* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Review Packet
Survey
Document related concepts
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Corona Borealis wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Nebular hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
Future of an expanding universe wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Star of Bethlehem wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Crab Nebula wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Hayashi track wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
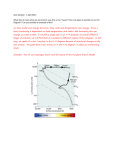
Name: ______________________________ Period: __________ Study Guide/Review/Extra Credit H-R Diagram Quiz You may earn up to half of your points back on your H-R Quiz. In order to do so, you must submit the incorrect answers with an explanation of why your new answer is correct. Example 1. What is the proper name of the H-R Diagram A. Heat-Radiance Diagram B. Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram C. That is the proper name D. Horizontal-Redshift Diagram My corrected answer is B, as the H-R Diagram is named for the two astronomers, Hertzsprung and Russell who were its main contributors. Review Sections Every 6 points that are correct, you will earn 1 extra credit point on the exam. Up to 18 points are available. The Life Cycle of Stars Section One – Sequencing (6 points) The stages below are not in the right order. Number the stages in the correct order. _____ The star begins to run out of fuel and expands into a red giant or red super giant. _____ Stars start out as diffused clouds of gas and dust drifting through space. A single one of these clouds is called a nebula _____ What happens next depends on the mass of the star. _____ Heat and pressure build in the core of the protostar until nuclear fusion takes place. _____ The force of gravity pulls a nebula together forming clumps called protostars. _____ Hydrogen atoms are fused together generating an enormous amount of energy igniting the star causing it to shine. Section Two – Vocabulary (7 points) Match the word on the left with the definition on the right. ____ black dwarf A. star left at the core of a planetary nebula ____ white dwarf B. a red super giant star explodes ____ nebula C. what a medium-mass star becomes at the end of its life ____ protostar D. a large cloud of gas or dust in space ____ supernova E. exerts such a strong gravitational pull that no light escapes ____ neutron star F. the earliest stage of a star ’s life ____ black hole G. the remains of a high mass star Section Three – Understanding Main Ideas - Low Mass Star (7 points) ____ 1. Red giant ____ 2. Where fusion begins ____ 3. Nebula ____ 4. Black dwarf ____ 5. The stage the sun is in ____ 6. White dwarf ____ 7. Planetary Nebula Section Four – Understanding Main Ideas - High Mass Star (7 points) ____ 1. Black Hole ____ 2. Supernova ____ 3. Protostar ____ 4. Gravity causes this to condense into a protostar ____ 5. Main sequence star ____ 6. When a star begins to run out of fuel and grows larger ____ 7. Neutron star Classifying Stars (28 points) Create a chart of the spectral class, color and temperature relationship of stars Class Color Temperature For each star give its: (15 points) - Color - Spectral Class - Size 1. Vega 2.8R 10000K 2. Betelgeuse 630R 3000K 3. Sun 1R 6000K 4. Rigel 70R 20000K 5. Arcturus 21R H-R Diagrams 4000K On the H-R Diagram (9 points) Label the x-axis Label the y-axis Color in each section with the appropriate color. Label each of the dotted sections: - Giants - Main Sequence - Super Giants - White Dwarves Calculate the following distances (3 points) a. .09’’ b. 0.2'' c. .005'' Describe what happens to the brightness in each of the following scenarios. Please use numbers, in your explanation (3 points) a. Luminosity is quartered d. Distance is tripled c. Distance is quartered Describe what happens to the size in each of the following scenarios. Please use numbers in your explanation (3 points) a. Luminosity is tripled b. Luminosity is quartered c. Temperature is quadrupled Conceptual Questions to Consider (24 points) What is the difference between type 1 and type 2 supernova? What is the relationship between a star’s mass and it’s lifetime? Why can we say a star is always trying to stay in equilibrium? What is the evolutionary process of a star like our sun? How are stars “born”? What are blue stragglers, how are they formed and where are they located?