* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture notes for Section 4.4
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
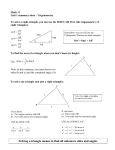
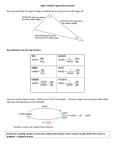
Tech Math 2 Notes Section 4.4 Page 1 of 3 Review Topics: Angle Precision 1 0.1 or 10 0.01 or 1 Angles and Accuracy of Trig Functions Trig Function Accuracy Example 2 sig. figs. sin17 0.29 , tan85 11 3 sig. figs. sin1.1 0.0192 , cos520' 0.996 4 sig. figs. cos 45.00 0.7071 , tan8013' 5.799 Calculating Other Trig Functions Definition Example cos 1 1 cot cot 82.3 0.135 sin tan tan 82.3 1 1 sec sec 22 1.1 cos cos 22 1 1 csc csc 72.67 1.048 sin sin 72.67 Section 4-4: The Right Triangle SOH CAH TOA: opp b hyp c opp b tan adj a 1 hyp c sec cos adj a sin adj a hyp c 1 adj a cot tan opp b 1 hyp c csc sin opp b cos In solving a triangle, you are given three parts of a triangle (one of which must be the length of a side), and then are expected to calculate the other three parts. Tech Math 2 Notes Section 4.4 Page 2 of 3 The sum of the angles of a triangle is 180, so for a right triangle (one angle 90), the two acute angles add up to the remaining 90 (mathematical lingo: they are complementary). To solve a right triangle: 1. Make a sketch of the triangle, label sides and angles consistently (a, b, and c for the legs and hypotenuse; A and B for the complementary angles), and label the given information. 2. Find a way to relate the unknown parts to the given information using a trig function (sine, cosine, or tangent) or the Pythagorean Theorem (a2 + b2 = c2). Try to use original given information to minimize rounding errors. 3. Check your work: a. Make sure the sides obey the Pythagorean Theorem. b. Make sure the angles add up to 180. c. Make sure unused trig functions give the right answers. d. Make sure that the longest side is opposite the largest angle, and the shortest side is opposite the smallest angle. Practice: 1. Solve a right triangle given two legs: 2. Solve a right triangle given a leg and a hypotenuse: Tech Math 2 Notes Section 4.4 3. Solve a right triangle given an angle and an adjacent side: 4. Solve a right triangle given an angle and an opposite side: 5. Solve a right triangle given an angle and the hypotenuse: Page 3 of 3