* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Muscles of the Upper Limb
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
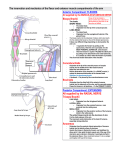
Muscles of the Upper Limb In general a skeletal muscle is a muscle that is attached to a bone through a tendon. Skeletal Muscles produce body motions; stabilize body positions, store and move substances within the body and also produce body heat. Skeletal Muscle works primarily in a voluntary matter. Muscles of the upper limb consist of muscles that attach to the shoulder girdle, including the arm, forearm, wrist, hand, and fingers. Muscles that act on the shoulder The Pectoralis Major The Deltoid forms the rounded contour of the shoulder, it originates from three separate set of fibers: Anterior fibers arise from the anterior border and upper surface of the lateral clavicle, Lateral fibers arise from the acromion of scapula, Posterior fibers arise from the spine of scapula. The Deltoid muscle inserts on the Deltoid Tuberosity of the humerus. The Different fibers are responsible separate actions: Anterior fibers flex and medially rotate arm at shoulder joint, Lateral fibers abduct arm at shoulder joint, Posterior fibers extend and laterally rotate the arm at the shoulder joint. The Deltoid Muscle is supplied by the axillary nerve. The Subscapularis Muscle is a large triangular muscle that fills the subscapular fossa of the scapula and forms part of the posterior wall of the axilla. The Subscapularis originates from the subscapular fossa of the scapula, and inserts on the Lesser Tubercle of the Humerus. The Subscapularis Muscle is responsible for medially rotating the arm at the shoulder joint. The Subscapularis is supplied by the upper and lower subscapular nerve. The Supraspinatus Muscle is a rounded muscle named for its location. It originates from the supraspinous fossa of the scapula, and inserts on the Greater Tubercle of the humerus. The Supraspinatus is responsible for assisting the deltoid muscle in abducting the arm at the shoulder joint. The Supraspinatus is supplied by the subscapular nerve. The Infraspinatus is a triangular muscle, also named for its location. It originates from the infraspinous fossa of the scapula, and inserts on the Greater Tubercle of the humerus. The Infraspinatus muscles are responsible for laterally rotating the arm at the shoulder joint. It is supplied by the subscapular nerve. The Teres Major is a thick flattened Muscle inferior to the teres minor. It originates from the inferior angle of the scapula and inserts on the lesser tubercle of the Humerus. The Teres Major extends the arm at the shoulder joint and assists in adduction and medial rotation of the arm at the shoulder joint. It is supplied by the lower subscapular nerve. The Teres Minor is a cylindrical, elongated muscle often inseparable from the Infraspinatus. It originates from the Inferior lateral border of the scapula and inserts onto the greater tubercle of 1 Muscles of the Upper Limb Humerus. It laterally rotates and extends the arm at the shoulder joint. The Teres Minor is supplied by the axillary nerve. Muscles of the Arm The Coracobrachialis is an elongated narrow muscle of the arm. It originates from the coracoids process of the scapula, and inserts on the middle of the medial surface of shaft of the humerus. The Coracobrachialis flexes and adducts arm at the shoulder joint. It is supplied by the Musculotaneous nerve. The Biceps brachii is the large muscle on the anterior surface of the arm; it has two heads, a long head and a short head. The Long head originates from the Supraglenoid Tubercle, and the Short head Originates from the coracoid process of the scapula. Both the Long head and short head of the Biceps Brachii insert on the radial Tuberosity of the humerus and Bicipital aponeurosis. The Biceps Brachii flexes the forearm at the elbow joint. It is supplied by the Musculotaneous nerve. The Brachialis is deep to the Biceps Brachii; it is the most powerful flexor of the forearm at the elbow joint. It originates from the distal, anterior surface of the humerus and inserts on to the ulnar Tuberosity and coranoid process of the ulna. The Brachialis flexes the forearm at the shoulder joint. It is supplied by the musculocutaneous and radial nerve. The Brachioradialis Originates from the lateral border of the distal end of the humerus, and inserts onto the styloid process of the ulna. The Brachioradialis flexes the forearm at the elbow joint. It is supplied by the radial nerve. Muscles on the forearm The Triceps brachii is the large muscle located on the posterior surface of the arm. It has three heads, the long head, the lateral head and the medial head. The long head originates from the infraglenoid tubercle, the lateral head originates from the lateral and posterior surface of the humerus superior to the radial groove, the Medial head originates from the posterior surface of the humerus inferior to the radial groove. All the heads inserts on the olecranon of the Ulna. The Triceps Brachii extends the forearm at the elbow joint, and also extends the arm at the shoulder joint. It is supplied by the radial nerve. The Aconeus is a small muscle on the posterior aspect of the elbow joint. It originates from the lateral epicondyle of the humerus, and inserts on the olecranon and superior portion of the shaft of the ulna. The Aconeus extends the forearm at the elbow joint and is supplied by the radial nerve. The Pronator teres originates from the medial epicondyle of the humerus and coranoid process of the ulna, and inserts onto the midlateral surface of the radius. The Pronator Teres pronates the 2 Muscles of the Upper Limb