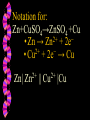* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electrochemistry
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
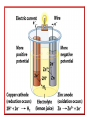
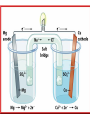
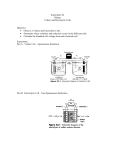
Honors Chemistry Electrochemistry Electricity: The transfer or movement of electrons. Electrochemistry: Electrical applications of redox reactions Redox: Zn+CuSO4→ZnSO4 +Cu • Zn → • 2+ Cu 2+ Zn + − 2e + − 2e → Cu Electrochemical Cell: device that uses redox reactions to produce or use electricity. •Galvanic (voltaic) cells are spontaneous reactions •Electrolytic cells are not spontaneous Electrodes: a metal or graphite surface on which oxidation or reduction can occur. Anode: electrode at which oxidation occurs. negative electrode for voltaic rxns. Cathode: electrode at which reduction occurs. positive electrode for voltaic. Half-Cell: Container in which a half reaction of a redox reaction occurs. Salt Bridge: a tube of an electrolyte that connects two voltaic half-cells allowing ions to move between compartments without mixing. Notation: anode ∣an. soln ∥ cath. soln ∣ cathode Mg(s) ∣ 2+ Mg (aq) ∥ 2+ Cu (aq) ∣ Cu(s) Notation for: Zn+CuSO4→ZnSO4 +Cu 2+ − • Zn → Zn + 2e 2+ − • Cu + 2e → Cu Zn| 2+ Zn || 2+ Cu |Cu Cell Potential (Ecell ): difference in electric potential energy between 2 electrodes of a voltaic cell. Voltage (volts): units for cell potential Electrode Potential: Reduction potential is the tendency for a reduction half-reaction (cathode). Oxidation potential is the tendency for an oxidation half-reaction (anode). Standard Cell Potential E°cell Standard conditions: [ ion ] =1 M P = 1 atm. T = 25°C Cell Potential (Ecell ) Sum of electrode potentials E°cell = E°red + E°ox E°cell=E°red − E°red of ox Standard Reduction Potentials Problem: (See p.664) Calculate E°cell produced by a voltaic cell with a 2+ nickel electrode in Ni solution and a silver electrode in solution of + Ag ions. Problem: Calculate the voltage produced by a voltaic cell with an Al 3+ electrode in Al solution and an iron electrode in a solution 2+ of Fe ions. Electrolysis: Use of electrical energy to bring about a chemical reaction. Electrolytic Cell: an electrochemical cell where electrical energy drives nonspontaneous reactions. Electroplating: depositing one metal on another by use of electric current.