* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 8th Grade Biographical Glosary
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
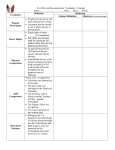
8th Grade Document Glossary Document Who created the document? Why? What effect did it have? List any people from the biographical glossary associated with the document under the document’s name. Colonial Era (chapter 2-5) Mayflower Compact Fundamental Orders of Connecticut An agreement established by men on the Mayflower that called for laws for the good of the colony & established the principle of selfgovernment Set of laws established in Conn. In 1639 that expanded the idea of representative government. Magna Carta English document from 1215 that guaranteed basic political rights. English Bill of Rights Agreement signed by William & Mary to respect the rights of English citizens & Parliament, including the right to free elections. Proclamation of 1763 British order that prohibited colonists from moving west of the Appalachian Mountains. Stamp Act A 1765 law passed by Parliament that required all legal & commercial documents to carry a stamp showing a tax had been paid. A series of laws enacted by Parliament to punish Mass. Colonists for the Boston Tea Party. Revolution (chapter 6 & 7) Intolerable Acts Declaration of Independence A 1776 document in which the colonies declared their independence from Great Britain. It listed their grievances against King George. Common Sense A pamphlet published by Thomas Paine that supported the American Revolution. Treaty of Paris (1783) Treaty that ended the American Revolution, confirming independence for the U.S. & setting boundaries of the new nation. Creating a Government and putting it in Place (chapter 8, government, & 9) Articles of Confederation Northwest Ordinance A document adopted by Continental Congress in 1777 7 approved by the states in 1781 that outlined the form of government for the new U.S. Described how the NW Territory was to be governed and set conditions for settlement & settlers’ rights. Constitution Document that outlines how the U.S. government works. Bill of Rights First 10 amendments to the U.S. Constitution that list citizens’ rights and freedoms. Federalist Papers A series of essays defending and explaining the Constitution. Anti-Federalist writings Writings that were against the ratification of the U.S. Constitution. Washington’s Farewell Address President Washington’s final address as he left the presidency in which he warned against creating political parties & the danger of U.S. forming permanent alliances with foreign nations. The Nation Expands and Experiences Growing Pains (chapter 10-14) Marbury v. Madison Case in 1803 that determined the Supreme Court had the power to abolish laws by declaring them unconstitutional. McCulloch v. Maryland Supreme Court case that upheld federal authority by ruling a state could not tax a national bank. Gibbons v. Ogden Supreme Court case that determined that the federal government regulates interstate commerce, not the states. Monroe Doctrine U.S. policy announced by President Monroe that European colonization in the Western Hemisphere would not be accepted. Missouri Compromise A series of laws that maintained the balance of power between slave states and free states. Indian Removal Act 1830 act that called for the government to negotiate treaties that would require Native Americans to relocate West. Worcester v. Georgia Supreme Court case in which the Cherokees appealed to keep their land from being seized by the state of Georgia. The Court, led by John Marshal, l ruled in their favor, saying only the federal gov. could make laws governing the Cherokees. Both Georgia & Pres. Andrew Jackson ignored the ruling. The right of a state to reject a federal law that it considers unconstitutional. Doctrine of Nullification Declaration of Sentiments Document presented at Seneca Falls Convention that stated “All men and women are created equal” and listed several complaints and a demand for rights. Civil Disobedience Peacefully refusing to obey laws one considers unjust. Civil War and Reconstruction (chapter 15- 18) Compromise of 1850 A series of laws by Congress intended to settle the major disagreements between free and slave states. Dred Scott v. Sandford An 1856 Supreme Court case in which a slave, Dred Scott, sued for his freedom because he had been taken to live in freed territories where slavery was illegal; he lost the case. Lincoln argued for the North and South to preserve the union. He assured the South he had no intention of abolishing slavery there, but spoke against secession. Encouraged remaining Southern states to secede from the Union, and that secession was a necessity, not a choice. Patriotic song written during the Civil War by Julia Ward Howe, a strong anti-slavery advocate. An executive order issued by President Lincoln Jan. 1, 1863 that freed the slaves in all states in rebellion against the union. Lincoln’s 1st Inaugural Address Davis’s 1st Inaugural Address Battle Hymn of the Republic Emancipation Proclamation Gettysburg Address Lincoln’s 2nd Inaugural Address 13th Amendment Given by Lincoln at dedication of a cemetery in Gettysburg for 3,500 soldiers buried there. He declared the nation was founded on the idea of all men are created equal and vowed to continue to fight for democracy. Given just before the end of the Civil War, Lincoln recalled the major cause of the war, and urged citizens to care for one another and work for a just and lasting peace. Constitutional Amendment that banned slavery & involuntary servitude in the U.S. 14th Amendment Constitutional Amendment that made all persons born or naturalized in the U.S., including former slaves, citizens. 15th Amendment Constitutional Amendment that stated citizens could not be stopped from voting based on race, color, or previous conditions of servitude. Offered 160 acres of land free to anyone who agreed to live on and improve the land for five years. Homestead Act Dawes Act Law enacted in 1887, that distributed reservation land to individual owners. Morrill Act Signed into law by Abraham Lincoln in 1862, this act set aside federal land to be used for the creation of agricultural colleges.