A substantial program: 50,000 patients are expected to be enrolled overall into the rivaroxaban clinical development program 33 Rivaroxaban : clinical studies A FIRST INDICATION TO ENTER THE MARKET RECORD Mid 2008 Venous Blood Clot Prevention in Major Orthopedic Surgery IN UK : • 59.205 Hip replacement operations / year incidence of nonfatal DVT: up to 5% • 56.652 Knee replacement operations / year incidence of non fatal DVT: up to 14% 34 nice.org.uk Venous Thromboembolism-Rivaroxaban : Final scope Rivaroxaban : clinical studies RECORD Rivaroxaban compared with Enoxaparin for: • Thromboprophylaxis after hip arthroplasty (RECORD 1 and 2) • Thromboprophylaxis after knee arthroplasty (RECORD 3 and 4) Randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, multicentre More than 12 500 patients Primary efficacy endpoints: Deep vein thrombosis, non-fatal pulmonary embolism, all-cause mortality Secondary efficacy endpoints: Major venous thromboembolism Primary safety endpoints: Major bleeding Secondary safety endpoints: Cardiovascular events, nonmajor bleeding 35 Eriksson BI, Borris LC, Friedman RJ; N Engl J Med. 2008;358(26):2765-2775. Record 1 Rivaroxaban vs Enoxaparin for thromboprophylaxis after hip arthroplasty Primary efficacy: 1595 patients Secondary efficacy: 1686 patients random 4541 patients S u r g e r y Mandatory bilateral venography F o l l o w u p Day 36 Day 65 Rivaroxaban 10mg/d Enoxaparin 40mg/d Primary efficacy: 1558 patients Secondary efficacy: 1678 patients Day 1 : First dose 6-10h after surgery Eriksson BI, Borris LC, Friedman RJ; N Engl J Med. 2008;358(26):2765-2775. : First dose 12h before surgery 36 Record 1 Results of the efficacy study… P<0,001 Incidence (%) 4 - 70 % 3 2 P<0,001 4 - 88 % 3 2 3,7 % 1 1 2% 1,1 % 0 0,2 % 0 Enoxaparin Rivaroxaban Enoxaparin Rivaroxaban 40 mg/d 58/1558 10mg/d 18/1595 40 mg/d 33/1678 10mg/d 4/1686 Primary efficacy: deep-vein thrombosis, nonfatal pulmonary embolism, death Secondary efficacy: Major venous thromboembolism Eriksson BI, Borris LC, Friedman RJ; N Engl J Med. 2008;358(26):2765-2775. 37 Record 1 2224 received Enoxaparin The safety study… 0,5 P=0,18 Incidence (%) 0,4 0,3 +0,2% 0,2 0,3% 0,1 0 0,1% 4433 patients 2209 received Rivaroxaban 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 Enoxaparin Rivaroxaban 5,8% 5,8% Enoxaparin Rivaroxaban 40mg/d 10mg/d 129/2224 128/2209 Nonmajor bleeding 40mg/d 10mg/d 2/2224 6/2209 Major bleeding . Eriksson BI, Borris LC, Friedman RJ; N Engl J Med. 2008;358(26):2765-2775 38 Record 1 Liver function tests : 1 Enoxaparin 40 mg once daily ALT > 3 x ULN On treatment Rivaroxaban 10 mg once daily 51 / 2129 2,7% 43 / 2128 2,0% During follow-up 6 / 1926 0,3% 3 / 1931 0,2% ALT > 3 x ULN + Bilirubin > 2 x ULN ON treatment 1 / 2142 < 0,1% 1 / 2143 < 0,1% During follow-up 0 / 1925 0,0% 0 / 1943 0,0% Ximelagatran: ALT ˃ 3 x ULN: 6% (37 patients / 612) vs Placebo: 1% (6 patients / 611) 1: 2: Eriksson BI, Borris LC, Friedman RJ; N Engl J Med. 2008;358(26):2765-2775. n engl j med 349;18 2 39 Approvals Venous Blood Clot Prevention in Major Orthopedic Surgery September 2008 the 16th : Health Agency of Canada approve Rivaroxaban. September 2008 the 30th : EMEA approve Rivaroxaban. 