* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1 - ) The link between the money and the goods and
Greg Mankiw wikipedia , lookup
Economic bubble wikipedia , lookup
Non-monetary economy wikipedia , lookup
Great Recession in Russia wikipedia , lookup
Money supply wikipedia , lookup
Ragnar Nurkse's balanced growth theory wikipedia , lookup
Monetary policy wikipedia , lookup
Nominal rigidity wikipedia , lookup
Business cycle wikipedia , lookup
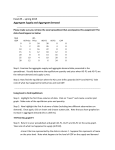
Izmir University of Economics Department of Economics Econ 102 Principles of Macroeconomics PROBLEM SET 5 Chapter 27 Multiple Choice Questions 1 - ) The link between the money and the goods and services market exists through the impact of a. tax revenues on the government budget. b. money supply on money demand. c. income on money demand and interest rate on investment. d. income on government spending. Refer to the information provided in the table below, which shows a hypothetical investment schedule, to answer the question that follows. Interest Rate (%) Planned Investment ($ Billion) 3 400 6 360 9 320 12 280 15 240 18 200 2 - ) Suppose the expenditure multiplier is 4. A drop in the interest rate from 15% to 9%, ceteris paribus, would increase equilibrium output by a. $20 billion. b. $160 billion. c. $240 billion d. $320 billion. 3- ) The effects of a change in the interest rate on equilibrium income can be summarized as follows. a. b. c. d. 1 Izmir University of Economics Department of Economics Econ 102 Principles of Macroeconomics 4- ) Expansionary fiscal policy refers to: a. an increase in the money supply b. an increase in taxes c. a decrease in the money supply d. either an increase in government spending or reduction in net taxes 5- ) Which of the following policy changes is associated with expansionary monetary policy? a. an increase in net taxes b. an increase in money supply c. an increase in government spending d. a decrease in money supply 6- ) Refer to the graph below. Which move best describes the impact of expansionary fiscal policy with crowding out? a. a shift of aggregate expenditure from AE1 to AE2 b. a shift of aggregate expenditure from AE1 to AE3 c. a shift of aggregate expenditure from AE2 to AE3 d. No change in equilibrium income. 7- ) The effect of contractionary monetary policy is as follows: a. b. c. d. 2 Izmir University of Economics Department of Economics Econ 102 Principles of Macroeconomics 8- ) The effect of contractionary fiscal policy is as follows: a. b. c. d. 9- ) Along the aggregate demand curve, each point represents: a. Equilibrium in the money market, regardless of the equilibrium situation in the goods market b. Macroeconomic equilibrium or equilibrium in all markets of the economy c. Simultaneous equilibrium in both the goods and money markets d. Equilibrium in the goods market, regardless of the equilibrium situation in the money market 10 - ) Behind the explanation as to why the aggregate demand has a negative slope is the fact that when the aggregate price level increases, a. Other prices and income remain fixed. b. A higher interest rate causes aggregate output to fall. c. The aggregate quantity of output demanded (Y) also increases. d. All of the above 11 - ) What is the impact of an increase in the quantity of money supplied on the aggregate demand curve? a. There is a move downward along the aggregate demand curve. b. The aggregate demand curve shifts to the left. c. There is a move upward along the aggregate demand curve. d. The aggregate demand curve shifts to the right. Essay Questions 1 - ) Briefly explain the effects of contractionary fiscal policy and expansionary monetary policy on the overall economy? Ms ↑ r↓ I↑ Y↑ Md↑ 2 - ) Briefly explain the “consumption link” and “real wealth effect”. Consumption link: P↑ Md↑ r↑ c↓ Y↓ an increase in the price level increases the demand for money, which leads to an increase in the interest rate which leads to a decrease in 3 Izmir University of Economics Department of Economics Econ 102 Principles of Macroeconomics consumption which leads to a decrease in aggregate output. The initial decrease in consumption contributes to the overall decrease in output. Planned investment does not bear all the burden of providing the link from a higher interest rate to a lower level of aggregate output. Real wealth effect: an increase in price level may lower the real value of stocks and housing. If stock prices and housing prices rise by the same percentage as the overall price level, the real value of wealth remain unchanged. If real wealth falls, this leads to a decrease in consumption, which leads to a decrease in aggregate output. So, change in consumption brought about by a change in real wealth results from a change in price level. Chapter 28 Multiple Choice Questions 1 - ) The graph that shows the relationship between the aggregate quantity of output supplied by all the firms in an economy and the overall price level is a. the aggregate supply curve. b. the aggregate production function. c. the production possibilities frontier. d. the aggregate demand curve. Figure 1 2 - ) Refer to Figure 1. This economy reaches capacity at a. $250 billion. b. $500 billion. c. $400 billion d. an output level that is indeterminate from this information because aggregate demand is not given. 4 Izmir University of Economics Department of Economics Econ 102 Principles of Macroeconomics 3- ) What determines the slope of the aggregate supply curve is a. how much more the economy can produce without any change in the price level. b. how fast the output level changes after a technological advance. c. how fast the price of factors of production respond to changes in the price level. d. None of the above Figure 2 4- ) Refer to Figure 2. Which of the following causes the economy to move from Point A to Point E? a. An oil embargo that increases the price of oil b. Technological progress c. An influx of immigrants d. An increase in the price level 5- ) Refer to Figure 2. Suppose the economy is at Point A, an increase in the price level moves the economy to Point a. E b. D c. B d. C 6- ) Refer to Figure 2. During the 1990s, many firms in the United States were investing in new capital. If the economy was originally at Point A, this would have caused a movement to Point 5 Izmir University of Economics Department of Economics Econ 102 Principles of Macroeconomics a. B b. D c. C d. E Figure 3 7- ) Refer to Figure 3. Suppose the equilibrium output is $600 billion, an expansionary monetary policy ________ equilibrium output and ________ the price level. a. decreases; leaves unchanged b. leaves unchanged; increases c. increases; increases d. increases; decreases 8- ) Refer to Figure 3. Suppose the equilibrium output is $600 billion, an oil embargo would probably decrease a. both the equilibrium output and the price level. b. the price level. c. equilibrium output and decrease the price level. d. equilibrium output Figure 4 9- ) Refer to Figure 4. Potential output 6 Izmir University of Economics Department of Economics Econ 102 Principles of Macroeconomics a. is $400 million b. is $700 million c. is $800 million d. cannot be determined from this information because aggregate demand is not given 10 - ) Refer to Figure 4. Which of the following statements characterizes an output level of $800 billion? a. It is sustainable over the long run without inflation. b. It is achievable only in the long run. c. It is attainable in the short run but it is associated with increases in the price level. d. It can be achieved only if investment is independent of the interest rate. 11 - ) Refer to the figure below. In which case is expansionary policy more effective? a. Expansionary policy is ineffective in either case. b. In the case on the right. c. Expansionary policy works well in both cases. d. In the case on the left. Essay Questions 1 - ) Describe the effectiveness or desirability of expansionary policy along the aggregate supply curve. See course book page 588-590. 2 - ) By using the AS/AD framework briefly explain the causes of inflation. 7 Izmir University of Economics Department of Economics Econ 102 Principles of Macroeconomics See course book page 590-593. 8