forearm at the radioulnar joint, and flexes the forearm at the elbow joint. It is supplied the medial Nerve. The Pronator quadratus is a square shaped muscle on the distal forearm. It originates from the distal portion of the shaft of the ulna and inserts onto the distal portion of the shaft of the radius. The Pronator Quadratus pronates the forearm at the radioulnar joints. It is supplied by the median Nerve. The Supinator is a broad muscle, curved around the upper third of the radius. It originates from the lateral epicondyle of the humerus, and near the radial notch of the ulna, it inserts onto the lateral surface of the proximal one-third of the radius. The Supinator supinates the forearm at the radioulnar joints. It is supplied by the deep radial nerve. The Flexor carpi radialis originates on the medial epicondyle of the humerus, it inserts on the second metacarpal, and the third metacarpal. The Flexor Carpi Radialis acts to flex and abduct the hand. It is supplied by the Median nerve. The Palmaris Longus is seen as a small tendon between the flexor carpi radialis and the flexor carpi ulnaris. It originates from the Medial epicondyle of the humerus and inserts onto the upper part of the flexor retinaculum, and the palmar aponeurosis. The Palmaris longus weakly flexes the hand at the wrist joint. It is supplied by the Median nerve. The Flexor Carpi Ulnaris originates from the Medial epicondyle of the humerus and the superior posterior border of the ulna, it inserts onto the Pisiform, Hamate, and the base of the fifth metacarpal. This muscle extends and adducts the hand at the wrist joint. It is supplied by the deep radial nerve. The Flexor digitorum superficialis is an extrinsic flexor muscle of the fingers at the proximal interphalangeal joints. It originates from the Medial epicondyle of the humerus, the coranoid process of the ulna, and a ridge along the lateral margin of the anterior surface of the radius. It inserts onto the middle phalanx of each finger. The Flexor digitorum superficialis flexes the middle phalanges of the fingers at the proximal interphalangeal joints, and it also flexes the metacarpophalangeal joints and wrist joint. This muscle is supplied by the Median nerve. The Flexor pollicis longus arises from the grooved anterior surface of the body of the radius and the interosseous membrane. It inserts onto the base of the distal phalanx of the thumb. The Flexor pollicis longus flexes the distal phalanx of the thumb at the interphalangeal joint. It is supplied by the Median nerve. The Flexor digitorum profundus originates from the upper 3/4 of anterior & medial surfaces of ulna, and inserts onto the inserts onto the base of the distal phalanx of the thumb. The Flexor digitorum profundus flexes the distal and middle phalanges of each finger at the interphalangeal 3 Muscles of the Upper Limb joints, the proximal phalanx of each finger at the metocarpophalangeal joint, and the hand at the wrist joint. It is supplied by the Median nerve. It is supplied by the Radial nerve. The Extensor carpi radialis longus is one of the five main muscles that control movements at the wrist. It originates from the lateral supercondylar ridge of the humerus and inserts onto the second metacarpal. The Extensor carpi radialis longus extends and abducts the hand at the wrist joint. It is supplied by the radial nerve. The Extensor carpi radialis brevis originates from the lateral epicondyle of the humerus and inserts onto the third metacarpal. This muscle and extends and abducts the hand at the wrist joint. The flexor carpi radialis brevis is supplied by the radial nerve. The Extensor digitorum is a muscle of the posterior forearm present in humans and other animals. It extends the medial four digits of the hand. It originates from the lateral epicondyle of the humerus and inserts onto the distal and middle phalanges of each finger. The Extensor digitorum extends the distal and middle phalanges of each finger at the interphalangeal joints, proximal phalanx of finger at the metocarpophalangeal joint. The Extensor Digiti Minimi originates from the lateral epicondyle of the humerus and inserts onto the tendon of the extensor digitorum on the phalanx. The Extensor digiti minimi extends the proximal phalanx of little finger at the metocarpophalangeal joint and the hand at the wrist joint. It is supplied by the deep radial nerve. The Extensor carpi ulnaris originates from the lateral epicondyle of the humerus and posterior border of the ulna, it inserts onto the fifth metacarpal. The Extensor carpi ulnaris extends and adducts the hand at the wrist joint. It is supplied by the deep radial nerve. The Abductor pollicis longus originates from the posterior surface of the middle of the radius and, ulna , and the interosseous membrane, it inserts onto the first metacarpal. The Abductor pollicis abducts the thumb at the carpometacarpal joint, thereby moving the thumb anteriorly. The Extensor pollicis brevis originates from the dorsal surface of the body of the radius below that muscle, and from the interosseous membrane and inserts onto the base of the first phalanx of the thumb. The Extensor pollicis brevis extends the proximal phalanx of the thumb. It is supplied by the Radial nerve. The Extensor pollicis longus originates from the lateral part of the middle third of the posterior surface of the body of the ulna below the origin of the Abductor pollicis longus, and from the interosseous membrane. It inserts onto the base of the distal phalanx of the thumb. The Extensor pollicis longus Extensor pollicis longus extends the terminal phalanx of the thumb; in combination with the Extensor pollicis brevis, it helps to extend and abduct the wrist. It is supplied by the deep radial nerve. 