* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download D. Alkaline
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
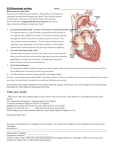
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
A&P Practice CBET Test By David Scott 1. The pH of Blood is: A. Slightly Acidic Slightly Alkaline B. Highly Acidic C. Highly Alkaline 2. The Thyroid Gland is located: A. At the base of the brain The front of the neck B. Superior to the Kidneys C. Frontal Lobe of the Brain 3. Systole occurs when: The Ventricles depolarize A. The Ventricles repolarize B. The Atria depolarize C. The Atria repolarize 4. What is the typical expected blood volume of a normal adult? A. 6.5 Liters 6.0 Liters B. 6.8 Liters C. 7.4 Liters 5. AAMI Standard Lead 3 is: A. White and Red Leads B. White and Green Leads C. Red and White Leads Red and Black Leads 6. The T wave represents: A. The repolarization of the Ventricles The depolarization of the Ventricles B. The repolarization of the Atria C. The depolarization of the Atria 7. Normal placement of a catheter for IBP is: A. The tip 1 cm above the transducer B. The tip 2 cm below the transducer C. The tip 1 cm below the transducer The tip level with the transducer 8. The plane that divides the superior and inferior halves of the body is: A. Sagital Plane B. Frontal Plane C. Transverse Plane D. Mid Plane 9. The adrenal glands are located: At the base of the brain A. The front of the neck Superior to the Kidneys B. Frontal Lobe of the Brain 10. Normal body temperature is: 36 degrees Celsius 37 degrees Celsius 38 degrees Celsius 37.9 degrees Celsius 11. 1000 mm (1 meter) equals: 25.4 inches 37 inches 36.6 inches 39.3 inches 12. 240 CC equals: 2.40 mL 240 mL 24.0 mL 2400 mL 13. The radius bone is located in: The upper arm The forearm The lower leg (shin area) The foot 14. The wall that divides the right and left side of the heart is called: Myocardium Vena Cava Atrium Septum 15. What is the name of the one-way valve that connects the right atrium to the right ventricle? Tricuspid valve Bicuspid valve Semi-lunar valve Mitral valve 16. What is the only vein in the body that caries oxygenated blood? Carotid vein Superior vena cava Inferior vena cava D. Pulmonary vein 17. Which of these has the highest pressure? ABP ICP CVP Pulmonary pressure 18. What is a myocardial infarction? A heart disease or arrhythmia Restriction or closure of the coronary arteries Restriction or closure of the Aorta Restriction or closure of the Ventricles 19. What type of gas is used in an intra-aortic balloon pump? Helium Oxygen Nitrous Oxide Nitrogen 20. What does an intra-aortic balloon pump do? Helps blood circulate from the right ventricle to the body Helps blood circulate from the left ventricle to the lungs through the pulmonary artery Helps blood flow from the left ventricle to coronary arteries Helps blood flow back from the lungs through the coronary vein 21. What does a balloon pump, and a defibrillator use in synch mode to trigger off of? The P wave The QRS complex The R wave The T wave 22. If you have a low gas alarm on an intra-aortic balloon pump what should you check first? The gas tank gauge to see if there is pressure in the cylinder. The catheter for blood The gas supply tubing for leaks The balloon for a rupture 23. What is a pH of 4? Acidic Electrolyte Base Alkaline 24. A blood pH of 7.4 is? Acidosis Alkalosis Normal Base stabilized 25. When the kidneys fail and the patient needs dialysis, the blood pH would be? Metabolic acidosis Metabolic alkalosis Metabolic stabilized Metabolic neutralized 26. What does oxygen attach to in the body? Hemoglobin Plasma Serum Carbon dioxide 27. If the tip of a catheter is lower than the transducer, then the blood pressure will read: Too high Too low This is normal 100 mmHg 28. Cardiac output is normally measured in? Volume over time Liters per minute Time over volume mL per minute 29. What does a cardiac output waveform look like? A saw tooth waveform A bell shaped curve A square wave Close to a SPO2 waveform 30. What happens when a cell is depolarized? Negatively charged potassium ions rush out, and positively charged sodium ions rush into the cell. Negatively charged potassium ions rush in, and positively charged sodium ions rush out of the cell. Positively charged potassium ions rush out, and negatively charged sodium ions rush into the cell. The cell undergoes mitosis 31. What is used to get rid of abnormal electrophysiological impulses in the heart? Cardiac ablation Heparin 82 mg of aspirin per day Intra-aortic balloon pump 32. If the SA node fails (the hearts natural pacemaker). What escape rhythm takes over first? Atria-ventricular rhythm Atria-ventricular node rhythm Ventricular rhythm Coronary node rhythm 33. What cardiac rhythm is a defibrillator set to cardioversion synch mode for? Atrial fibrillation Ventricular fibrillation Asystole Atrial tachycardia 34. What cardiac rhythm would use the defibrillation (non-synch) mode on a defibrillator? Atrial fibrillation Ventricular fibrillation Asystole Atrial tachycardia 35. 2.5 Kg = 5.5 lbs 5.25 lbs 6.00 lbs 5.75 lbs 36. What is the main organ responsible for regulating acid/base and electrolyte balance in the body? Kidneys Pancreas Liver Gall Bladder 37. What ECG lead is used for respiration? Lead 2, black and red leads Lead 1, white and black leads Lead 3, red and black leads Lead 2, white and red leads