* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
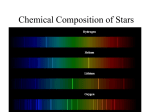
Download Which part of the spectrum can be separated into
Non-standard cosmology wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Astronomy Study Guide 1. Which part of the spectrum can be separated into rainbow like colors? Answer: visible light 2. Which waves have the shortest wave lengths? Longest? Answer: gamma; radio 3. What is a spectroscope/prism used for? Answer: split white light into colors 4. What kind spectrum is used to determine the composition of the stars outer layer? Answer: absorption 5. If a star spectral lines are shifted towards the red end of the spectrum then the star must be? Answer: moving away from Earth 6. What do they compare red shifts and blue shifts to? Answer: reference elements on Earth 7. What theory states how the universe began? Answer: Big Bang Theory 8. Two types of evidences for the big bang theory are… Answer: red shifts and cosmic background radiation 9. One theory about the death of the universe is called the… Answer: Big Crunch 10. Which scientist proposed the 3 planetary motion laws? Answer: Kepler 11. What is the shape of a planet’s orbit? Answer: elliptical 12. Hubble’s law says that a galaxy’s speed is proportional to.. Answer: distance 13. What force keeps the planets in orbit and who proposed this? Answer: gravity; Newton 14. Greater red shifts or blue shifts indicate ___________ Answer: greater speeds 15. What causes the seasons? Answer: Earth’s tilt 16. What is the Doppler effect? Answer: apparent change in wavelength due to movement toward or away from the observer 17. What are the 7 forms of EMR? Answer: radio, microwave, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, x-rays, gamma 18. What color on the visible light spectrum is most energetic? Answer: violet 19. What does a star’s spectrum tell the observer about the star? Answer: composition, movement 20. What type of spectrum is produced by a typical incandescent light bulb? Answer: continuous 21. Who developed a geocentric model of the solar system that explained what retrograde motion is? Answer: Ptolemy 22. What is retrograde motion? Answer: apparent backward movement due to different orbital speeds 23. Who discovered Jupiter’s 4 largest moons with a telescope? Answer: Galileo 24. Harmonic law relates a planet’s distance to the sun with _______. Answer: period (revolution time) 25. What is the visible layer of the sun? Answer: photosphere 26. What are the two layers of the sun’s atmosphere? Answer: chromospheres (inner) and corona (outer) 27. What are granules? Answer: bright markings on the photosphere; tops of convection currents 28. What are solar flares? Answer: explosive events on the sun’s surface 29. By studying sunspots, scientists have determine that the sun _______. Answer: the sun rotates 30. What happens to gravity if mass increases? Distance increases? Answers: gravity increases; gravity decreases Astronomy Study Guide 1. Which part of the spectrum can be separated into rainbow like colors? Answer: 2. Which waves have the shortest wave lengths? Longest? Answer: 3. What is a spectroscope/prism used for? Answer: 4. What kind spectrum is used to determine the composition of the stars outer layer? Answer: 5. If a star spectral lines are shifted towards the red end of the spectrum then the star must be? Answer: 6. What do they compare red shifts and blue shifts to? Answer: 7. What theory states how the universe began? Answer: 8. Two types of evidences for the big bang theory are… Answer: 9. One theory about the death of the universe is called the… Answer: 10. Which scientist proposed the 3 planetary motion laws? Answer: 11. What is the shape of a planet’s orbit? Answer: 12. Hubble’s law says that a galaxy’s speed is proportional to.. Answer: 13. What force keeps the planets in orbit and who proposed this? Answer: 14. Greater red shifts or blue shifts indicate ___________ Answer: 15. What causes the seasons? Answer: 16. What is the Doppler effect? Answer: 17. What are the 7 forms of EMR? Answer: 18. What color on the visible light spectrum is most energetic? Answer: 19. What does a star’s spectrum tell the observer about the star? Answer: 20. What type of spectrum is produced by a typical incandescent light bulb? Answer: 21. Who developed a geocentric model of the solar system that explained what retrograde motion is? Answer: 22. What is retrograde motion? Answer: 23. Who discovered Jupiter’s 4 largest moons with a telescope? Answer: 24. Harmonic law relates a planet’s distance to the sun with _______. Answer: 25. What is the visible layer of the sun? Answer: 26. What are the two layers of the sun’s atmosphere? Answer: 27. What are granules? Answer: 28. What are solar flares? Answer: 29. By studying sunspots, scientists have determine that the sun _______. Answer: 30. What happens to gravity if mass increases? Distance increases? Answers: