* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download EE 416/JEE316
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
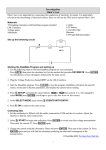
Equipment Review To assure that everyone is up to speed for the hurdles ahead, the first lab of the semester is traditionally an easy review of electrical laboratory fundamentals. There will, however, be a short write-up required of each student. Each student must turn in a report showing the names of his group's members, a signed scope trace printout, the signed sheet of current sensor data, and the current sensor analysis. Student Preparation. Students who have neglected to carefully read this document may reasonably expect to take some lumps in the course of this review. Careful preparation includes, but is not necessarily limited to, the following: (i) Review of what a variable resistor (rheostat) is and does. (ii) Review how the power supplies in Urbauer 115 are correctly wired into a circuit and how their outputs are controlled. (iii) Review of the correct ways of connecting a digital multimeter (DMM) to measure current, voltage, and resistance. (iv) Review of how to use the HP Model 4261 LCR meter. (v) Consult a reference book to discover how to use a Variable Transformer (Variac). Individual lab reports are the rule for Equipment Review, Batteries, Single Phase Transformers, Synchronous Machines, and Induction Motors. All other lab reports will be assigned to one or another of the partners. Equipment Review - 1 - 1a. Rheostats. Somehow determine the maximum and minimum resistances of the left power rheostat. Conclude by setting the resistance to one-half its maximum value; leave the left rheostat at this value for the remainder of Section 1. Note that each rheostat has a maximum rated current of 4.5 A. Finally, call over the Instructor and explain what you did and why. 1b. Connect +5 VDC (with respect to lab ground) to the left end of the left rheostat’s winding, connect the wiper arm to the left end of the right rheostat, and connect the right end of the right rheostat to 5 VDC (with respect to lab ground). Do NOT turn the power supplies on yet. 1c. Insert an ammeter into the circuit. Place a voltmeter across the right rheostat. Calculate the expected current and voltage. Then call the Instructor over and have your work checked. 1d. Lastly, with the Instructor watching, switch the power on and see what happens. In particular, calculate the percent deviation between your measurements and your calculations. 1e. Turn the power off, disconnect everything, and neaten up the work area. 2a. Oscilloscope and Function Generator. PPthe output of “Probe Comp” to Channel 1 input using a 10X Probe. Connect PPTurn on scope by pressing "ON/STBY" and follow the instructions on the screen. Press “Power” on. Press Press Press "AUTOSET" to obtain a trace. Press "DISPLAY". “Auto-Scale” and and understand upper Purpose" status line. Pressobserve "INTENSITY" and use the "General knob to vary the intensity. Press "Graticule Full" and change the screen with "Full" and "Frame". Press Vectors". “1” to turn on"Style Channel 1 options. Press "Clear Menu". 2b. Change theand horizontal sweep control and observe the effect. Press “Coupling” set coupling to"SEC/DIV' DC. 2c. Connect the output of the HP3310A Function Generator to CH1 input of the scope. Press “Quick Meas” and measure frequency, period, and peak-peak voltage of the square Set the 3310A output to a 2 Vp-p sine wave at frequency of 1 kHz. wave. Press "AUTOSET" to obtain a stable display on the screen. Vary the horizontal position and the vertical position controls and observe the effects. Press “Cursors” and the usevertical the appropriate and Yand functions to measure period and peak-peak Change "VOLTS/DIV"Xcontrol observe the effect. Change the horizontal sweep 'SEC/DIV" control and observe the effect. voltage of the square wave. Adjust Press "TRIGGER MENU'. Press "CH1 '. The sweep triggering will be obtained from CH1. “Horizontal” time (sweep) knob and observe theTRIG" square wave. Pressscale "Ext" and connect "Sync Output" on thethe 331effect OA toon "EXT on the scope. The sweep triggering will be obtained from the 331 OA. Press "CLEAR MENU'. Vary the DC offset control (+/-) on the 331 OA and observe the display. It is taken for granted in this course that the student will carefully look up any word or phrase which he does not understand. You learn something every time you do so. And it can save a lot of embarrassment. Equipment Review - 2 - Adjust horizontal position (left-right arrows) knob and observe the effect on the square wave. Set the