* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download zenith - Gardner-Webb University
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Archaeoastronomy wikipedia , lookup
Equation of time wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Hebrew astronomy wikipedia , lookup
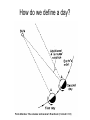
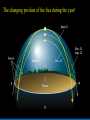
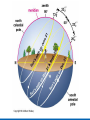
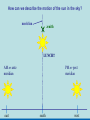
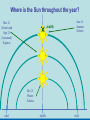
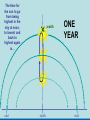
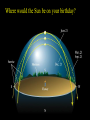
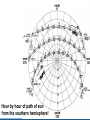
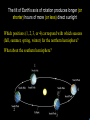
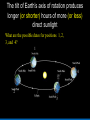
Did you get the Key Ideas from the Seasonal Stars Lecture Tutorial? Post Tutorial Question What component of Earth’s motion causes the stars to rise earlier on successive nights? A) its rotation about its axis B) its orbit around the Sun C) the tilt of its rotation axis North Star Aquarius Pisces Capricornus Aries 1 day Sagittarius Taurus Scorpius 365 days Libra Gemini Virgo Cancer Leo Figure 1 Taurus Aries Gemini South Pisces Cancer E Figure 2 – What it would look like if you were the observer in Figure 1 W Two months from the time shown what constellation will be high in the Southern sky, at Midnight? At Noon? What sign will a person be if they are born at that time? For more practice at this – Look back at Part I of the “Seasonal Stars” Lecture Tutorial Post Tutorial Question One night, you see the star Sirius rise at exactly 7:36 PM. The following night it will rise A) slightly earlier. B) at the same time. C) slightly later. Post Tutorial Question One evening at midnight, you observe Leo high in the southern sky at midnight. Virgo is to the east of Leo and Cancer is to the west. One month earlier, which of these constellations was high in the southern sky at midnight? A) Leo B) Virgo C) Cancer How do we define what time it is? What time is it now? http://www.jgiesen.de/SiderealTimeClock/index.html How do we define what time it is? What time is it now? http://www.jgiesen.de/SiderealTimeClock/index.html How do we define a day? Tutorial: Solar vs. Sidereal Day p.11 Work with a partner! Read the instructions and questions carefully. Discuss the concepts and your answers with one another. Come to a consensus answer you both agree on. If you get stuck or are not sure of your answer, ask another group. If you get really stuck or don’t understand what the Lecture Tutorial is asking, ask me for help. Which takes longer to complete? A) one solar day. B) one sidereal day. C) Both take the same amount of time. Image that Earth begins orbiting the Sun twice as fast while maintaining the same rotation rate. It now orbits once around the Sun every 6 months. In this case, what happens to the length of the solar day? A) It gets slightly longer. B) It does not change. C) It gets slightly shorter. D) It is cut in half. E) It doubles. The changing position of the Sun during the year! How can we describe the motion of the sun in the sky? meridian east X Zenith or overhead south west How can we describe the motion of the sun in the sky? meridian zenith LUNCH!! PM or post meridian AM or ante meridian east south west Where is the Sun at noon today? zenith here or there? east south west Where is the Sun at noon today? zenith What about tomorrow at noon? there east south west What about the path of the Sun? zenith What about tomorrow at noon? there JUST A LITTLE LOWER !! east south west Where is the Sun throughout the year? Mar 21 (Vernal) and Sept 21 (Autumnal) Equinox zenith June 21 Summer Solstice Dec 21 Winter Solstice east south west The time for the sun to go from being highest in the sky at noon, to lowest and back to highest again is… east zenith south ONE YEAR west Where would the Sun be on your birthday? Hour by hour of path of sun from the southern hemisphere! Position of the Sun when photographed during the day of the winter and summer solstice Shadow Paths Sundial Time Lapse Path of the Sun when photographed from Phoenix, the Mars rover, up near the north pole of Mars. Sun at the exact same time of the day over the course of a full year. The shape is called an analemma. This picture shows every 10 days. Altitude of the Sun Animation • • • Note where the sun rises and sets Note how the altitude of the sun changes during a day and over the course of the year. Note how the shadow changes during a day and over the course of the year. http://astro.unl.edu/naap/motion3/animations/sunmotions.swf Tutorial: Path of the Sun p.87 Work with a partner! Read the instructions and questions carefully. Discuss the concepts and your answers with one another. Come to a consensus answer you both agree on. If you get stuck or are not sure of your answer, ask another group. If you get really stuck or don’t understand what the Lecture Tutorial is asking, ask me for help. Under which of the following circumstances will a vertical flagpole not cast a