* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Economics Goals 7-9 - Public Schools of Robeson County
Survey
Document related concepts
Economics of fascism wikipedia , lookup
Ragnar Nurkse's balanced growth theory wikipedia , lookup
Production for use wikipedia , lookup
Steady-state economy wikipedia , lookup
Modern Monetary Theory wikipedia , lookup
Economic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Long Depression wikipedia , lookup
Business cycle wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Italy under fascism wikipedia , lookup
Austrian business cycle theory wikipedia , lookup
Helicopter money wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative easing wikipedia , lookup
Early 1980s recession wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
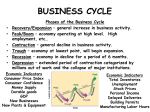
Economics Goals 7-9 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 1. If one large company owned all of the hotels in one country, that company would have a a. free market. c. monopoly. b. nonprofit organization. d. dividend. 2. The law of supply states that a. businesses will provide more products when they can sell them at higher prices. b. businesses will provide fewer products when they can sell them at higher prices. c. consumers will purchase fewer products when they must buy them at higher prices. d. consumers will purchase fewer products when they can buy them at lower prices. 3. A pencil factory is losing money, even though sales are high. The owners do not want to fire employees or lower their wages. They cannot raise the price of the pencils and remain competitive. They need to find a way to a. raise more capital. c. increase stockholder dividends. b. increase worker productivity. d. increase labor costs. 4. In the 1800s, laws were passed to help prevent a. conglomerates. c. sole proprietorships. b. mergers. d. monopolies. 5. Corporations are owned by a. partners. c. managers. b. stockholders. d. entrepreneurs. 6. A small, family-owned bakery is an example of a a. sole proprietorship. c. conglomerate. b. corporation. d. nonprofit organization. 7. All Americans enjoy the following economic freedoms EXCEPT the freedom to a. buy and sell various goods. c. own property. b. fix prices. d. earn a profit. 8. An enterprising high school student wants to publish and sell a national high school newsletter. He will most likely set up his business as a a. corporation. c. trust. b. conglomerate. d. monopoly. 9. Capital is a. land and other natural resources. b. money used to pay salaries. c. manufactured goods used to make other goods. d. all money coming into a business. 10. The law of demand states that a. businesses will provide more products when they can sell them at higher prices. b. businesses will provide fewer products when they can sell them at higher prices. c. consumers will purchase fewer products when they must buy them at higher prices. d. consumers will purchase fewer products when they can buy them at lower prices. 11. A corporation's board of directors does all of the following EXCEPT a. set the corporation's policies. c. appoint corporate officers. b. decide what dividends to pay. d. manage daily business operations. ____ 12. You have purchased several shares in a company. During its second year of operation, the corporation builds up numerous debts, and ultimately fails. What will most likely happen? a. You will be held at least partially responsible for the corporation's debts. b. The most money you will lose is what you paid for your shares. c. The officers of the company will be held responsible for the corporation's debts. d. The corporate assets will be sold and reinvested in the company. ____ 13. All of the following are roles played by the U.S. government in the economy EXCEPT a. preventing pollution of the environment. b. protecting consumers from harmful products. c. regulating profits of the largest corporations. d. providing loans to businesses. ____ 14. Bonds are essentially a. of two kinds—common and preferred. b. loans to a corporation. c. designed to help prevent trusts. d. illegal except for those issued by public utility companies. ____ 15. Last Christmas a popular toy was sold out all over town. When a local toy store received a shipment, it advertised the toy at twice its normal price. The store doubled the price due to a. scarcity. c. increased productivity. b. competition. d. a monopoly. ____ 16. The U.S. economy is characterized by many freedoms and is often called a a. democracy. c. free market economy. b. free for all. d. Darwinian economy. ____ 17. The issue of scarcity of natural resources a. demands government intervention. b. results from governmental regulations of industry. c. is not a problem in the United States. d. helps determine their market value. ____ 18. The relationship between supply and demand is a. predictable. c. weak. b. unpredictable. d. erratic. ____ 19. The tools owned by a self-employed electrician are a. liabilities. c. capital. b. required by law. d. copyrighted. ____ 