* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 11-cough sars bronchitis
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
Ministry of Health of Uzbekistan
TASHKENT MEDICAL ACADEMY
"Approved"
Vice Rector for
Academic Affairs
Department: PEDIATRICS GPs
Item: P E D I A S T I
TECHNOLOGY TRAINING
the practical lesson number 12 on topic
Cough. SARS bronchitis, treatment and rehabilitation. Uncomplicated
pneumonia in children older than 2 years. Asthma, mild course. Diagnosis and
treatment in a hovercraft. Rehabilitation and medical examination of children
with severe asthma. Acute bronchiolitis, diagnosis, emergency care, and
referral to a specialist. Rehabilitation and clinical examination.
Compiled by:
Yahyaeva KZ - Ass., PhD Medical Sciences
Education technology approved:
At the faculty meeting minutes №
Subject: Coughing. SARS bronchitis, treatment and rehabilitation. Uncomplicated
pneumonia in children older than 2 years. Asthma, mild course. Diagnosis and
treatment in a hovercraft. Rehabilitation and medical examination of children with
severe asthma. Acute bronchiolitis, diagnosis, emergency care, and referral to a
specialist. Rehabilitation and clinical examination.
1. Location classes
- Department of Pediatrics GPs, hospital.
2. Duration of study subjects
Duration of study subjects - 315 minutes
3. Purpose of the lesson
To consolidate and deepen the students' knowledge about pain in the abdomen,
develop skills of early diagnosis, differential diagnosis and tactics GPs on
remediation and clinical examination.
4. Pedagogical objectives:
- To teach students the criteria for diagnosis.
- Discuss the correct choice of drug correction of basic vital functions of organs
and systems.
- Demonstrate the principles of differential diagnosis.
- Consider the criteria of possible complications.
- Organization of specialized advice to the sick child.
- To teach students draw up a plan recreational activities.
- Introduce to prevention.
5. Learning outcomes
The student should know:
1.Chasto common diseases occurring cough syndrome
2.Astmatichesky status, the principles of first aid
3.Printsipy treatment and prevention of bronchitis, pneumonia, asthma in SVP
4.Bronhialnuyu asthma, mild course. diagnosis, treatment in a hovercraft.
Rehabilitation and medical examinations of children with severe asthma
7. Acute bronchiolitis, diagnostics, emergency care. Rehabilitation and clinical
examination.
The student should be able to:
1.Diagnostirovat acute bronchiolitis, to provide emergency assistance and referred
to a specialist
2.Naznachit treatment depending on the clinical variant and current bronchitis in a
hovercraft. 3.Sostavit plan follow-up and rehabilitation of children who have had
bronchitis, pneumonia,
asthma.
4. To provide emergency assistance in the attack of asthma
6. Methods and techniques of teaching
Brainstorming, pen in the middle of the table, a graphic organizer - a conceptual
table
7. Learning Tools
Manuals, training materials, patient handouts, video, banner, KVP-Pediatrics.
8. Forms of learning
Individual work, group work, team
9. Conditions of Learning
Audience, the Chamber
10. Monitoring and evaluation
Oral control: control issues, the implementation of learning tasks in groups,
performing skills, CDS
11. Motivation
Timely outpatient treatment of acute upper respiratory tract, lung flow bronhilnoy
asthma, proper medical check-up and rehabilitation of patients with severe asthma,
acute pneumonia significantly reduce their transition to severe and threatening
condition requiring hospitalization in intensive care units.
12. Intra and interdisciplinary communication
The knowledge gained in the departments of children's diseases, physical therapy,
anatomy, physiology, allergy, GPs therapy will play a big role in the early
diagnosis, timely hospitalization and treatment of children with acute bronchitis,
pneumonia, asthma (mild course) in an outpatient setting, and prevent the
development of severe complications and respiratory pathology.
13. Contents classes
13.1. The theoretical part
Characteristic cough: cough - is a complex, multi-reflector and protective
adaptive response of the body designed to disrupt the respiratory tract foreign
bodies and / or pathologic tracheobronchial secretions and thus to maintain the
effective conduct of the air stream to the respiratory tract. Cough - a dramatic
expulsion from the lungs and respiratory air which is delayed before the closed
glottis. Cough volume depends on the pressure of exhaled air, and its tone - on the
properties and characteristics of the walls of the airways. Coughing occurs when
changes in the pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and pleura and irritation cough
center and ear canal. As a reflex act cough can be caused by irritation of the
endings of the vagus and glossopharyngeal nerves, located in the mucous
membrane of the respiratory tract: pharynx, larynx, trachea and larger bronchi. In
the smallest bronchi and alveoli are no such endings, so there is no irritation of
nerve endings and there is no cough reflex.
