* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Economics ~ Final Exam Review
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
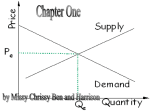
Economics ~ Final Exam Review UNIT 1: AN INTRODUCTION TO ECONOMICS Chapter 1: What is Economics? Section 1: The Basic Problem in Economics p 3 Objectives: How do wants and needs differ? Why does scarcity face all people at all times? What are the 4 factors of production? Section 2: Trade-Offs p. 12 Objectives: How are trade-offs and opportunity costs related? How can society’s trade-off’s be shown on a production possibilities curve? Section 3: What do Economists Do? p. 18 Objectives: How do economists use models to study the real world? Why are there different schools of economic thought? Chapter 2: Economic Systems and the American Economy Section 1: Economic Systems p. 31 Objectives: What 3 questions must all economic systems answer? What are the major types of economic systems and their differences? Section 2: Characteristics of the American Economy p. 40 Objectives: What is the role of government in our free enterprise economy? How do freedom of enterprise and freedom of choice apply to the American economy? What roles do private property, the profit incentive, and competition play in the American economy? Section 3: The Goals of the Nation p. 46 Objectives: What are the major goals of a market economy? How can people balance economic rights with economic responsibilities? UNIT 3: Microeconomics: Markets, Prices, and Business Competition Chapter 7: Demand and Supply Section 1: Demand p. 169 Objectives: How does the principle of voluntary exchange operate in a market economy? What does the law of demand state? How do the real income effect, the substitution effect, and diminishing marginal utility relate to the law of demand? Section 2: The Demand Curve and Elasticity of Demand p. 177 Objectives: What does the demand curve show? What are the determinants of demand? How does the elasticity of demand affect the price of a given product? Section 3: The Laws of Supply and Supply Curve p. 186 Objectives: What is the law of supply? How does the incentive of greater profits affect quantify supplied? What do a supply schedule and supply curve show? What are the 4 determinants of supply? Section 4: Putting Supply and Demand Together p. 194 Objectives: How is the equilibrium price determined? How do shifts in equilibrium price occur? How do shortages and surpluses affect price? How do price ceilings and price floors restrict the free exchange of prices? Chapter 9: Competition and Monopolies Section 1: Perfect Competition p. 233 Objectives: What are the 5 conditions of perfect competition? Why is agriculture often considered an example of perfect competition? How does perfect competition benefit society? Section 2: Monopoly, Oligopoly, Monopolistic Competition p. 239 Objectives: What are 4 characteristics of a pure monopoly? What characterizes an oligopoly? What are 5 characteristics of monopolistic competition? Section 3: Government Policies Toward Competition p. 248 Objectives: What is the difference between interlocking directorates and mergers? What is the purpose of federal regulatory agencies? How has some regulation hurt consumers? UNIT 5: MICROECONOMICS: THE NATION’S ECONOMY Chapter 13: Measuring the Economy’s Performance Section 1: National Income Accounting p. 343 Objectives: What 4 categories of economic activity are used to measure GDP? How do the 3 measures of income – national, personal, and disposable- differ? Section 2: Correcting Statistics for Inflation p. 350 Objectives: What is the relationship between the purchasing power of money and the rate of inflation? How do the consumer price index and the producer price index differ in what they measure? Section 3: Aggregate Demand and Supply p. 356 Objectives: Why is there an inverse relationship between aggregate quantity demanded and the price level? What causes the aggregate supply curve to slope upward? How do you use aggregate demand and supply analysis to determine the equilibrium price level? Section 4: Business Fluctuations p. 360 Objectives: What are the phases of a typical business cycle? Section 5: Causes and Indicators of Business Fluctuations p. 364 Objectives: What are some of the potential causes of business fluctuations? What are the 3 broad categories of economic indicators? Chapter 15: The Federal Reserve System and Monetary Policy Section 1: Organization and Functions of the Federal Reserve System p. 399 Objectives: How is the Federal Reserve System in the US organized? What are the functions of the Fed? Section 2: Money Supply and the Economy p. 407 Objectives: What are the differences between loose money and tight money policies? What is the purpose of the fractional reserve banking? How does the money supply expand? Section 3: Regulating the Money Supply p. 412 Objectives: How can the Fed use reserve requirements to alter the money supply? How does the discount rate affect the money supply? How does the Fed use open-market operations? What are some of the difficulties of carrying out monetary policy? UNIT 6: THE INTERNATIONAL SCENE NETFLIX and UpFront Article related to: Death by China Objective: Identify the concerns and issues that have arisen b/c of allowing China to join the World Trade Organization