20. The free-enterprise system means that Americans a. are able to run their businesses in the way they think is best. b. are entitled to receive free products from stores. c. do not have to pay taxes during their first year in business. d. depend on the government to tell them how to operate. ____ 21. Some goods can be produced more efficiently by larger companies. Such a situation is called a. a trust. c. an economy of scale. b. a monopoly. d. free enterprise. ____ 22. The U.S. economic system can best be described as a a. command economy. c. mixed economy. b. traditional economy. d. market economy. ____ 23. The duty of a corporation’s board of directors is to a. keep the corporation from paying dividends. b. pay off debts if the corporation fails. c. represent stockholders in making decisions for the corporation. ____ 24. ____ 25. ____ 26. ____ 27. ____ 28. ____ 29. ____ 30. ____ 31. ____ 32. ____ 33. ____ 34. ____ 35. d. oversee the day-to-day operations of the corporation. In a corporation, stockholders a. have little or no say in the business. b. elect the board of directors. c. make no profit if the business succeeds. d. are responsible for their share of the debt if the business fails. Which country has a command economy? a. South Korea c. Russia b. North Korea d. China An essential factor of a free market economy is the a. bankruptcy protection system. c. profit motive. b. credit industry. d. U.S. Constitution. In a command economy, most of the capital, tools, and production equipment are a. outdated. c. owned by the government. b. privately owned. d. unregulated. The four forms of money in the United States are a. coins, paper money, checks, and certificates of deposit. b. coins, paper money, checks, and credit. c. checks, paper money, barter, and credit. d. coins, paper money, credit, and certificates of deposit. Money is a. a means of exchange. b. printed by the Internal Revenue Service. c. a medium used for barter. d. a substitute for credit. The government does not print a a. $100 bill. c. $25 bill. b. $50 bill. d. $1 bill. A high school graduate has $500. She wants to save this money in the least risky way. Thus she should avoid a. buying savings bonds. c. buying stocks. b. buying certificates of deposit. d. opening a credit union account. Americans save money in all of the following ways EXCEPT a. buying luxury items on sale. c. buying stocks. b. investing in certificates of deposit. d. buying bonds. In the United States, paper money is printed a. at the Treasury Department’s Bureau of Engraving and Printing. b. at the Federal Reserve Bank. c. at mints in Denver and Philadelphia. d. by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation. Bonds are a. a risky but potentially lucrative investment. b. forms of common stock. c. a relatively safe investment. d. also called certificates of deposit. By buying a share in a mutual fund, the purchaser a. is guaranteed some kind of profit. b. owns a small share of a large number of stocks. c. owns preferred stock. d. owns a large share of a small number of stocks. ____ 36. Money market funds a. do not guarantee a specified amount of interest. b. guarantee a specified amount of interest. c. buy stocks only in high tech markets. d. are insured by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation. ____ 37. Economic expansion requires capital for new factories, tools, and other goods. What is the source of that capital? a. the mint c. people’s savings b. credit unions d. the government ____ 38. The fairness of the activities of unions and employers is judged by the a. Labor-Management Administration. c. secretary of labor. b. National Labor Relations Board. d. Taft-Hartley Commission. ____ 39. The nation is experiencing a recession. The government decides to lower taxes to encourage people to a. join labor unions. c. increase their productivity. b. spend more money. d. save more money. ____ 40. Unions and employers reach nonbinding solutions to their differences through a. jurisdictional strikes. c. arbitration. b. picketing. d. mediation. ____ 41. Before the time of the Great Depression, most economists believed that the government should a. let the business cycle run its course. b. do everything possible to control inflation. c. take over businesses that were about to fail. d. give people jobs during difficult economic times. ____ 42. When union members go on strike a. they work more slowly than usual. b. companies lose money. c. workers lose their unemployment benefits. d. they must return to work with in 80 days. ____ 43. Wages, payments for raw materials, transportation, rent, and interest on borrowed money are a. means of production. c. components of monetary policy. b. costs of production. d. components of fiscal policy. ____ 44. All of the following can be causes of economic problems EXCEPT a. too much government spending. c. high productivity. b. too much consumer borrowing. d. too many bank loans. ____ 45. The major purpose of unions is to a. help prevent disputes between labor and