Cough is one of the common complaints about which patients seek medical
attention. It is generally regarded as pulmonary cough symptom, but you must
remember that there are more than 53 causes of cough. Among them are not only
bronchopulmonary pathology, but also heart disease, sinus, gastrointestinal tract,
the effect of certain medications, and many other conditions. Cough is acute when
the duration is less than three months. The main causes of acute cough are
infections (pneumonia, acute bronchitis, acute respiratory infections - viral
respiratory infections, whooping cough, pleurisy), toxic and mechanical effects
(inhalation of toxic substances inhaled irritants - smoke, dust, foreign body
bronchus, aspiration). To differentiate the causes of acute cough a careful survey of
the patient and the identification of associated symptoms (presence of sputum,
rhinitis, fever, fatigue, headaches, muscle aches, etc.). In most cases, acute cough
is no difficulty in diagnosis, and short lightweight cough usually does not result in
serious consequences.
Difficulties arise, as a rule, determine the cause of chronic, poorly corrected by
coughing. Duration of chronic cough is more than 3 months. The reasons for its
diverse, bronchopulmonary disease (chronic bronchitis, bronchial asthma,
bronchial cancer, interstitial lung disease, tuberculosis, postnasal wicking
syndrome, lung cancer, metastatic tumors, etc.), extra-pulmonary pathology
(tumors of the mediastinum, aortic, mitral stenosis, left ventricular failure ,
sinusitis, gastroesophageal reflux disease, psychiatric disorders), the side effects of
drugs.
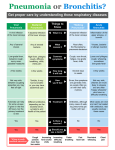
Types of cough. See the handout
Acute respiratory infections - Etiology: parainfluenza types 1 and W, adenovirus
1-W, Y, U11 types of RS-virus, rhinovirus, influenza viruses, and mycoplasma.
Clinically manifest as acute rhinitis, acute otitis media, sinusitis, pharyngitis,
laryngitis, tonsillitis. Treatment is symptomatic: the daily volume of fluid increases
by 1.5-2 times, the room temperature up to 20 degrees. Toilet nose and
vasoconstrictive nasal drops to 1-3 day illness. In the first 2 days of use leukocyte
interferon 0.25 ml in both nasal stroke every 1.5-2 hours or 2 times a day to
prevent contact children. The treatment of influenza A2 - rimantadine - 4.4 mg / kg
per day - 2 times a day for children older than 1 goda.Shkolnikam arbidol 0.8 g /
day - inside, prevention - 0.2g/sut. When bacterial etiology ARI - antibiotics orally.
Bronchitis.
- Acute (simple) bronchitis
- Acute obstructive bronchitis, bronchiolitis
- Acute bronchiolitis obliterans
- Recurrent bronchitis (simple)
- Recurrent acute oblitiriruyuschy bronchitis (asthma)
- Chronic bronchitis obliterans
Acute Bronchitis - common manifestation of SARS, occurs without clinical signs
of bronchial obstruction. In children, the first half of bronchitis caused by
Chlamydia. Preschoolers and school bronchitis accompanied mycoplasma
infection - is it different: asymmetry rales, purely catarrhal symptoms of the upper
respiratory tract, conjunctival redness century without discharge. Adolescents and
bronchitis caused Chlamidia pneumoniae, sometimes as late onset asthma debut.
Home treatment: antibiotics, expectorants (marshmallow root extract, potassium
iodide, ammonia-anise drops) and mucolytic (mukodin, mukopront, bronkatar,)
drugs.
Acute obstructive bronchitis, bronchiolitis - proceeds syndrome of bronchial
obstruction. For bronchiolitis is abundant finely wheezing and respiratory failure,
for obstructive bronchitis - wheezing. Severity was associated with the degree of
obstruction. Outpatient treatment to be children with mild.
Acute bronchiolitis obliterans - a serious illness or adenovirus immunopathological
nature, leading to the obliteration of the bronchioles and arterioles and chronic
bronchiolitis with obliteration. The disease is very severe with the increase of
respiratory failure, with the outcome in the obliteration after the acute period rales
over the affected department does not disappear, and subsequently amplified
during SARS.