40 Rivaroxaban : clinical studies OTHERS INDICATIONS TO EXTEND THE MARKET EINSTEIN 2010 Venous Blood Clot Treatment ROCKET AF 2010 Stroke Prevention in patients with Atrial Fibrillation MAGELLAN 2011 Prevention of VTE in hospitalised, medically ill patients ATLAS ACS TIMI 46 2012 Secondary Prevention of Acute Coronary Syndrome 41 Rivaroxaban : clinical studies ROCKET AF Rivaroxaban compared with vitamin K antagonist for the prevention of stroke and Embolism Trial in Atrial Fibrillation Randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, multicentre 14 000 patients Primary efficacy endpoints: Composite of stroke and non central nervous system systemic embolism Primary safety endpoints: Composite of major and non-major clinically relevant bleeding events Expected regulatory filing date: 2010 42 Rivaroxaban : clinical studies EINSTEIN Evaluating Rivaroxaban in patients with acute symptomatic deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism (PE) Randomised, open label, parallel-group, multicentre Rivaroxaban vs enoxaparin plus vitamin K antagonist 7500 patients Primary efficacy endpoints: recurrent DVT, fatal and non fatal Pulmonary Embolism Primary safety endpoints: Major and non-major clinically relevant bleeding events Expected regulatory filing date: 2010 43 44 Mode action anticoagulants Tissue factor (TF) VIIa- TF VII IX IXa Heparin VIIIa Warfarin X Xa Va Thrombin Prothrombin Fibrinogen Fibrin 45 New anticoagulants TF/VIIa ORAL PARENTERAL X IX VIIIa Rivaroxaban IXa AT Xa Apixaban Fondaparinux Idraparinux Va Ximelagatran Dabigatran Fibrinogen II IIa Fibrin New anticoagulants. J Thromb Haemost 2005;3:1843–1853 46 Xarelto® advantages Convenient use: Oral administration Once-daily anticoagulant No dose adjustment for majority of patients No monitoring Use both in and out of hospital in an acute and chronic setting 47 Xarelto® advantages Predictable profil: Reversible - Rapid onset and offset of action - Anticoagulation from the first dose Dose dependant - Safe and effective regulation of coagulation 48 Xarelto® advantages A low risk use Dose margin between the antithrombotic effect and the risk for increased bleeding is large Low risk of food and drug interactions Stops quickly after cessation of therapy Non invasive use 49 Rivaroxaban vs AVK AVK warfarine Coumadine® Rivaroxaban Xarelto® Coagulation monitoring ++ No monitoring Difficulty to maintain therapeutic range Simple dosing regimen Food and drug interactions No food interactions Limited drug interactions Half-life: 20-60h Half-life: 5-9h High protein binding (99%) Low protein binding Slow onset Tmax = 2-4h 50 Circulation 2007;116;131-133 Rivaroxaban vs LMWHs LMWHs Enoxaparin Lovenox® Rivaroxaban Xarelto® Need for injection Oral administration Once or twice-daily dosing Simple dosing regimen in and out of hospital monitoring and dose adjustment no monitoring Need to give pre-operatively according to European label First dose after surgery Short-term use 51 Indirect inhibitors of FXa TF/VIIa X IX VIIIa Rivaroxaban IXa AT Xa Fondaparinux Idraparinux Va II IIa Fibrinogen Fibrin 52 Rivaroxaban vs Fondaparinux Fondaparinux Arixtra® Rivaroxaban Xarelto® Glaxo Smith Kline Need for injections Oral administration Complicated synthesis with more than 50 steps Synthesis in 6 steps Reduced capacity to inhibit FXa when it is incorporated within prothrombinase complex Inactivate free FXa and FXa incorporated within the prothrombinase complex Circulation 2007;116;131-133 53 Rivaroxaban vs Idraparinux Idraparinux Sanofi-Synthelabo Need for injections Rivaroxaban Xarelto® Oral