offset to I V positive. Press "VERTICAL MENU". Adjust vertical voltage scale andonobserve the effect on the square wave. Press "AC"(amplitude) and observe knob the effect the display. Press "GND" and observe the effect on the display. Press "DC" and arrows) observe the effect on observe the display. Adjust vertical position (up-down knob and the effect on the square Press "CLEAR MENU'. Press "MEASURE". Adjust trigger level knob 6 volts and observe the effect Press to "Period" and note the measured value.on the square wave. Press "Frequency" and note the measured value. Press "PK-PK" and note display. the measured value. Press “Run/Stop” and observe resulting Press "Remove Measrment" to remove measured values. Press "Select Measrment". Press “Run/Stop” again. Press "CLEAR MENU". Press "CURSOR". Connect the output of “Probe Comp” to Channel 2 inputUse using a second 10X Probe. Use the "H Bars" to measure the voltage. the "General Purpose" knob and 'TOGGLE" to move the bars. Use the "V Bars" measure the the period. Press 2 and then “Auto-Scale” andtoobserve display. Press 'Off". Press "CLEAR MENU" 2b. wave. Observe square and triangular outputs of the 3310A function generator at various frequencies. Connect the sync output of the 3310A to CH2 of the scope and observe the wave shape relative to the output of the 3310A that is displayed on CH1. 2c. Print a copy of the scope display using the Oscilloscope Display Hardcopy Directions. 3. Hall Effect “Current Gun” Clamp-on Probe. This device has two ranges, one of 10 A maximum and the other of 100 A maximum. We shall take for granted the probe's behavior at large currents and study its behavior at small currents. Use the Load Box (see diagram at end of handout) to connect the DC wall outlet (allegedly set to 25 V) in series with a digital readout DC current measuring device, i.e., AC/DC Current Shunt with DMM to measure voltage across it, and the two 50- rheostats to obtain a metered source driving a load which can be varied from 0 to 100 . Also, use a Hall effect current probe connected to the other DMM to measure the current in the circuit. Vary the current from 0.25 A to 4.25 A in steps of 0.5 A. Carefully record the readings of the DMMs connected to the shunt and the Hall effect current probe. 4. Maximum power. A circuit diagram of the Load Box is provided later in this document. In this review, the Load Box will be used as a source of a large inductor of approximately 10 mH and 2 . Using the Hewlett-Packard model 4261A LCR meter, determine the resistance and inductance of your load box’s inductor. Then connect the load box in series with the A description of the physical principles behind this probe can be found in the chapter on Power Measurements. Operating manuals for the several different types of current sensors you will use during the course are given below. Equipment Review - 3 - parallel combination of the two rheostats; denote this parallel combination as R. Power the load box by way of a 60 Hz AC Variac set to an output voltage of roughly 25 Vrms. By measuring the voltage across R with a DMM and the current through R with a DMM, determine the power P(R) dissipated in R as a function of its resistance. is a maximum. Measure the resistance of 5. Clean Up. Adjust R until P(R) R at this maximum. Turn off all electrical equipment. Put away all miscellaneous items you collected for the experiments. Tidy up your area. 6. Object Lesson. Finally, head for the two drawers labelled “banana cord set” and straighten their contents. Reflect that neatness in stowing equipment makes life a lot more pleasant for those who come after you. Report for Equipment Review. A. The Cover Page shall contain the experiment title, the date of the experiment, your name, the names of the group's members, and the signed disclaimer. Include also: B. The signed printout of the scope trace. C. The measured and calculated values from Part 1d. D. The signed data sheet for the currents. E. A plot of the Hall Effect Current Gun probe current versus the shunt current and a linear regression of one versus the other. F. A laconic and lucid discussion of D. G. A sheet containing your detailed theoretical prediction of the rheostat resistance that absorbed maximum power and the experimentally determined value of this resistance. Include the experimental data. Comment informatively. If you have prepared by carefully reading the handouts, you will know who is supposed to have signed what. Equipment Review - 4 - Equipment Review - 5 - Equipment Review - 6 - Equipment Review - 7 - Equipment Review - 8 - Equipment Review - 9 - Equipment Review - 10 -