Recurrent obstructive bronchitis, obstructive bronchitis, which are repeated
episodes against SARS. Unlike obstructive asthma episodes have paroxysmal
character and develop in response to the impact of noncommunicable allergens.
Sometimes recurrent episodes may be associated with chronic aspiration of food.
In some children recurrent obstructive bronchitis is the debut of asthma. Usually
recorded at the age of 3 years, after 4 years of diagnosis was changed to asthmatic
bronchitis. Treatments such as the treatment of FIC. In remission - of antitreatment in pulmonary rehabilitation centers and sanatoriums.; Need conservative
or operative rehabilitation cron. foci nasopharynx, oral cavity of a sick child and
the surrounding family members.
The principles of healthy frequently and chronically ill children see dispensing
Textiles
Bronchial asthma - definition of "repeated episodes of obstruction, which are
reversible, either spontaneously or under the influence of therapy" is not quite
appropriate for children, as early infancy and there is recurrent obstructive
bronchitis. In contrast to the ROB in asthma exacerbations have a character attack
and / or developed, at least in some cases, in response to the impact of
noncommunicable allergens. In the development of asthma leading role played by
bronchial hyperresponsiveness and allergic inflammation of the bronchial mucosa.
Violation of bronchial patency is caused by spasm, mucosal edema, and mucus
hypersecretion.
Severe asthma is characterized by a high degree of airway hyperresponsiveness,
high airway resistance to air flow and a sharp decline in the clinical efficacy of
drugs bronchodilators. All three components of severe asthma are associated with
inflammation in the airways.
Diagnosis of asthma.
If the medical history reveals:
-Frequent bronchitis with allergic manifestations, communications cough or
bronchitis sekspozitsiey allergen
-Cough, shortness of breath on exertion, anxiety, hyperventilation, leaving the
cold, persistent cough, especially the night; Capacity seasonal respiratory
symptoms;
- Improvements in the state of relocation and the deterioration in returning home;
- Occasional feeling of constriction in the chest;
- Extrapulmonary allergic manifestations clinically and in history.
At present, the diagnosis, monitoring status, identify triggers and assess the
effectiveness of therapy in asthma using individual portable peak flow meter,
which measures the peak expiratory flow (PEF).
Treatment: 1.Lechenie acute phase of asthma.
2.Bazisnoe treatment - Limiting exposure to the allergen, treatment of
identified comorbidities that may be associated with the pathogenesis of asthma,
pharmacological basic therapy, specific immunotherapy, supporting non-drug
therapy, teaching children with asthma and their parents.
Prevention of asthma. Primary - the exclusion of occupational exposures and
diseases of the mother during pregnancy, prevention of repeated respiratory
infections in children, breast-feeding, food-limited allergens, hypoallergenic
organization of life and reduction of exposure to chemical agents in the home.
Secondary - preventing the manifestation of asthma in children with severe
manifestations of atopy (atopic dermatitis, small forms of respiratory allergy.)
Tertiary - prevention of asthma worsening, disability and death, provides a set of
measures of secondary prevention, effective treatment of the disease attacks and
adequate basic therapy.
Pneumonia - an acute inflammatory disease of the lung characterized by
infiltration of the alveolar exudate and filling, physical and radiological data.
Diagnosis: 1. Shortness of breath - 60 per minute in children 1 month. life, 50 min.
in children 2-12 months., 40 days in a mine 4.1 years.2. Indrawing of the
intercostal spaces, groaning (kryahtyaschee breath) nasolabial triangle cyanosis,
signs of toxicosis ("sick" appearance, not eating and drinking, drowsiness,
impaired consciousness, severe pallor, elevated body temperature), the state is
regarded as a severe pneumonia is more likely. In these cases, you need to send to
the hospital.
Treatment: antibiotics, antipyretics, antihistamines, resolving and physiotherapy
(see Pediatrics. Shabalov N.P.2005)
Rehabilitation of children - a gradual increase in physical activity, exercise,
combined with breathing exercises.
Prevention: a set of socio-hygienic measures, good nutrition, hardening,
environmental improvement home, preventing ARI pneumonia vaccination
Dispensary observation subject: children with acute pneumonia, with recurrent
bronchitis, chronic pneumonia, asthma, respiratory allergies.
Acute bronchiolitis is one of acute obstructive bronchitis with the defeat of small
bronchi and bronchioles are usually viral. Ill mostly children of the first 2 years:
odyka 70-90 breaths per minute, difficulty exhaling with auxiliary muscles
vtzheniem compliant places the chest, swelling of the nose, perioral cyanosis.