management. b. increase worker productivity. c. help workers bargain for better wages and working conditions. d. allow workers to control how businesses are run. ____ 46. Union members on strike try to prevent the hiring of replacement workers by a. forcing them to join the union. c. collective bargaining. b. starting a blacklist. d. picketing. ____ 47. A business owner needs an objective third party to settle a dispute between labor and management. She wants both labor and management to be bound by the recommended solution. She calls a(n) a. local union organizer. b. arbitrator. c. representative from the Department of Labor. d. mediator. ____ 48. The Taft-Hartley Act gives the president the power to postpone a strike only when a. the nation is at war. b. the strike would threaten the national welfare. c. labor and management could settle their dispute by using a mediator. d. the strike would cause widespread unemployment. ____ 49. Workers at a local plant are dissatisfied with their working conditions, but they cannot walk off their jobs. The workers want to get management's attention by slowing down production, so they participate in a a. collective bargaining session. c. job action. b. jurisdictional strike. d. mediated strike. ____ 50. The opposite of a peak is a a. trough. c. strike. b. boom. d. contraction. ____ 51. In 2005, the AFL-CIO a. became the largest association of unions in the United States. b. lost about one-third of its membership. c. agreed to use union money to support political campaigns. d. changed its name to the International Brotherhood of Teamsters. ____ 52. When the demand for goods and services increases, a. the economy is in a bust. b. costs of production are too high. c. inflation results. d. the business cycle has reached a peak. ____ 53. An economic contraction can lead to a. a recession. c. increased costs of production. b. an expansion. d. inflation. ____ 54. Rising productivity usually leads to a. higher wages. c. lower prices. b. higher profits. d. all of the above ____ 55. Consumers contribute to the country's economic troubles when a. they refuse to join credit unions. b. they save their money instead of spend it. c. incur too much credit debt and save too little money. d. break strikes. ____ 56. If the Fed is lowering the interest rates that banks pay it, the country a. is entering a boom. c. is experiencing a rise in productivity. b. is entering a recession. d. is experiencing high inflation. ____ 57. In the early days of the United States, many Americans were a. factory workers. c. members of one of the first unions. b. self-employed. d. unemployed. ____ 58. A severe contraction in the business cycle is called a(n) a. recession. c. expansion. b. trough. d. inflation. ____ 59. When the economy reaches its lowest point, it is said to be in a(n) a. recession. c. expansion. b. trough. d. inflation. ____ 60. A trough that lasts a long time is called a(n) a. depression. c. inflation. b. expansion. d. peak. ____ 61. The United States has a a. pure market economy. c. mixed economy. b. limited command economy. d. traditional economy. ____ 62. In a free-enterprise economy, the two major groups that make decisions that affect the economy are a. the government and the voters. c. the producers and the consumers. b. the producers and the government. d. the Republicans and the Democrats. ____ 63. The money in the U.S. economy moves in a circular flow among a. businesses, government, and individuals. b. industry, imports, and consumers. c. Congress, consumers, and the national debt. d. foreign nations, businesses, and consumers. ____ 64. Competition a. is responsible for the inflation rate. b. encourages producers to invent new products. c. is essential to a command economy. d. is unrelated to the supply of goods and services. ____ 65. When there is a surplus of a particular product, a. the prices remain the same. c. there is a lack of competition. b. the prices will decrease. d. the demand will increase. ____ 66. Money invested in new business is a. called venture capital. c. guaranteed by the government. b. an open-market operation. d. called a bond. ____ 67. If a corporation fails to make a profit, a. the Fed will decrease its interest rate. c. it will have a surplus. b. the value of its stock will decline. d. the economy is in a contraction. ____ 68. Which of the following is NOT a stage in the business cycle? a. expansion c. trough b. peak d. loop ____ 69. When interest rates are high, a. many individuals and businesses borrow money. b. many individuals and business do not borrow money. c. the economy will expand. d. stock prices are usually low. ____ 70. One of the effects of the September 11, 2001, terrorist attacks was a. more U.S. companies opened factories in foreign countries. b. the New York Stock exchange did record business. c. the U.S. economy was weakened. d. oil and gas refineries were shut down. ____ 71. The number of building permits issued is an example of a a. leading indicator. c. lagging indicator. b. coincident indicator. d. none