* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2.1 – What is a Power
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
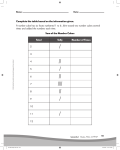
Unit 2 – Powers and Exponent Laws 2.1: What is a Power? Math 9 Investigate (page 52): Squared: Use the tiles to make as many different-sized larger squares as you can. Write the area of each square as a product. Record your results in a table. Number of Tiles Area (square units) Side Length (units) Area as a Product 1 1 1 1X1 4 4 2 2X2 9 9 3 3X3 16 16 4 4X4 25 25 5 5X5 36 36 6 6X6 49 49 7 7X7 64 64 8 8X8 Hints: - Area = side length X side length (1unit X 1 unit = 1 square unit) How many tiles would you need to show a square with a side length of 2? (4) Could you use tiles to show an area of 2? (yes, but it would be a rectangle) The side length of the squares increases by 1 each time. Patterns: o In each row, the number of tiles is equal to the area of the square. The area is the product of 2 side lengths. Cubed: Use the cubes to make as many different-sized larger cubes as you can. Write the volume of each cube as a product. Record your results in a table. Number of Cubes Volume (cubic Edge Length Volume as a units) (units) Product 1 1 1 1X1X1 8 8 2 2X2X2 27 27 3 3X3X3 64 64 4 4X4X4 125 125 5 5X5X5 216 216 6 6X6X6 Hints: - Volume = length X width X height (3 X 3 X 3 = 27) Check answer by taking cube apart and counting all the cubes. How do you know that you have made a cube? (Its length, width and height are the same). The edge length of the cubes increases by 1 each time. Patterns: o In each row, the number of cubes is equal to the volume of the cube. The volume is the product of 3 edge lengths. Reflect & Share: Area is a measure of the amount of surface area. Ex. Square = 5 X 5 = 25 = 52 Volume is a measure of the amount of space occupied. Ex. Cube = 5 X 5 X 5 = 125 = 53 Unit 2 – Powers and Exponent Laws Math 9 Connect: Introduce base, exponent and power to students, and go through example. Give students some numbers and have them write them in Standard Form, Repeated Multiplication and as Powers. 9 squared = 81 (standard) = 9 X 9 (repeated multiplication) = 92 (as a power) Example 1 – Writing Powers Write as a power. a) 7 X 7 X 7 X7 = 74 9 cubed = 729 (standard) = 9 X 9 X 9 (repeated multiplication) = 93 (as a power) b) 2 X 2 X 2 X 2 X 2 X 2 X 2 X 2 = 28 Example 2 – Evaluating Powers Write as repeated multiplication and in standard form. a) 26 = 2x2x2x2x2x2 b) 64 = 6x6x6x6 = 64 = 1296 c) 6 = 61 c) 55 = 5x5x5x5x5 = 3125 Assignment: pg 55-56 #4, 5, 7 (a,b,c), 8 (a,b,c), 9(a,b,c), 11, 12(a,b,c,d) Quick Review: 1. Identify the base, exponent. a) 78 Base= 7 Exponent=8 b) 23 Base= 2 Exponent=3 2. Write the following as a power and in standard form a) 4x4x4 = 43 = 64 b) 6x6 = 62 =36 Example 3 – Evaluation Expressions Involving Negative Signs - When the negative sign is within the brackets, the base is a negative integer. When the negative sign is outside the brackets, it changes the value of the power. Identify the base of each power, then evaluate the power. a) (-2)3 = (-2)(-2)(-2) Base = -2 = -8 c) - (-4)3 = - (-4)(-4)(-4) = - (-64) b) -54 = -(5x5x5x5) Base = 5 = 64 = -625 Base = -4