Initially dry cough, haunting, rapidly absorbed into the wet. The chest inflated,
over light background ea elongated mass exhalation auscultated fine moist rales.
Treatment of hospitalization. First aid, see handout
Clinical supervision for children with acute prnevmoniyu see handout
Clinical supervision for children who have had recurrent bronhit.sm. the handout
Medical check-up for children with asthma, see the handout
Emergency care for respiratory failure. See handout
USING "brainstorming"
The goal: to deepen, expand, refine, consolidate knowledge, translate theoretical
knowledge into mental and practical skills, professional skills.
The main provisions of the method of "brainstorming."
- There were no comments and criticisms, which remove the formation of ideas;
- Greeting soaring thought, given that the unusual idea, the better it is;
- The combination of ideas and their development;
- Brief statement without arguments deployed.
Questions:
1. Prevention and treatment of asthma
2. Methods of diagnosis of asthma
3. Treatment guidelines and patient education
5.Pravilo peak flow in patients with and interpretation of its parameters
6. Clinical examination and rehabilitation of patients with SARS, severe
pneumonia, bronchitis
7. Clinical examination and rehabilitation of patients with bronchial asthma.
Indications for hospitalization and referral to a specialist.
8.Neotlozhnaya help with asthma attacks of asthma in an outpatient setting
USING "knob on the center of the table"
Objective: ability to expand stereotype, abstract from sushestvenno restrictions
develop dynamic mental activity.
The main provisions of the method of "pen in the middle of the table"
- It is proposed assignment to the group. Each student will write your answer and
sends it to a neighbor, and put his pen into the middle.
- The teacher controls the group and participation of each student.
- The correct version is written in the notebook.
The analytical part of
- The decision of situational problems
- Analysis of clinical cases
Case studies:
1.U girls 8 years suddenly after playing with the cat came home wheezing and
coughing, and chest ssadnenie. In history - allergic diathesis, grandmother
asthmatic bronchitis.
Question: How to remove the "spastic" state? Answer: Apply the emergency
treatment for asthma attacks.
2. 8 month baby. For the 2nd day of increased cough, increased body temperature
to 38 degrees, there was heavy breathing, became restless, refuses the breast.
Assess the child. Administer first aid. Determine the location of treatment sick
child.
3. Child is 6 months. 2nd day of coughing, increased body temperature to 37
degrees, not quickened breath, calm, from the chest does not give up. Calm sleep.
Assess the child. Determine the location of treatment sick child.
3. 5 - year-old child was discharged from hospital with a diagnosis of
complications of severe pneumonia.
Determine the dispensary group. Make a plan for follow-up and rehabilitation.
4.Rebenok is followed up by a GP with a diagnosis of bronchial asthma is
remission. What are the specific treatment, which is carried out in a period of
remission.
5. During a night of sleep in 3 years. child appeared "barking" cough. Happy
condition remained satisfactory. Your presumptive diagnosis and treatment plan in
outpatient settings.
6. The child coughs long (about 1 month). What tactics doctor.
7. The child choking lasted for 1-2 hours. After administration of aminophylline /
drip in an outpatient setting. What is your further action.
13.2.2. Graphic organizer.
heart Defects
diaphragmatic hernia
heart failure
gastroesophageal reflux
Diseases of the
cardiovascular system
Diseases of the
digestive system
DDCT
Respiratory tract
diseases
Respiratory
diseases
Cough
iatrogenic causes
The impact of drugs
bronchial asthma
Intubation anesthesia
cough caused by
kapoten
Aspiration of a
foreign body
Systemic disease
of the lungs
viscidosis
Smoking
(passive)
13.3. The practical part
Inspection, supervision of children in a doctor's office, who complain of cough.
Step by step examination of an infant
14. Control forms of knowledge, skills and abilities
- Oral
- Decision of situational problems
- Demonstration of practical skills
- CDS
15. The evaluation criteria of the current control
№
progress
in%
1
96-100%
2
91-95%
mark
The level of knowledge of the student
Full correct answer to the questions on the
etiology, pathogenesis, classification, clinic and
treatment. Sums up and makes decisions, think
creatively, independently analyzes. Situational
problems solves correctly, with full justification of the
Excellent "5" answer.
Actively and creatively involved in interactive
games, take the right decisions and summarize.
Recipes are written in accordance with the
dosage form and with a valid indication of the dose
and indications for use.
