* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Section 2.3
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
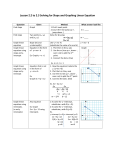
Mr. Borosky Section 2.3 Algebra 2 2.3 Graph Equations Of Lines p. 89-97 Objective: 1. You will graph linear equations in slope intercept or Standard Form. Parent Function – the most basic function in a family (group of functions with shared characteristics. The Parent function for LINEAR FUNCTIONS is f(x) = x which is graphed on p. 89. y-Intercept – where the graph crosses the y-axis. of y when x = 0. It is the ordered pair (0,y). It is the value Slope Intercept Form - equation of a line in the form y = mx + b, where m = slope and b = y intercept. Steps to graph a line using Slope Intercept Form. 1. Write the equation in Slope Intercept Form (Solve for y) 2. Identify the y-intercept, “b”, and use it to plot the point (0,b) or (0,y). This point is ON the y-axis. 3. Identify the slope, “m”, and use it to find additional points by using the RISE over the RUN. 4. Draw a line through the points. (You need at least 3 points) Standard Form – equation of a line in the form Ax + By = C where A, B, and C are integers. If you have fractions, multiply by the common denominator to get rid of them. x-Intercept – where the graph crosses the x-axis. of x when y = 0. It is the ordered pair (x,0). It is the value Steps to graph a line using Standard Form. 1. Write an equation in Standard Form 2. Identify the x-Intercept by plugging in 0 for y and solving for x. Plot the point (x,0). 3. Identify the y-Intercept by plugging in 0 for x and solving for y. Plot the point (0,y). 4. Draw a line through the points. Every line can be written in Standard Form, but Vertical lines cannot be written in Slope Intercept Form. Horizontal Lines – the graph of y = # Vertical Lines – the graph of x = # 2.3 Graph Equations Of Lines p. 89-97 Page 1 of 1