* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download g_srt_a_2_assessment_items - Howard County Public School
Dessin d'enfant wikipedia , lookup
Steinitz's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Four color theorem wikipedia , lookup
Apollonian network wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
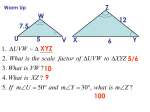
Geometry Unit 1 Items to Support Formative Assessment Transformations, Similarity, and Congruence Part II: Similarity Understand similarity in terms of similarity transformations. G.SRT.A.2 Given two figures, use the definition of similarity in terms of similarity transformations to decide if they are similar; explain similarity transformations the meaning of similarity for triangles as the equality of all corresponding pairs of angles and the proportionality of all corresponding pairs of sides. G.SRT.A.2 Task In the image of the Louvre Pyramid shown below, a small triangle is seen outlined above the entrance. Is that smaller triangle similar to face of the pyramid itself? Justify your answer. You may use rulers, protractors, compasses and graph paper. Assume all lines that appear parallel are parallel. Assume all lengths that appear congruent are congruent. Image source: https://www.google.com/url?sa=i&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=images&cd=&docid=tU2ie1lVgnPNEM&t bnid=T0oO4mZMgPWmEM:&ved=&url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.flickr.com%2Fphotos%2Fstormcrypt%2F3839121170%2F&ei=TNPeUZruEqbtygGXyIGoDw&bvm=bv.48705608,d.aWc&psig=AFQjC NFb8uOE0iby6P8210wH94qv0CmvfA&ust=1373643980593933 Solution: Yes, the small triangle is similar to the face. This can be shown a number of ways and doesn’t necessarily require tools. One possible solution If each small rhombus pane of glass is 1 unit of measurement, the small triangle above the entrance is 4 units long on two sides. The top vertex is formed by a rhombus. The face of the pyramid has side lengths Howard County Public Schools Office of Secondary Mathematics Curricular Projects has licensed this product under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License. of 18 units. The top vertex is also formed by a rhombus. The sides of the small triangle are parallel to the sides of the face. The sides have been enlarged proportionally. The top vertices are congruent. The base angles are congruent because of corresponding angles. Therefore, the triangles are similar. G.SRT.A.2 Item 1 Are the two polygons similar? Justify your answer. Solution: No, they are not similar. Justifications can include ● Using the distance formula to demonstrate that the sides did not enlarge proportionally (AD = 7.21 and A’D’ = 11.66, whereas AB = 2 and A’B’ = 4) ● Using slopes to demonstrate that the lines containing the sides are not parallel to each other (The slope of the line containing segment AD is 2/3 and the slope of line containing segment A’D’ is 3/5) ● Showing that a center of dilation as the point where each line containing a pre-image vertex and its corresponding image vertex intersect does not exist Howard County Public Schools Office of Secondary Mathematics Curricular Projects has licensed this product under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License. G.SRT.A.2 Task 2 Find the missing point, F, of △DEF, if △ABC is similar to △FGD. Solution: By the Pythagorean Theorem, BC = √34 and GD = 5√34 so the scale factor is 5. AB = 2√5 so point F needs to be 10√5 spaces away from G. AC = √26 so point F needs to be 5√26 spaces away from C. To find point F, students may want to try to use the Pythagorean Theorem to draw right triangles that are similar to the triangles that can be formed using the legs of triangle ABC. Point F( -25, 5) G.SRT.A.2 Item 3 Howard County Public Schools Office of Secondary Mathematics Curricular Projects has licensed this product under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License. In the figure shown above, segment DE is parallel to segment BC. Explain how you can verify that triangle ABC is similar to triangle ADE. Solution: Because the two triangles share a common vertex at Point A, angle A is congruent to angle A in both triangles by the reflexive property. Since segment DE is parallel to segment BC, angle D is congruent to angle B and angle E is congruent to angle C because they are corresponding angles. Note: The requirements for this item can be extended to have them verify proportionality of corresponding sides using measurement tools or patty paper. The ratio of sides is ⅖ (or 2:5). G.SRT.A.2 Item 4 Given the parallelogram below, create two similar parallelograms, one larger and one smaller. Justify that your new parallelograms are similar using definitions of similarity. Howard County Public Schools Office of Secondary Mathematics Curricular Projects has licensed this product under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License. Solution: The side lengths of the pre-image are 5 and 13. Similar figures should have side lengths increased proportionally. Students also need to verify that the angles have been preserved by showing that the slopes of the image and pre-image are the same (thereby showing that corresponding angles would be congruent). Notes: Students may wish to transfer the image to additional graph paper. Howard County Public Schools Office of Secondary Mathematics Curricular Projects has licensed this product under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License.