* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Archaeoastronomy wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Lunar theory wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Hebrew astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Standard solar model wikipedia , lookup
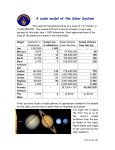
Update TOC with 2nd Activity = “Stars at a Glance – Stellar Parallax” Because of Light Pollution, 70% of Americans cannot see the Milky Way. Flagstaff Dark Skies Coalition: Their mission is to “celebrate, promote, and protect the glorious dark skies of northern Arizona”. Believe people should be able to experience “seeing the stars” Helping to set regulations for building lights Fewer Glare-free Lower wattage International Dark Sky Association: Developed to protect our views of the night-skies. How are we doing in North Bend-Snoqualmie? http://www.blue-marble.de/nightlights/2010 Do: Fonzie Thumb Shift Do: Mini-Lab Parallax Answer: Reflect & Connect p 466: # 1 Watch Parallax Simulation: Read & Take Notes p 467: Stellar Parallax Answer: Reflect & Connect p 468: # 1a and 1c Read/Notes p 469: Monster Units Answer: Reflect & Connect p 470: # 2, 3 Why Does the Moon Follow You Around? Driving down a road with mountains in the distance, you'll notice that the mountains don't seem to move much at all, while the farm houses closer to the road move much faster, but still a lot slower than the mailboxes blurring past you right beside the road. This is the same situation as the moon ‘following you’. The Moon is simply a much bigger ‘mountain’, and it's much further away. This is called parallax. The angle between you and a nearby object changes much more rapidly as you pass them than the angle does for far away objects. Take a flashlight into a dark room and stand next to a wall. Start wiggling the flashlight, and you'll see the bright spot on the wall moving a little. Back away from the wall, and keep wiggling the flashlight just as much as before. The spot will move faster and further as you increase your distance from the wall. If you get far enough away, you can try to hold the light still, but the spot will still wiggle a bit just because your hand is not perfectly steady. Also remember this - the Moon is about a thousand miles wide, and you would therefore have to go 1000 miles just to have it move 1 of its widths across the sky. How long does it take you to drive a thousand miles? Light-Years One Light-year [ly] is the distance light can travel in one year. Speed of light in a vacuum (‘empty space’) ≈ 3 x 108 meters/second In one year, light travels ≈ 9.5 x 1012 meters Proxima Centauri (the nearest star to Earth, excluding our Sun) is 3.99 x 1016 meters from Earth. We can’t actually see this star… it is too far, and too ‘dim’. Using Dimensional Analysis, we find the Proxima Centauri = 4.22 ly away. ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Astronomical Units Astronomical Unit [AU] is the average distance from the Earth to the Sun. 1 AU ≈ 1.5 x 108 kilometers. 1 AU < 1 ly. Astronomers use AU to measure distances within our solar system, and ly to measure larger distances. AU allow us to compare ‘relative distances’. The distances, below, are approximate mean distances. It has to be taken into consideration that the distances between celestial bodies change in time due to their orbits and other factors. The Moon is 0.0026 ± 0.0001 AU from the Earth The Earth is 1.00 ± 0.02 AU from the Sun --------------------------Mercury is 0.39 ± 0.09 AU from the Sun Venus is 0.72 ± 0.01 AU from the Sun Mars is 1.52 ± 0.14 AU from the Sun Jupiter is 5.20 ± 0.25 AU from the Sun Saturn is 9.58 ± 0.53 AU from the Sun Uranus is 19.23 ± 0.85 AU from the Sun Neptune is 30.10 ± 0.34 AU from the Sun Proxima Centauri is ~268,000 AU from the Sun Luminosity Luminosity is the power output of a star (CORRECTION to the text: it is NOT a measure of energy output) Sun luminosity ≈ 3.8 x 1026 Watts Rather than use such large numbers, we can compare a star’s luminosity relative to the Sun. The Sun has luminosity = 1 Lsun Proxima Centauri has luminosity = .000138 Lsun Proxima Centauri is MUCH less luminous in addition to being 4.2 ly away. Even if it were only 1 AU, we would barely be able to see it because puts forth too little power. * We will be using a similar comparison for the masses of celestial bodies, compared to the mass of the sun. Homework Tonight: Scientific Notation WS #2: Do all ODD problems *If student achieves 90%or better, they will not have any further scientific notation homework!