* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Demand Led Recession
Non-monetary economy wikipedia , lookup
Participatory economics wikipedia , lookup
Nouriel Roubini wikipedia , lookup
Ragnar Nurkse's balanced growth theory wikipedia , lookup
Fiscal multiplier wikipedia , lookup
Great Recession in Russia wikipedia , lookup
Austrian business cycle theory wikipedia , lookup
Full employment wikipedia , lookup
Transformation in economics wikipedia , lookup
Nominal rigidity wikipedia , lookup
2000s commodities boom wikipedia , lookup
Business cycle wikipedia , lookup
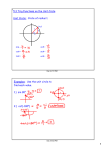
Name What starts the recession? What happens in the recession? Why does it happen? Name What starts the expansion? What happens in the expansion? Why does it happen? Demand Led Recession Keynesian Theory Misperception Theory Supply Led Recession Real Business Cycle Theory A drop in AD (a A drop in AD (a A drop in AS (a decrease in C, I, G, or decrease in C, I, G, or decline in resources) NX) NX) Prices fall Prices fall Prices rise Income falls Income falls Income falls Unemployment rises Unemployment rises Unemployment rises (stagflation) With the drop in AD With the drop in With the decrease in and interest rates, prices (macro event), resources there are prices don’t full companies fewer goods adjust downward misperceive this as a produced in the (stickiness). This decline in demand for economy. This creates a surplus of their good (micro pushes prices higher goods. Companies event). Companies and interest rates respond by cutting respond by cutting higher. production and production and laying workers off laying workers off Demand Led Expansion Keynesian Theory Misperception Theory A rise in AD (an increase in C, I, G, or NX) Prices rise Income rises Unemployment falls With the rise in AD and interest rates, prices don’t full adjust upward (stickiness). This creates a shortage of goods. Companies respond by increasing production and hiring more workers A rise in AD (an increase in C, I, G, or NX) Prices rise Income rises Unemployment falls With the rise in prices (macro event), companies misperceive this as an increase in demand for their good (micro event). Companies respond by increasing production and hiring more workers Supply Led Expansion Real Business Cycle Theory A rise in AS (an increase in resources) Prices fall Income rises Unemployment falls With the increase in resources there are more goods produced in the economy. This pushes prices lower and interest rates lower. 1. Consumers become more confident: ( AD / AS ) will ( Inc / Dec ) which causes, in the short run, income to ( Inc / Dec ), unemployment ( Inc / Dec ), and prices to ( Inc / Dec ). This economy would be described as undergoing a ( Recession / Expansion ). 2. The Government raises taxes on consumers: ( AD / AS ) will ( Inc / Dec ) which causes, in the short run, income to ( Inc / Dec ), unemployment ( Inc / Dec ), and prices to ( Inc / Dec ). This economy would be described as undergoing a ( Recession / Expansion ). 3. Americans increase their purchases of I-Pods which are produced in China: ( AD / AS ) will ( Inc / Dec ) which causes, in the short run, income to ( Inc / Dec ), unemployment ( Inc / Dec ), and prices to ( Inc / Dec ). This economy would be described as undergoing a ( Recession / Expansion ). 4. The price of oil and gas increases as supplies lessen: ( AD / AS ) will ( Inc / Dec ) which causes, in the short run, income to ( Inc / Dec ), unemployment ( Inc / Dec ), and prices to ( Inc / Dec ). This economy would be described as undergoing a ( Recession / Expansion ). 5. The US pulls out of Iraq and military spending is cut: ( AD / AS ) will ( Inc / Dec ) which causes, in the short run, income to ( Inc / Dec ), unemployment ( Inc / Dec ), and prices to ( Inc / Dec ). This economy would be described as undergoing a ( Recession / Expansion ). 6. The French increase their preference for American made cars: ( AD / AS ) will ( Inc / Dec ) which causes, in the short run, income to ( Inc / Dec ), unemployment ( Inc / Dec ), and prices to ( Inc / Dec ). This economy would be described as undergoing a ( Recession / Expansion ). 7. Global warming harms agricultural production: ( AD / AS ) will ( Inc / Dec ) which causes, in the short run, income to ( Inc / Dec ), unemployment ( Inc / Dec ), and prices to ( Inc / Dec ). This economy would be described as undergoing a ( Recession / Expansion ). 8. The internet increases the speed of job matching and natural rate of unemployment falls: ( AD / AS ) will ( Inc / Dec ) which causes, in the short run, income to ( Inc / Dec ), unemployment ( Inc / Dec ), and prices to ( Inc / Dec ). This economy would be described as undergoing a ( Recession / Expansion ). 9. Investors become optimistic and sentiments improve: ( AD / AS ) will ( Inc / Dec ) which causes, in the short run, income to ( Inc / Dec ), unemployment ( Inc / Dec ), and prices to ( Inc / Dec ). This economy would be described as undergoing a ( Recession / Expansion ). 10. For all of the above, what happens in the long run? Income returns to the long run equilibrium or “full employment” levels. And the unemployment rate returns to the natural rate of unemployment.