Full correct answer to the questions on the etiology,
pathogenesis, classification, clinic and treatment.
Excellent "5"
Sums up and makes decisions, think creatively,
independently analyzes. Situational problems solves
3
4
86-90%
81-85%
5
76-80%
6
71-75%
7
66-70%
correctly, with full justification of the answer.
Actively and creatively involved in interactive
games, take the right decisions and summarize.
Recipes are written in accordance with the
dosage form is one grammatical error.
Full correct answer to the questions on the etiology,
pathogenesis, classification, clinic and treatment, but
have 1-2 errors in the response. Own analyzes.
Inaccurate decisions situational problems, but with the
right approach.
Excellent "5"
Actively and creatively involved in interactive
games, take the right decisions and summarize.
Recipes are written according to the dosage
form, but there are 2-3 grammatical errors.
good "4"
Full correct answer to the questions on the etiology,
pathogenesis, classification, clinic and treatment, but
there are 2-3 errors in the response. Own analyzes.
Situational problems solved correctly, but not
sufficiently justify the answer.
Actively and creatively involved in interactive
games, take the right decisions and summarize.
Recipes are written according to the dosage
form, but there are 2-3 grammatical errors.
Right, but not the full coverage problem. Student
knows the classification, indications for the use of
drugs, but not fully versed in the mechanism of action
and the development of side effects. Understands the
good "4"
issue, says confidently, is a faithful representation.
Actively and creatively involved in interactive
games, take the right decisions and summarize.
Recipes are written according to the dosage
form, but not completely given indications.
Right, but not the full coverage problem. Student
knows the classification, indications for the use of
drugs, but not fully versed in the mechanism of action
and the development of side effects. Understands the
good "4"
issue, says confidently. On case studies does not give
complete
solutions.
Recipes are written according to the dosage form,
but not completely given indications for use, there are
2-3 grammatical errors.
The student knows the classification is
satisfactorily "3"
not complete lists the indications for the use
8
61-65%
satisfactorily "3"
9
55-60%
satisfactorily "3"
10
50-54%
unsatisfactorily "2"
of drugs, basic properties, but poorly versed
in the mechanism of action. Understands the
issue, said confidently, has accurate
representations only on specific issues topic.
Situational problems solved correctly, but
there is no justification of the answer.
Recipes are written with the correct
indication of the dose, but not all are
indications for use and there is an error in
specifying the release form.
The correct answer to half the questions.
Errors in classification errors in testimony to
the use of drugs. Tells not confident is
accurate representations only on specific
issues topic. Making mistakes in solving
situational problems. Recipes are written with
grammatical errors.
The correct answer to half the questions.
Errors in classification errors in testimony to
the use of drugs. Says not sure there is a
partial view on the subject. Situational
problems solved is not true. Recipes are
written with grammatical errors.
Questions not answers. Student does not
know the classification, properties of drugs.
Does not know the mechanisms of action and
side effects of drugs. Situational problems
solved is not true. Can not write
prescriptions.
16. Flow chart classes
№ stage of training
forms of employment
duration
1
Lead-in teacher (study subject)
2
Discussion of homework
3
4
5
6
7
8
Examination of the patient in the clinic or
day hospital
Improvement of practical skills, work
with dummies, clinical and laboratory
equipment, devices
Discussion of the practical part of the
training
Discussion of the topic classes, abstract
message, seminar, discussion
Working in a group. Demonstration
videos on the topic, analysis of situational
problems, computer programs, business
games, etc.
The conclusion of the teacher in this
lesson. Assessing the students on a 100
point system and its announcement.
Dacha assignments to students for the
next class (set of questions)
Min.
10
The
survey,
an
explanation
Patient survey, work
with outpatients
Working with clinical
and
laboratory
equipment
The
survey,
an
explanation
Abstract
messages,
seminar discussion
30
60
60
15
60
Demonstration,
interactive
forms, 60
active and passive
Information, questions
20
for self-study
17. Test questions
1. Prevention and treatment of asthma
2. Methods of diagnosis of asthma
3. Treatment guidelines and patient education
5.Pravilo peak flow in patients with and interpretation of its parameters
6. Clinical examination and rehabilitation of patients with SARS, severe
pneumonia, bronchitis
7. Clinical examination and rehabilitation of patients with bronchial asthma.
Indications for hospitalization and referral to a specialist.