shadow as seen from the continental United States? A. B. C. D. E. 0/0 every day at noon every day at the time when the sun is highest in the sky when the sun is highest in the sky on the summer solstice when the sun is highest in the sky on the winter solstice none of the above If you are located in the continental U.S. on the first day of October, how will the position of the Sun at noon be different two weeks later? A. B. C. D. E. It will have moved toward the north. It will have moved to a position higher in the sky. It will stay in the same position. It will have moved to a position closer to the horizon. It will have moved toward the west. For an observer in the continental U.S., which, if any, of the x’s (a – e) in the figure below correctly shows the position of the Sun’s shadow at noon? Choose all that could be correct. Note that the position of the Sun’s shadow at noon on the Winter and Summer Solstices are shown. NORTH For an observer in the continental U.S., which of the three shadow plots, shown at right, correctly depicts the Sun’s motion for one day? x x B. C. D. E. x x x x Shadow plot B x x WEST A. x Shadow plot A x x x x x x x x x x EAST x x x Shadow plot C SOUTH Shadow plot A Shadow plot B Shadow plot C More than one of the plots are possible, on different days of the year. None of the plots are possible. Time? What causes Seasons? Angular Momentum • If something is spinning, the axis of rotation resists a change in direction. Precession 26,000 years Time? What causes Seasons? Hour by hour of path of sun from the southern hemisphere! When the Sun is high in the sky during the day, the number of daylight hours is greater and the amount of direct sunlight received is greater. This results in Summer. When the Sun is high in the sky during the day, the number of daylight hours is greater and the amount of direct sunlight received is greater. This results in Summer. When the Sun is low in the sky during the day, the number of daylight hours is less and the amount of direct sunlight received is less. This results in Winter. When the Sun is low in the sky during the day, the number of daylight hours is less and the amount of direct sunlight received is less. This results in Winter. The tilt of Earth’s axis of rotation produces longer (or shorter) hours of more (or less) direct sunlight The tilt of Earth’s axis of rotation produces longer (or shorter) hours of more (or less) direct sunlight Which positions (1, 2, 3, or 4) correspond with which seasons (fall, summer, spring, winter) for the northern hemisphere? What about the southern hemisphere? 1 4 2 3 Looking at the images below, which letter (a-e) best represents winter in the United States? Sunlight Sunlight a c d 2 3 b Sun Note: this drawing is not to scale. In fact you could fit more than 11,000 Earths between the Sun and the Earth. e The tilt of Earth’s axis of rotation produces longer (or shorter) hours of more (or less) direct sunlight What are the possible dates for positions 1, 2, 3, and 4? 1 4 2 3 Time? Seasons on Mars? Tutorial: Seasons p.91 Work with a partner! Read the instructions and questions carefully. Discuss the concepts and your answers with one another. Come to a consensus answer you both agree on. If you get stuck or are not sure of your answer, ask another group. If you get really stuck or don’t understand what the Lecture Tutorial is asking, ask me for help. Which of the locations identified with an “x” for each of the situations (A – E) would experience the coolest temperature over the course of one day? Which of the following describes one reason that the Northern and the Southern Hemispheres have different seasons at the same time? a. The Earth is closer to the Sun during summer in the Southern Hemisphere and is farther from the Sun during winter in the Northern Hemisphere. b. During a day of the year when the Sun is high in the sky in the Northern Hemisphere it will be low in the sky in the Southern Hemisphere. c. Earth is tilted, so the Sun is closer to one hemisphere than the other, which causes one hemisphere to be in winter and the other in summer. d. The energy received at Earth from the Sun changes throughout the year providing more energy to one hemisphere than the other. e. None of the above. Which of the following locations experiences the smallest amount of change in sunlight over the course of a year? h of the following locations experiences the smallest amount of change in sunlight a. north pole b. south pole c. equator d. They all experience the same amount of change in sunlight over a year. ourse of a year? north pole south pole equator They all experience the same amount of change in sunlight over a year. If Earth were tilted more (60o rather than 23.5o), then during winter at your location you would: a. experience cooler temperatures. b. experience warmer temperatures. c. not experience any significant change in temperature. GO CONFIDENTLY IN THE DIRECTION OF YOUR DREAMS!! LIVE THE LIFE YOU’VE IMAGINED