4 Muscles of the Upper Limb The Extensor indicis originates from the posterior surface of the body of the ulna and inserts onto the tendon of the extensor digitorum of the index finger. This muscles The Extensor indicis extends the index finger, and by its continued action assists in extending the wrist. It is supplied by the deep radial nerve. Muscles of the hand The muscles of the hand are divided into three groups: Thenar (lateral aspect of the palm), Hypothenar(medial aspect of the palm),Intermediate(midpalmar). THENAR: The Abductor pollicis brevis is a flat, thin muscle located just under the skin. It originates from the flexor retinaculum of the hand, the tubercle of the scaphoid bone, and the tubercle of the trapezium and inserts onto the lateral side of the proximal thumb. The Abductor pollicis brevis abducts the thumb at the carpometacarpal joint; it is supplied by the Medan nerve. The Opponens pollicis is a small, triangular muscle in the hand, which functions to oppose the thumb. It is one of the three Thenar muscles, lying deep to the abductor pollicis brevis and lateral to the flexor pollicis brevis. It originates from the flexor retinaculum of the hand and the tubercle of the trapezium and is inserted on the lateral side of the first metacarpal. The Opponens pollicis flexes the thumb's metacarpal at the first carpometacarpal joint, which aids in opposition of the thumb. It is supplied by the Median nerve. The Flexor pollicis brevis is a muscle in the hand that flexes the thumb. It is one of three thenar muscles. It originates from the Flexor retinaculum, trapezium, and trapezoid and inserts onto the lateral side of the proximal phalanx of the thumb. The Flexor pollicis brevis flexes the thumb at the first metacarpophalangeal joint It is supplied by the Median and ulnar nerves. The Adductor pollicis is a muscle in the hand that functions to adduct the thumb. It has two heads: oblique and transverse. The oblique head originates from several slips from the capitate bone, the bases of the second and third metacarpals, the intercarpal ligaments, and the sheath of the tendon of the flexor carpi radialis, the Transverse head originates from the lower two-thirds of the palmar surface of the third metacarpal bone. Both heads have the same insertion onto the medial part of the base of the proximal phalanx of the thumb. The adductor pollicis adducts the thumb at the carpometacarpal joint. It is supplied by the ulnar nerve. HYPOTHENAR (medial aspect of the palm): The Abductor digiti minimi muscle originates from the Pisiform and the tendon of the flexor carpi ulnaris, and inserts onto the medial side of the proximal phalanx of the little finger. This muscle abducts and flexes the little finger at the metacarpophalangeal joint. It is supplied by the ulnar nerve. 5 Muscles of the Upper Limb The Flexor digiti minimi brevis muscle originates from the hamate bone, and the palmar surface of the flexor retinaculum of the hand, and is inserted onto the ulnar side of the base of the first phalanx of the little finger. The flexor digiti minimi flexes the little finger. It is supplied by the ulnar nerve. The Opponens digiti minimi muscle originates from the flexor retinaculum and the hamate bone and inserts onto the medial side of the fifth metacarpal. This muscle draws the 5th metacarpal anteriorly and rotates it, bringing little finger into opposition with thumb. It is supplied by the ulnar nerve. INTERMEDIATE (midpalmar): The lumbrical muscles are intrinsic muscles in the fingers that allow flexion at the metacarpophalangeal joints, while maintaining extension at the interphalangeal joints. There are four of these small, worm-like muscles on each hand. These muscles are unusual in that they do not attach to bone. Instead they attach proximally to the tendons of flexor digitorum profundus. This muscle originates from the lateral sides of the tendon and flexor digitorum profundus of each finger and inserts onto the lateral sides of the tendon of the extensor digitorum on the proximal phalanges of each finger. It is supplied by the Median and ulnar nerve. The Palmar interossei are small muscles in the hand that lie on the anterior aspect of the metacarpals. They are smaller than the dorsal interossei of the hand, which lie between the metacarpals. There are three palmar interossei muscles they all originate from the sides of the shafts of the metacarpals of all digits(except the middle one) and insert onto the sides of the bases of the proximal phalanges of all digits (except the middle one). The palmar interosseous muscles adduct the fingers towards the middle finger. It is supplied by the ulnar nerve. The Dorsal interossei are muscles that occupy the space between the metacarpals. It originates from the adjacent sides of the metacarpals and inserts on to the proximal phalanx of each finger. The dorsal interossei abducts fingers 2-4 at the metacarpophalangeal joints; flexes fingers 2-4 at the metacarpophalangeal joints; and extend each finger at the interphalangeal joints. It is supplied by the ulnar nerve. 6 Muscles of the Upper Limb Works Cited Gerard J.Tortora, M. T. (2009). Principles of Human Anatomy. Danvers, MA: John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Musculoskeletal Radiology. (2007). Retrieved November 7, 2009, from Department of radiology, University of washington: http://www.rad.washington.edu/academics/academic-sections/msk Wikipedia. (2001, January 10). Retrieved November 6, 2009, from Wikipedia: the free encyclopedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Category:Muscles_of_the_upper_limb 7