8.Neotlozhnaya help with asthma attacks of asthma in an outpatient setting
Tests:
1. Signs of acute pneumonia
1) cyanosis, shortness of breath *
2) finely wheezing *
3) Wired wheezing
4) Cough *
5) nasal discharge, fever
2. Signs of NAM
1) perioral cyanosis
2) Shortness of breath *
3) Rapid breathing *
4) Bradycardia
5) flushing of the skin
3. For bronchiolitis is characterized by:
a) the general plight +
b) absence of cough
c) respiratory rate is 60 to 1 min +
d) a box shade percussion
e) the nostrils flaring with breathing +
4. When bronchiolitis appoint:
a) humidified oxygen +
b) fluid therapy
c) + prednisone
d) aminophylline
d) heparin
5. Mark the correct statements about bronchiolitis:
A) occurs only in children up to 2 years
B) occurs in both children and adults +
B) often expressed acute disease +
D) changes in the type of obstruction light +
D) all wrong
Questions with correct answers for self
6. To a part of respiratory diseases in children predisposes FOLLOWING
anatomical and physiological characteristics:
- Narrow and short upper respiratory tract;
- The relative dryness of mucous membranes;
- Reduced drainage function of bronchi;
shallow breathing;
- A deep breath.
- Wide and short airways
- Moisture content of the mucous membranes
- Increased drainage function of bronchi
8. AT atopic bronchial asthma asthma attacks can be triggered by:
-Household dust;
-Animal hair
- Pollen
- Aspirin
- Antibiotic
- Taking vitamins
- Reception of sweets
9.TYAZHEST bronchial asthma is determined by:
- Lung function;
- The frequency of seizures;
volume used drugs;
duration of seizures.
the presence of concomitant allergic
skin diseases;
inflammation of the intestine
exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis
allergies to pollen
10.K ASTHMA complications include:
pneumothorax
atelectasis.
fibrosis
status asthmaticus
intussusception
pulmonary heart
11.PRI asthma attacks of respiratory failure due to:
bronchospasm
hypersecretion
swelling of the bronchial mucosa
edema of the larynx
pulmonary edema.
swelling of the brain
hypo-secretion
bronchodilation
12. Features of the course of asthma attacks in young children ARE:
minimum severity of bronchospasm;
predominance vazosekretornogo component;
abundance of moist rales in the lungs;
significant expression of bronchospasm;
Pneumonia is 13.POKAZATELYAMI GRAVITY
pronounced cardiovascular changes
severe respiratory failure
the degree of toxicity
cough
localized wheezing
deadened sound
14. Complications of pneumonia is
pneumothorax
myocarditis
acute pulmonary heart
cardiovascular changes
severe respiratory failure
the degree of toxicity
Acute pneumonia is 15.SIMPTOMAMI
dyspnea
cyanosis
grunting respiration
cough
fine moist rales
rhinitis
sore throat
dry rales
srednepuzyrchatye rales
16.DLYA streptococcal pneumonia is characterized by
regional (bronchopulmonary) lymphadenitis expressed intoxication
small bubbling rale
suppurative complications (pleuritis, osteomyelitis)
acute onset of SARS without prior
lobe lesion
obstructive syndrome
blush on her cheek with one hand
17. According to the classification of bronchitis
Divide
for acute simple bronchitis
for acute obstructive bronchitis
for bronchiolitis
for recurrent bronchitis
of chronic bronchitis
for asthmatic bronchitis
on toxic bronchitis
for allergic bronchitis
18. EASY FOR ACUTE BRONCHITIS Characteristic
dry cough at the beginning of the disease
cough for 4-8-day sickness
dry rales on both sides
large bubbling rale
increased lung markings on chest radiograph
small bubbling rale
cough early in the disease
deadened sound from one side
19. At a bronchiolitis notes
serious condition
cyanosis nasolabial triangle
emphysema
boxed shade percussion
fine moist rales
no cough
respiratory rate no higher than 32 in 1 min
bradycardia
absence of emphysema
20. TYPICAL OF ASTHMA CLINIC IS ¬
expressed asthma
Asthmatic Bronchitis
allergic bronchitis
Thrust spasmodic cough
severe emphysema
18. Recommended Reading
Summary
1. Lecture materials
2. Handout
More
1. childhood diseases. Shabalov NP, SP, 2005
2. childhood diseases. Baranov AA., SP, 2006
3.Pediatricheskaya gastroenterology. Belousov, Yu.V., 2006
4. syndromic diagnosis in pediatrics. Baranov AA, Ivanovo, 1997
5.Modern drugs. Encyclopedic Reference, M., 2006