* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Part 2: Listing
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
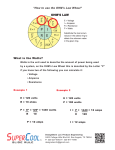
Electricity Review Sheet Part 1: Definitions 1. electrical circuit – the closed path through which electric current flows 2. current – the flow of electrons 3. series circuit – a circuit with only one path for the current to flow through 4. parallel circuit – a circuit with more than one path for the current to flow through 5. electrical conductor – a material that allows the flow of electric current 6. electrical insulator – a material that does not allow the flow of electric current 7. static electricity – the net accumulation of electric charge on an object 8. resistance – the tendency of a material to resist the flow of electrons Part 2: Listing 9. List 3 examples of good conductors. Copper, Iron, Saltwater 10. List 3 examples of good insulators. Plastic, Wood, Air Part 3: Fill in the Blank 11. Give the unit used to measure the following: a. voltage __volts__ b. current __amps__ c. resistance __Ohms__ d. power __Watts or Kilowatts__ 12. Power lines use _alternating_ current because the current flows in different directions 13. Batteries use __direct__ current because the current flows in one direction. Part 3: Circuit Diagrams 14. Label the following circuit diagram parts: a. b. RESISTOR POWER SOURCE c. OPEN SWITCH 15. Draw a series circuit with 2 light bulbs, 3 resistors and a power source. 16. Draw a parallel circuit with 1 light bulb on a branch, 1 resistor on another branch and a power source. Part 4: Calculations V=IxR P=IxV E=Pxt 17. What is the current flowing through a wire with a 3 ohm resistor and a 6 volt battery? I=V I=6 I = 2 amps R 3 18. Calculate the voltage across a 2 ohm resistor with 4 amps of current. V=IxR V=4x2 V = 8 volts 19. How much power does a lamp use if the current is 2 amps and the voltage is 120 volts? P=IxV P = 2 x 120 P = 240 Watts 20. A microwave uses 1200 watts of power. If the outlet supplies 120 volts, what is the current? I=P I = 1200 I = 10 amps V 120 21. A television uses 2400 watts of power and 20 amps of current. What is the voltage of the outlet? V=P V = 2400 V = 120 volts I 20 22. How much energy does a 1.5 kilowatt hairdryer use if it is on for 0.1 hours? E=Pxt E = 1.5 x .1 E = 0.15 kwh 23. How long is a 0.05 kilowatt light bulb on if it uses 6 kwh of energy? t=E t= 6 t = 120 hours P 0.05