* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Stretching and Shrinking Procedural Guide - OMS-SPED-Page
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
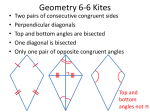
Stretching and Shrinking Procedural Guide 1. In similar figures: a. ANGLES stay the same b. Side Lengths change 2. Types of coordinate rules and their effect on similar figures: a. When ‘x’ and ‘y’ are multiplied by the same number = they stay similar b. When ‘x’ and ‘y’ are multiplied by different numbers = they are no longer similar 3. Coordinate rules and their effect continued x- coordinate When ‘x’ is added by a number = moves figure to the right When ‘x’ is subtracted by a number = moves figure to the left y-coordinate When ‘y’ is added by a number = moves figure up When ‘y’ is subtracted by a number = moves figure down 4. Writing a rule given x and y coordinates a. Choose corresponding points, write the coordinates down Ex: Original Image (2, 4) (3, 6) b. Divide your corresponding coordinates – 3 ÷2 and 6÷4 = 1.5 c. The answer of 1.5 is the rule/scale factor: Original Image (x, y) (1.5x, 1.5y) 5. Scale Factor (Definition and Example) Scale Factor the ratio used to enlarge or reduce similar figures. The difference in the measurement of 2 figures that is similar. *In order to find scale factor: Divide corresponding side lengths of two similar figures If you are making: a figure larger, the SF is greater than > 1 If you are making a figure smaller, the SF is less than < 1 6. How can you find the scale factor & side lengths from a smaller figure to a larger figure (Give an example) New Original x 1 12 4 New Original x 1 12 = Scale factor = 3 4 Side length = 3 (3 x 1) Cross multiply: 4x = 12 Divide by 4: 4÷4 12÷4 X=3 7. How can you find the scale factor and side lengths from a larger figure to a smaller figure? (Give an example) Original New Scale Factor: 2 1 2 x 5 Original New 2 = 1 5 x 2x = 5 x=2.5 Side Length = 2.5 7. Give a formula and example for: a. Perimeter and scale factor- add all sides/ multiply it with Scale Factor b. Area and scale factorRectangle= A = l x w Triangle = A = ½ bh 8. Ratio within similar figures (definition and example) Ratio= A comparison of two quantities (often written as a fraction) Can use a ratio to see if figures are similar: Within Ratio Ratios within the same figure 2 4 4 2 or 1 (1:2) 4 2 4 = 2 (1:2) 8 4 They are similar! 8 1 or (1:4) 4 Between Ratio: Ratios between figures 3 = 1 (1:4) 12 4 4 1 3 12 They are similar! 1 and 4 are corresponding sides 3 and 12 are corresponding sides 9. Difference between Ratio and scale factor Scale Factor- how much one figure increases or decreases Ratio- Compares lengths between and within figures 10. Adjacent and Congruent (definitions) Adjacent = next to each other congruent = means equal (sides, angles) *When 2 figures are congruent their sides are equal Complementary and Supplementary Angles: Complementary= two angles whose sum measures 90˚ Supplementary = two angles whose sum measures 180˚ 11. Find the height using the following: (draw diagram, write formula and example Shadow and similar figure: *USE CROSS MULTIPLICATION New is always the image that has x Original has all it’s measurements Original New Mirror and similar figure These are 2 similar triangles! Modified by McDonald