* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nutrition and Achieving High Level Fitness
Survey
Document related concepts
Obesity and the environment wikipedia , lookup
Gastric bypass surgery wikipedia , lookup
Vegetarianism wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbohydrate diet wikipedia , lookup
Food politics wikipedia , lookup
Body fat percentage wikipedia , lookup
Diet-induced obesity model wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Food choice wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
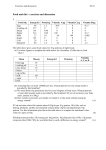
Nutrition Notes Nutrition and Achieving High Level Fitness Exercise, training, and ______________ helps develop your fitness Nutrition – the process by which the body uses ______________ for maintenance of life, growth, normal functioning of every organ and tissue, and the production of energy Food provides: o ______________ (energy) o Stamina and vigor for daily activities o Basis for sound, healthy skin, teeth, hair, muscles, and bones Dietary Reference Intake Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) o amount necessary to meet nutritional needs Six Essential Nutrients ______________ , ______________ , ______________ , ______________ , ______________ ______________ Vocab ______________ o Common unit of measurement used to express the potential energy of food Every food you eat contains calories ____________ o A chemical that causes damage to the cells. _______________ o helps prevent and possibly repair damage done to body by the free radicals. ______________ Function: Major source of energy, in the form of sugar, supplies fiber Food Sources: Fruits, vegetables, grains Recommended Percentage in Diet: ______________ % or higher o (______________ % from complex carbohydrates, ______________ % from simple) o Limit intake of refined carbs (table sugar, sweets, pastries, soft drinks) Three groups of carbs Monosaccharide (______________ sugar) o Fructose – fruit sugar, Glucose – corn sugar Disaccharides (______________ sugar) o Sucrose – table sugar, cane sugar, Lactose – milk sugar, Maltose – malt sugar Polysaccharides (______________ sugars) o Starch – plant sugars, Cellulose – plant fiber Sugar Intake Eating honey, sugar, soft drinks, candy bars or any sweets does not provide ______________ energy. To maintain a consistent energy level, eat a diet high in ______________ carbohydrates (grains, cereals, vegetables) ______________ Function: Important for growth, maintenance, repair of tissue Food Sources: ______________ , fish, meat, low-fat dairy products, eggs, dried peas, beans Recommended Percentage in Diet: ______________ % ______________ o Building blocks of protein ______________ amino acids o Substances making up protein which much be supplied each day by food ______________ protein o A protein food which contains all the essential amino acids needed by the body Animal sources of protein are usually complete Plant sources are usually incomplete Combination of plant sources can be used in diet to form complete protein ______________ Function: Source of stored energy, provide and carry the fat soluble vitamins (ADEK) Food Sources: o Monounsaturated fat - olive oil and canola oil, usually ______________ and found in vegetables, most ______________ type o Polyunsaturated fat - safflower oil, margarines, usually liquid and found in vegetables o Saturated fat - meat, butter, milk, solid shortenings; usually in ______________ form and found in ______________ sources, contribute to heart disease and should be avoided Recommended Percentage in Diet: ______________ % ______________ - Basic building blocks of fats ______________ A waxy, fatty-like material manufactured in the body and used by the body in chemical processes. Found in foods of ______________ origin. Excess cholesterol is deposited on the lining of the ______________ . Narrowing of arteries can lead to cardiovascular problems. Two Types of Cholesterol o ______________ Good cholesterol, picks up extra cholesterol and eliminates it from the body o ______________ Bad cholesterol, contributes to clogging of arteries by depositing the extra cholesterol on the lining of the arteries ______________ o Protein wrapped molecule which transports cholesterol and fats through bloodstream Total cholesterol o Normal ------------------ Below ______________ o Moderately High -------------- 170 -199 o High ------------------------Above ______________ LDL cholesterol o Normal ----------------------Below ______________ o Moderately high ---------------110-129 o High ---------------------------Above ______________ Lower your cholesterol Cut back on food high in cholesterol o ______________ , meat, butter, whole milk Avoid ______________ , which are vegetable oils that have become saturated through hydrogenation o Cocoa butter, coconut and palm oils, lard Avoid ______________ high in fat (hamburger, sausage, bacon) Reduce ______________ fat ( since it raises LDL in your blood) ______________ Structural part of plants which is neither digested nor absorbed by the body Serves as an ______________ “house cleaner” Ex. Beans, romaine lettuce, brown rice, whole wheat, oranges Fiber is not found in ______________ foods. ______________ Function: Important in activating numerous reactions within the body Food Sources: Varies with the specific minerals - a ______________ of foods is necessary Recommended Percentage in Diet: Adequate intake indicated by the RDA o Balance is important; too much of one mineral can ______________ functioning of another Microminerals o Needed in ______________ quantities (100 milligrams a day) Ex: ______________ , potassium, chloride, calcium, phosphorus, and magnesium Trace minerals o 14 other minerals o Needed in ______________ amounts (few micrograms a day) Examples of minerals ______________ – regulated balance of fluids, ability for muscles to contract ______________ - assists in red blood cell formation ______________ - maintains strong bones and teeth ______________ - helps maintain a proper fluid balance in our blood tissues (sodium and chloride) ______________ Function: Aid in absorbing and using the nutrients. Each vitamin has one or more specific functions in the body. Food Sources: Varies with the specific vitamins - a ______________ of foods is necessary Recommended Percentage in Diet: Adequate intake indicated by the RDA Fat-soluble Stay stored in your body for awhile (______________ tissues and liver) — some stay for a few days, some for up to ______________ months Vitamin ______________ o Eyesight. helps you grow properly and aids in healthy skin. Vitamin ______________ o Strong bones and strong teeth. helps your body absorb the amount of calcium it needs. Vitamin ______________ o Maintains a lot of your body's tissues, like the ones in your eyes, skin, and liver. Important for the formation of red blood cells. Vitamin ______________ o Helps clot blood Water Soluble Dissolve in water and are not stored in the body o Must be in your diet ______________ o Can be affected by ______________ methods, lost in water they were cooked in Vitamin________ o keeping body tissues, such as gums and muscles in good shape, helps a cut heal, helps your body resist infection. o EX: citrus fruits, cantaloupe, strawberries, tomatoes, broccoli, cabbage, kiwi fruit Vitamin ________ o More than one B vitamin. (B1, B2, B6, B12, etc. ) o Helps make energy and set it ______________ when your body needs it. Involved in making ______________ blood cells, which carry oxygen throughout your body. o Ex: whole grains, fish and seafood, poultry and meats, eggs, dairy products, leafy green vegetables, beans and peas Vitamin Supplements If you eat ______________ calorie diet o Most likely get adequate supply of vitamins o Extra vitamins do not increase strength/endurance, energy, build muscles, or enhance athletic performance Those who may need a vitamin supplement: o Dieters who take in less than ______________ calories o People with food ______________ who cannot eat certain foods o Vegetarians who do not eat animal foods o Heavy ______________ or heavy drinkers Taking vitamin supplements ______________ compensate for a diet that is deficient in nutrients. ______________ Function: Provides a medium within the cells in which the chemical reaction of the cells takes place; helps regulate body temperature, digest food, excretion, glandular secretion, formation of blood plasma Food Sources: Beverages and liquids in ______________ Recommended Percentage in Diet: ______________ quarts daily