* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
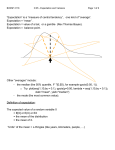
BIOINF 2118 N 05 - Expectation and Variance Page 1 of 4 “Expectation” is a “measure of central tendency”, one kind of “average”. Expectation = “mean” . Expectation = value of a bet, or a gamble (Rev.Thomas Bayes). Expectation = balance point. Other “averages” include: - the median (the 50% quantile, - the mode (the most common value). Definition of expectation: The expected value of a random variable X = E[X] or E(X) or EX = the mean of the distribution = the mean of X. “Units” = x-thingies ). BIOINF 2118 N 05 - Expectation and Variance Page 2 of 4 For a discrete random variable (RV): The expected value is only defined if . (“Absolute convergence “) For a continuous RV: where f is the density (p.d.f.) of X. The expected value is only defined if (“Absolute convergence “) (How can the mean NOT exist? The Cauchy distribution …) The expectation of a function r( ) is or Let X and Y have a joint distribution with pmf or pdf f. If r is a function of X and Y, then the expected value of r(X,Y) is defined by or depending on whether X and Y are discrete or continuous. Absolute convergence is still required for the expected value to be defined. BIOINF 2118 N 05 - Expectation and Variance Page 3 of 4 The Laws of Large Numbers What’s so special about expectation? The distribution of the sample mean converges to the point distribution with a p.m.f. equal to 1 on E(X ) and zero everywhere else, X1 X2 X3 Average -----------------------------------------------> The Variance of a RV The variance, or 2nd central moment, of a RV X is defined as The variance measures the spread of a distribution. “Units” = square-x-thingies Example: If , then the mean of X is - If X 1,...,X n are i.i.d. with mean and variance and the variance is . , then what are mean and variance of X ? - What are the mean and variance of binomial? Bernoulli? uniform? Poisson? The Standard Deviation is the square root of the variance. “Units” = x-thingies. The Coefficient of Variation is Standard Deviation / Mean. Scale-free!! (The CV only makes sense if X is non-negative.) BIOINF 2118 N 05 - Expectation and Variance Page 4 of 4 Higher moments The kth central moment, of a RV X is defined as Any distribution that is symmetric around the mean has all odd central moments = 0. The skewness measures the lop-sidedness of a distribution. . Notice that it is scale-free. The kurtosis measures the lumpiness of a distribution. . Notice that it is also scale-free. If X is normal, kurtosis = 0. Covariance For two RV’s X and Y, the covariance between them is . Correlation To get scale-free measure of association, we define the correlation, . Scale-free! (“Dimensionless”)