of the above ____ 72. The increase or decline of personal incomes is an example of a a. leading indicator. c. lagging indicator. b. coincident indicator. d. none of the above ____ 73. Tariffs, import quotas, and embargoes are all examples of a. opportunity costs. c. reciprocal trade agreements. b. interdependence. d. trade barriers. ____ 74. Which of the following is NOT one of the government's goals in regulating business? ____ 75. ____ 76. ____ 77. ____ 78. ____ 79. ____ 80. ____ 81. ____ 82. ____ 83. ____ 84. ____ 85. ____ 86. a. protecting workers c. limiting certain industries b. encouraging competition d. limiting negative effects Which of the following is NOT a key way that the government implements its fiscal policy? a. printing new money c. spending b. taxing d. making payments If the government lowers taxes, the economy may be a. entering a recession. c. at a high point b. expanding. d. none of the above If consumers have less money to spend, a. demand increases with the inflation rate. b. demand drops, and prices go down. c. the government lowers taxes. d. people make more business investments. If Mexico is able to grow grapes better than any other country, when it comes to growing grapes, Mexico has a. an absolute advantage. c. an import quota. b. a trade barrier. d. a comparative advantage. Congress decreases spending when it wants to a. encourage foreign trade. b. encourage economic growth. c. slow economic growth and prevent inflation. d. issue government bonds. Public transfer payments are paid with a. credit. c. the national debt. b. tax dollars. d. none of the above Fiscal policy is used a. for immediate relief in the business cycle. b. with long-term effects in mind. c. with short-term effects in mind. d. very seldom. If an easy-money policy is in effect, a. the overall demand for goods and services increases. b. the overall demand for goods and services decreases. c. economic growth is discouraged. d. the economy is in a trough. The Fed can change the amount of money available by a. petitioning Congress. b. discouraging foreign exports and imports. c. raising and lowering interest rates. d. raising and lowering taxes. When the Fed sells government securities, a. the economy speeds up. c. Social Security loses money. b. the economy is in a depression. d. the economy slows. When the Fed lowers its reserve requirement, a. more money is loaned out by banks. c. the economy slows. b. more money is saved. d. interest rates are affected. International trade is made possible by a. the Fed. c. specialization. b. the United Nations. d. self-sufficient countries. ____ 87. If Costa Rica chooses to produce coffee, it cannot produce bananas. By producing coffee it has made a(n) a. trade barrier. c. absolute advantage. b. trade-off. d. none of the above ____ 88. The term used by economists to explain an economic sacrifice is a. embargo. c. opportunity cost. b. comparative advantage. d. import quota. ____ 89. Countries may choose to employ a voluntary trade restriction in order to a. help domestic businesses. c. encourage global competition. b. raise revenue through tariffs. d. lower inflation rates. ____ 90. During periods of inflation, a. banks voluntarily lend less money. c. unemployment is always low. b. people can buy less with their money. d. more people are able to save money. ____ 91. The government can influence the business cycle in all of the following ways EXCEPT with a. increased taxation. c. its collective bargaining policy. b. its fiscal policy. d. its monetary policy. ____ 92. All of the following are freedoms in the U.S. economy EXCEPT the freedom to a. compete. c. earn a profit. b. form a monopoly. d. own property. ____ 93. Government regulation in a free market is a. limited. c. insignificant. b. unlimited. d. prohibited by law. ____ 94. Buyers show their preferences for goods and services when they purchase in a a. command economy. c. traditional economy. b. system of free competition. d. all of the above ____ 95. Essential to the free economic system is the a. profit motive. c. issuance of government bonds. b. inflation rate. d. copyright law. ____ 96. If the economy is in a recession, the federal government may a. decrease its own spending. c. raise taxes to pay for unemployment. b. increase its own spending. d. have to reduce its welfare rolls. ____ 97. Nonprofit organizations a. are not taxed by the government. b. are always organized like corporations. c. are sole proprietorships. d. are examples of trusts. ____ 98. When a company has very high profits, a. the government may intervene. b. the market price of its stock usually increases. c. it is known as a conglomerate. d. it is charging too much for its goods and services. ____ 99. Who pays a business’s debts in a failed sole proprietorship? a. the owner of the business c. the stockholders b. the employees of the business d. none of the above ____ 100. National banks are chartered under a. city ordinances. c. home rule. b. federal laws. d. state laws. ____ 101. To keep prices