administration Half-life = 130 hours once- Half-life: 5-9h weekly administration but lack an antidote: risk of bleeding Significant excess bleeding (P<0.0001) halted a trial of idraparinux for stroke prevention in patients with atrial fibrillation 54 The Lancet doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60168-3 Oral direct anticoagulants TF/VIIa X IX VIIIa IXa Rivaroxaban Xa Apixaban Va Ximelagatran Dabigatran Fibrinogen II IIa Fibrin 55 Rivaroxaban vs Dabigatran Oral direct thrombin inhibitor Dabigatran Pradaxa® Rivaroxaban Xarelto® Boehringer Ingelheim Bioavailability: 3,5-5% Bioavailability: 60-80% Renal excretion: 80-100% CI with renal impairment (creatinine clearance< 30 ml/min) Renal excretion: 66% Could be used until creatinine clearance > 15ml/min Clearance: 88.8-135.6 l/h Clearance: 9.8–16.6 l/h Double pro-drug Active drug Twice-daily Once-daily 56 Rivaroxaban vs Ximelagatran Oral direct thrombin inhibitor Ximelagatran Exanta® Rivaroxaban Xarelto® Astra Zeneca Elevation in liver enzymes First 3 weeks of treatment: ALAT elevations > 3 times ULN was lower with rivaroxaban than enoxaparin Pro-drug Active drug Bioavailability: 17.4–24.3% Bioavailability: 60-80% Elimination: renal Elimination: renal and fecal 57 Circulation 2007;116;131-133 Rivaroxaban vs Apixaban Oral direct anti-FXa Apixaban Bristol-Myers Squibb Rivaroxaban Xarelto® Twice daily Once daily Clinical development more advanced Bioavailability: 50% Bioavailability: 60-80% Clearance is mainly via Clearance via 2 pathways biliary/fecal route better in (65% renal) patients with renal insufficiency Half-life: 9-14h Half-life: 5-9h 58 Circulation 2007;116;131-133 59 Anticoagulants’s evolution sales 2006 2014 0.1 0.2 LMWHs Warfarin 0,5 0,4 2,1 Total = 3,1 B $ U.S sales (B $) Heparin 2,2 4,5 1,5 Other inj. Anticoag Novel oral Anticoag 0.1 Total = 8,5 B $ U.S sales (B $) 60 JNJ Investor relations site Rivaroxaban estimated sales (Millions €) 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 50 120 250 350 400 420 450 300 1200 2200 3100 4000 80 180 300 550 800 250 350 650 850 30 80 120 3280 4800 6220 RECORD (VTE prev) ROCKET (AF) EINSTEIN (VTE treat) MAGELLAN (VTE prev hosp patients) ATLAS (ACS 2nd prev) TOTAL 50 120 630 1980 61 Company, Exane BNP Paribas estimates Impact on healthcare costs based on the RECORD 3 study Target: Calculate the impact on healthcare resources in the US The costs of symptomatic VTE was assumed that: Nurses spend three minutes per day administering a subcutaneous Enoxaparin dose and training patients to self-inject for out-patient use. Duration of hospitalization was 5 days. Asymptomatic events had no impact on healthcare costs 62 Kwong L, et al. Blood. 2007;110(11):Abstract #1874 Impact on healthcare costs based on the RECORD 3 study Results: Total cost associated with healthcare resources use in the US: Enoxaparin: 290 $ per patients - 67 % Rivaroxaban: 95 $ per patients 63 Kwong L, et al. Blood. 2007;110(11):Abstract #1874 To conclude • Xarelto is considered to be the most important project in Bayer's pharmaceutical pipeline • could have a sales potential of more than 50 millions € in 2009 and more than 6 Billions € in 2015 • The treatment of chronic indications promises to be far more lucrative 64 Special thanks We especially want to thank Ms Gras, Mr Tartar, Mr Willand and Mr Marboeuf for their help and the time they gave us 65