* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download key stage 2 year group : t - Aldingbourne Primary School
Bicycle lighting wikipedia , lookup
Architectural lighting design wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Light pollution wikipedia , lookup
Photopolymer wikipedia , lookup
Daylighting wikipedia , lookup
Bioluminescence wikipedia , lookup
Gravitational lens wikipedia , lookup
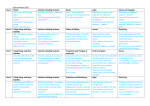
KEY STAGE 2 YEAR GROUP : 3 TERM : AUTUMN THEME : LIGHT / EARTH AND BEYHOND KEY VOCABULARY : light, shadow, transparent, opaque, translucent, block, direction, light travels, source, straight lines Expressions of comparison eg. Fainter, darker LEARNING GOALS ACTIVITIES TIME ALLOCATION To know that light To name light sources- discuss manmade and 4 hours travels from a natural. source Look at a selection of light sources in a darkened That it travels in all room. directions in straight Draw diagrams using arrows to show how light lines travels from these sources. Travelling rays of Use the light box to investigate what happens to light can be shown in the rays of light when objects are put in the way.( the form of arrows Blocking light) Make use of tooth combs as well as radiating out from some transparent, opaque and reflective objects. the source Know that light Look at natural shadows in the school grounds. At 4 hours cannot pass through what other times might they have seen shadows. some materials and Have they played the shadow chasing game? that this leads to the What can the children remember about how they formation of shadows. That shadows change in length and position during the day( when using the sun as a light source) That the position of the sun appears to change throughout the day That the sun does not move but, it`s apparent movement is caused by the are formed? Use OHP to look at shadows formed by opaque objects only. Do we always get a true image produced? Children make shadow images of their own heads. Can they make the image of their head larger and smaller. If so what do they have to do in relation to where they are and the position of the light source? Investigation activity Answer questions from collected or produced data. Read and interpret chart data. Measure the length of a shadow using standard 2 hours measures. Make a table to show how the length of a shadow changes throughout the day. ( A good class activity during a sunny day!) `Skylab` demonstration of the rotating globe Earth spinning on it`s axis. That shadows can be used to tell the approximate time of day. Know that light is reflected off different surfaces eg. Mirrors and polished metals That when light is reflected it can change direction That more light is reflected from a shiny surface than a dull one. Know that the Earth, Sun and moon are approximately spherical Look at reflections from different materials using 2 hours the light box Use concave, convex mirrors Make a periscope. A simple one per group or a project for one group to show the rest of the class. Visit from `Skylab` Look at photos to show the curved surface of the Earth Observe and record the changing phases of the moon for a homework task INVESTIGATIONS That opaque All materials allow light to pass through – true or false objects/ materials do Remind children of earlier shadows work not let light through Present children with a range of opaque, and that transparent transparent and translucent materials/ objects objects/ materials do Each group may also be encouraged to supply a few Use their knowledge of their own to test and experience to Make their predictions make predictions Use the OHP to test materials / objects Decide whether In conclusion relate predictions to results. Were their results support they expected? If not then why not? their predictions Do all materials allow light to pass through ? How do shadows move during the day ? Which surfaces reflect light the best ? Skylab – can you demonstrate, using models, how the Earth, Sun and Moon work in relation to one another. VERY SIMPLIFIED. USEFUL DOCUMENTS : QCA : Unit 3F Light and shadows