* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit V Review Sheet Answer Key
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
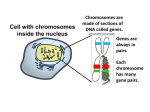
Name: ________________________________ Class: ________ Date: __________ Directions: Use your notes, class materials, and textbook as you answer the following questions. For all Multiple Choice questions explain why your answer is correct. 1. Asexual and Sexual Reproduction Describe what mitosis is and why it is a critical cell process. Illustrate the process of mitosis. Mitosis is a type of asexual reproduction in which an exact copy of a cell is made. It is an important process because it helps living organisms to grow, repair and replace cells in the body. 2. Describe or diagram each of the following methods of asexual reproduction: binary fission, budding, and vegetative. Type of Illustration Description Example Genetic make up Asexual of adult and Reproduction offspring Splitting of Bacteria Identical Binary Fission the cell into (pictured left) two identical cells **Budding 3. New organism begins to grow off of the parent organism; new organism may stay attached or break off **Hydra **Identical A student observes a unicellular organism under a microscope. After a while, the organism begins to split into two cells, as shown in the diagram. Which of these best describes the process shown in the diagram? A. binary fission B. meiosis C. osmosis D. sexual reproduction 1 Name: ________________________________ 4. Class: ________ Date: __________ Reproductive cells are produced during A. mitosis B. meiosis C. fertilization D. budding 5. Compare mitosis and meiosis: purpose, number of cell divisions, products… PURPOSE TYPE OF PRODUCTS REPRODUCTION MITOSIS Growth, repair, Asexual Two (2) Identical replacement of cells Daughter Cells that are Diploid MEIOSIS Production of egg and Sexual Four Haploid sperm cells; cause of Daughter Cells each genetic variation having ½ of the total # of chromosomes 6. Corals are marine animals that often live in tropical seas. Many types of corals have unicellular algae living in their tissues. The algae provide up to 98 percent of the corals' food. The corals provide protection and inorganic nutrients for the algae. Some coral cells undergo meiosis. Which of these would not occur during meiosis? A. formation of a zygote B. chromosomes crossing-over C. production of gametes D. reduction in number of chromosomes 7. Diagram crossing over and explain its effect. Crossing over is when two homologous chromosomes (chromosomes that hold the same type of genetic information, such as eye color) touch and exchange information. This exchange of information produces genetic variation because the offspring are not identical to their parents or to each other. In the example above, the first two chromosomes contain only capital letters and the second two contain only lower case. Once crossing over occurs, there is a mixture of capital and lower case letters present on the chromosomes. As you see, none of the chromosomes are exactly like the other once crossing over has occurred. 2 Name: ________________________________ Class: ________ Date: __________ 8. Explain how fertilization increases genetic variation within the zygote. Fertilization increases genetic variation because it is the meeting of the egg and sperm. This meeting causes some traits to be passed from both the mother and father, making a mix of traits (genetic variation) in the offspring. 9. Sea stars are genetically different from each other and from their parents. These genetic differences are the result of A. mitosis B. cloning C. sexual reproduction D. asexual reproduction 10. Using the diagram, describe reproduction in angiosperms. “A” represents an anther, which is where the pollen, or sperm, of a flowering plant (angiosperm) is produced. The pollen is made through the process of meiosis. Mendelian Genetics 11. In humans, the allele for long eyelashes is dominant (L) and the allele for short eyelashes is recessive (l). A female who is heterozygous for long eyelashes and a male with short eyelashes have a child. What is the probability that their offspring will have short eyelashes? A. 0% B. 25% C. 50% D. 75% l l L l Ll Ll ll ll 3 Name: ________________________________ Class: ________ Date: __________ Use the information below to answer the next two questions. In a species of fly, the allele for red eyes (R) is dominant to the allele for brown eyes (r). Red eye color in the flies is not sex-linked. Students crossed male and female flies that had red eyes and recorded the eye color of their offspring. Their data are shown below. 12. Using the data in the table, what is the approximate ratio of red eyed offspring to brown eyed offspring? A. 1:1 B. 2:1 C. 3:1 D. 4:1 13. Explain why sex-linked traits are more often expressed in males. Males are XY and females are XX, so because males only have that one X, if they get an affected X chromosome, they will automatically have the trait. 14. A color blind female marries a man with normal vision. They have three children: two boys and a girl. One of the boys is colorblind. Use a Punnett square to show the possible genotypes. Show the genetic pattern using a pedigree. Xc Xc X Y XcX XcY XcX XcY Protein Synthesis 15. What part of the DNA carries the genetic code? Nitrogen bases, phosphate groups, or sugars? 16. Which of these represents the structure of messenger RNA? A. B. C. D. 4 Name: ________________________________ Class: ________ Date: __________ 17. Which of these statements best explains how genes and proteins are related? A. Genes are segments of DNA that code for proteins. B. Proteins are segments of DNA that code for genes. C. Genes are the building blocks of proteins. D. Proteins are the building blocks of genes. 18. Explain how proteins are made by using information from RNA. The mRNA picks up the genetic code from the DNA in the nucleus. mRNA carries this message from the nucleus out into the cytoplasm, where it transfers the message to tRNA. tRNA gathers the needed amino acids and takes them to the ribosomes. At the ribosome, rRNA links the amino acids together and sends the finished protein out into the cell to determine a trait. 19. Which of the following is correctly matched with its function? A. rRNA - contains codes to make new ribosomes B. DNA - carries the amino acids to the ribosomes C. tRNA - combines with proteins to make up ribosomes D. mRNA - carries genetic codes from nucleus to the ribosomes 5