from rising, the Federal Reserve may a. try to increase the growth of the money supply. ____ 102. ____ 103. ____ 104. ____ 105. ____ 106. ____ 107. ____ 108. ____ 109. ____ 110. ____ 111. ____ 112. b. purchase government bonds from banks. c. try to slow down the growth of the money supply. d. keep the money supply constant. A member of a labor union wants to take out a low-interest loan to buy a new car. She will probably apply for the loan at a a. savings bank. c. commercial bank. b. credit union. d. savings and loan association. The banking needs of the U.S. government are handled by a. the National Credit Union Administration. b. the Federal Savings and Loan Bank. c. a savings bank. d. Federal Reserve banks. A wholesale grocer with good credit might a. buy only what he or she can pay for immediately in order to protect his or her credit rating. b. buy a truckload of goods on credit, agreeing to pay for them later. c. raise prices to increase what he or she can buy. d. use credit more often than he or she should. With a negotiable order of withdrawal (NOW) account, customers a. can write checks and receive interest on their money in the same account. b. can usually keep the balance as low as they want. c. invest most of their money in bonds. d. may not withdraw funds for a specified period of time. The most numerous banks in the United States are a. credit unions. c. savings and loan associations. b. commercial banks. d. savings banks. To combat strikers, employers in the past did all of the following EXCEPT a. hire armed guards. c. kept lists of workers active in unions. b. form organizations to oppose unions. d. agree union demands. A closed shop is a. a workplace where all employers are required to belong to a union. b. a factory that was shut down by the owner to prevent a strike. c. when an American factory sends jobs overseas. d. another term for a job action. Which of the following does NOT aid the American economy? a. reductions in government spending b. increased consumer savings c. purchasing inexpensive foreign-made products d. increased productivity Employers faced with worker slowdowns sometimes initiated a. lockouts. c. a job action. b. collective bargaining. d. right-to-work laws. In recent years, unions have a. grown very rapidly. b. not grown as rapidly as in the past. c. become obsolete. d. been criticized by the federal government. The National Labor Relations Board was established by the a. Wagner Act. b. Taft-Hartley Act. ____ 113. ____ 114. ____ 115. ____ 116. ____ 117. ____ 118. ____ 119. ____ 120. ____ 121. ____ 122. ____ 123. ____ 124. c. Landrum-Griffin Act. d. American Federation of Labor–Congress of Industrial Organizations. The Fair Labor Standards Act a. prevents businesses from hiring teenagers. b. created the minimum wage. c. revised the Wagner Act. d. prevents certain abuses by union officials. In recent years, the desire to lower labor costs has a. caused a decrease in the minimum wage. b. led some American businesses to open factories in foreign countries. c. caused unemployment in the United States to reach record lows. d. caused interest rates to rise. Negotiating between labor union leaders and employers is called a. a job action. c. picketing. b. arbitration. d. collective bargaining. The Taft-Hartley Act of 1947 gave the president the right to a. prohibit open shops. b. force companies to agree to union demands. c. delay a strike under certain circumstances. d. examine the financial affairs of union officials. Profits made by a sole proprietorship go to the a. individual shareholders. c. owner of the business. b. local government. d. various partners. The American Red Cross and the Boy Scouts are examples of a. nonprofit organizations. c. partnerships. b. monopolies. d. corporations. A newspaper editor relies most heavily on his or her a. motor skills. c. language skills. b. number skills. d. perceptual skills. The economy has just come out of a trough and is beginning to expand. Before long, prices skyrocket. One major cause of this inflation may be that a. taxes are too high. c. worker productivity is increasing. b. people are saving too much money. d. banks are lending too much money. One advantage of a partnership over a sole proprietorship is that the a. business can raise money by selling stock. b. business has more capital with which to work. c. partners will not have to hire employees. d. partners are not responsible for any debts of the business. The three indicators used by economists to predict changes in the business cycle are a. coincident, lagging, and leading indicators. b. coincident, public, and private indicators. c. shortage, surplus, and public opinion. d. monetary, manufacturing, and service indicators. The period of high unemployment and business closings in the 1930s is called the a. New Deal. c. business cycle. b. Great Depression. d. Hooverville. Most U.S. currency is put into circulation through a. commercial banks. c. the Federal Reserve system. b. the consumers. d. the Department of the Treasury.