* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Viruses*
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
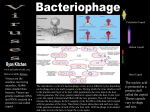
Viruses* Nonliving: no cells, don’t use energy, reproduce on its own Nucleic acid wrapped in protein Obligate endoparasites: only reproduces inside host cells Called bacteriophages or Phage* if it infects bacteria Structure o Genome: DNA or RNA; double or single stranded, contains info to make a virus o Capsid: protein shell, surrounds genome o Envelope: membranous cover over capsid; derived from host, contains viral proteins and glycoproteins (proteins+carbs), Protects against the host defenses o Shapes: Rods, Polyhedrons (sphere–like) & Complex (head, tail, tail fibers) Reproduction o Lytic cycle:* results in death of host cell, virulent viruses (disease causing) 1. Phage (virus) attaches; capsid binds at receptor site 2. Nucleic acid is injected DNA: proteins synthesized RNA: retroviruses (backward), HIV ▫ Reverse Transcriptase:* copies RNA into DNA 3. DNA is used to make parts for virus Enzymes to kill cell & make genome Protein parts (capsomeres) for capsid 4. Phage assembled, capsid around nucleic acid 5. Viruses emerge destroying cell (lysis) ▫ Host cell may defend itself with restriction enzymes that chop up virus genome o Lysogenic cycle:* does not result in the killing of the cell – temperate viruses 1. Virus binds the cell; capsid binds a receptor site 2. Nucleic acid is injected 3. DNA (or RNADNA) molecule incorporates itself into a specific site of host chromosome = prophage* Will be copied every time the host cell reproduces, can remain in your DNA 4. At some time virus comes out and goes through lytic cycle Diseases o Polio, AIDS, chicken pox, scabies, colds, flu, hepatitis, herpes, mononucleosis o Vaccine:* inactivated form of a virus (protein only), triggers immune response without illness. Body is prepared when virus attacks, kills before disease sets in o Several drugs now available to slow virus reproduction o Cancer: uncontrolled growth and division of cells Virus inserts & excises during lysogenic cycle, can cause damage to host genes that can be passed on Oncogenes: genes involved in triggering Origins: Evolved after cells, probably from a host cell genomes that could move