* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Origins of World War II
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of the Winter War wikipedia , lookup
Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact wikipedia , lookup
Fascism in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Swedish iron-ore mining during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
German–Soviet Axis talks wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
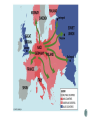
Why dictators rose to power in Europe in the 1920s and 1930s How Hitler, Mussolini and Stalin were similar and different as leaders The policy of appeasement How appeasement impacted WWII Why the US and GB choose to align themselves with the Soviets In Europe in the 1930s, the stage was set for the rise of dictators who would rule in a TOTALITARIAN system Complete rule by a single party and it’s leader All aspects of people’s lives are controlled without opposition Harsh punishment of Germany Led to resentment Soviet Union lost a great deal of land Including several ports Italy felt like they didn’t get enough Led to resentment New democracies set up But had no help in rebuilding No tradition of rule US was not a member The League was a failure Peace was not kept in the world No way to enforce disarmament Germany and Italy drop out of the League The Great Depression extended beyond the US Large numbers of people were unemployed Led to discontentment In an environment of discontentment, dictators could easily rise to power Adolf Hitler Der Fuhrer National Socialist German Workers Party (Nazi) Nationalism, racism, expansionism, anti-communist The Third Reich – the Nazi state Benito Mussolini Il Duce Fascism – strong central government headed by a powerful dictator Military expansion and extreme nationalism Joseph Stalin The Man of Steel Communist Collective farms, state run industry Stalin was paranoid Attempted to destroy all opposition Various Military Leaders Including Hideki Tojo (appointed Prime Minister and Army Minister) Hirohito was emperor of Japan Looked to expand Japan’s power in the Pacific Wanted more land and resources Germany begins mobilizing for war in 1935 Germany takes the Rhineland in 1936 Germany and Italy support fascist revolution in Spain Italy invades Ethiopia and later takes Albania Germany annexes Austria Germany occupies the Sudetenland Munich Pact signed France and Britain were hesitant to enter another war, due to problems with WWI and war debt. In 1938, France and Britain met with Hitler and allowed Germany to take Sudetenland if no other land was taken – APPEASEMENT Germany takes over the rest of Czechoslovakia Germany,Japan, and Italy form the Axis Powers Soviet-German Non-Aggression Pact of 1939 Germany invades Poland Blitzkrieg – “lightning war” Britain and France declare war on Germany Soviet Union acquires part of Poland and ports in the Baltic states Germany, Italy and Japan sign the Tripartite Pact Hungary, Bulgaria and Romania join the Axis – 1940 Denmark and Norway fall to Germany – 1940 Netherlands, Belgium and Luxembourg fall to Germany – 1940 Germany marches on France, takes over Paris – 1940 Vichy France Germany attacks Great Britain Battle of Britain – “the Blitz” Germany invades Yugoslavia and Greece Germany invades the Soviet Union The Soviet Union allies with Britain and France Axis Powers Allied Powers Germany United States Canada Italy Britain China Japan France Denmark Soviet Union Greece Australia Netherlands Belgium New Zealand Brazil Norway Yugoslavia Poland Hungary Romania Bulgaria South Africa 1. Explain why dictators rose to power in Europe in the 1920s and 1930s. Describe how Hitler, Mussolini and Stalin were similar and different as leaders. 2. Explain the policy of appeasement. How did appeasement impact the starting of WWII? 3. The US and Great Britain’s objectives were different than the Soviet objectives for war. So, why did the US and GB choose to align themselves with the Soviets?